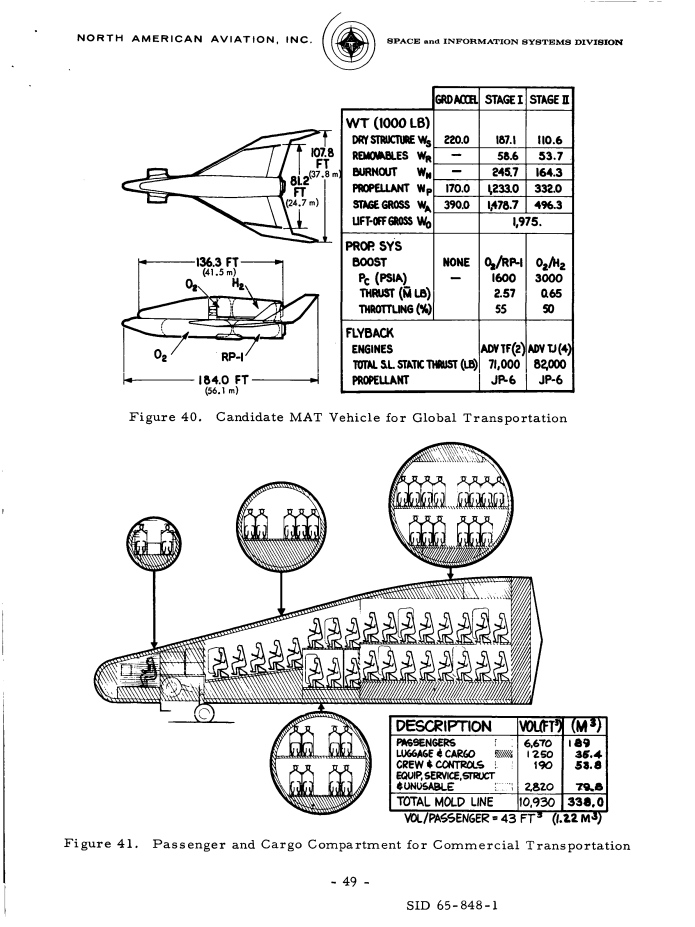
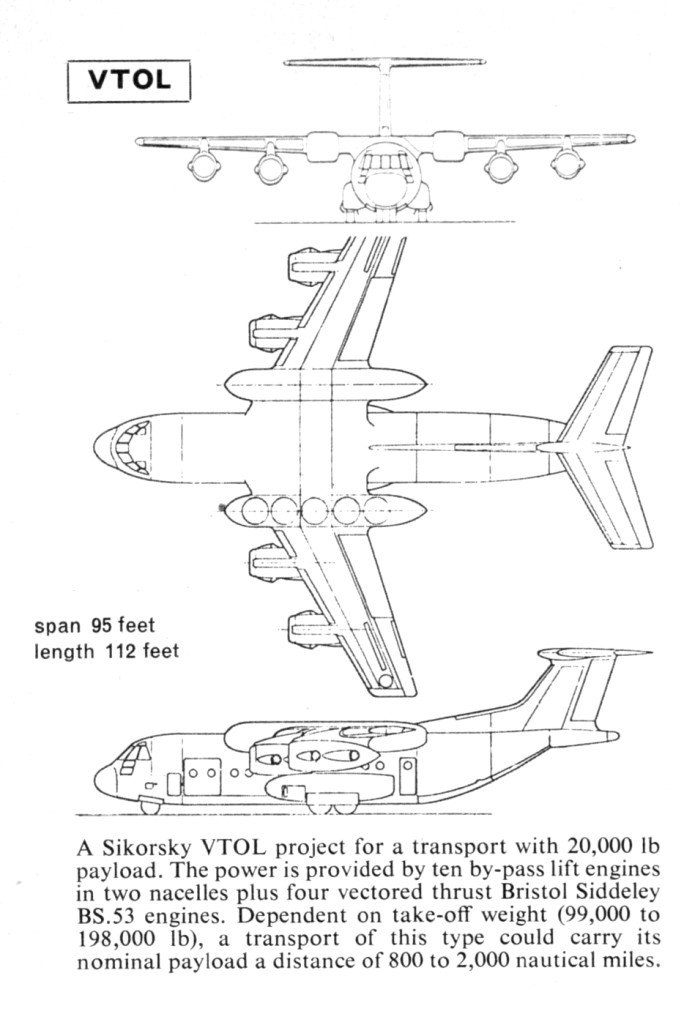
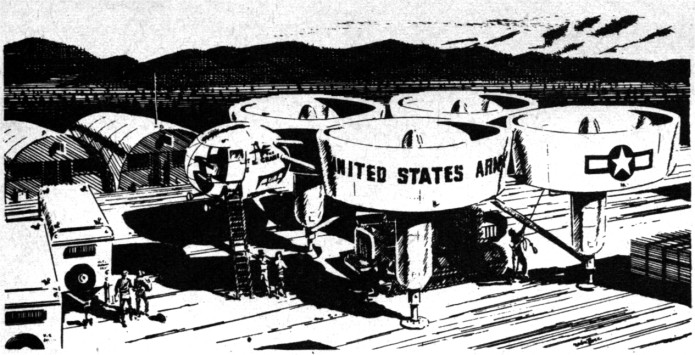
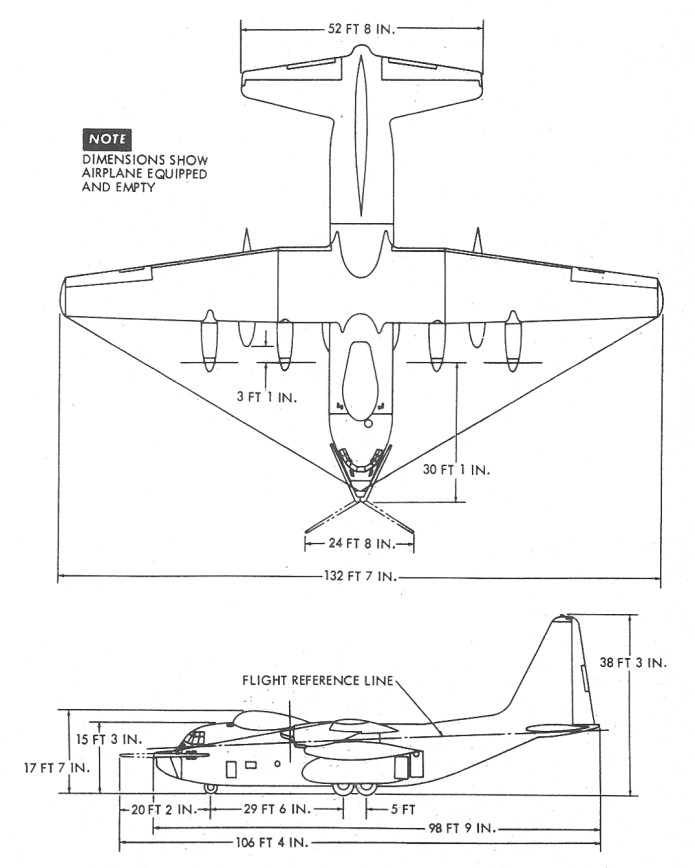
In 1965 North American Aviation produced a study for NASA about reusable space launch vehicles to support forthcoming expected space stations. Included within that study was an alternate use of rocket vehicles… point-to-point hypersonic commercial passenger transportation. This concept goes back to the late 1940’s and has continued to the present day, with the Elon Musk suggesting that the SpaceX Starship could be used for that purpose. The idea is interesting and it certainly *could* work. But could it be commercially cost effective? History with craft such as the Concorde and the Shuttle argue strongly against an early vehicle like this doing anything but losing truckloads of cash every time it launches.
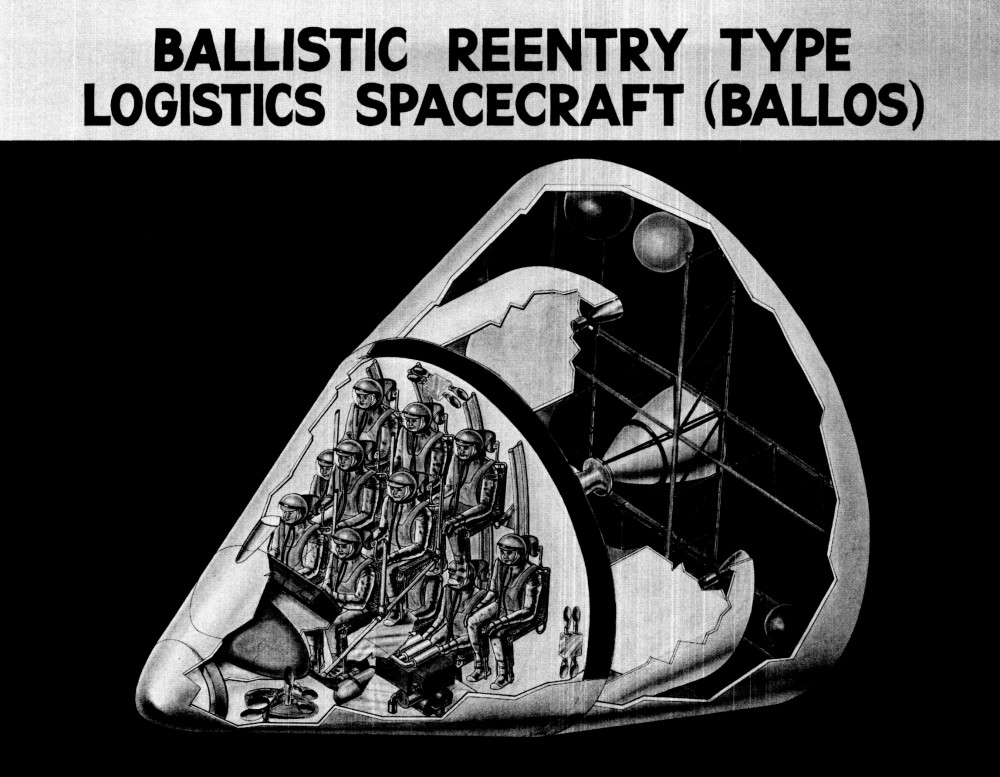
Artwork circa 1964 depicting the Lockheed BALlistic LOgistics Spacecraft (BALLOS), a sort of super-sized Apollo capsule meant for the transportation of a dozen astronauts (10 passengers, 2 crew) at once to and from any one of the doubtless dozens of space stations that the United States would surely have in orbit by the mid 1970’s. Launch vehicle would be a Saturn Ib.
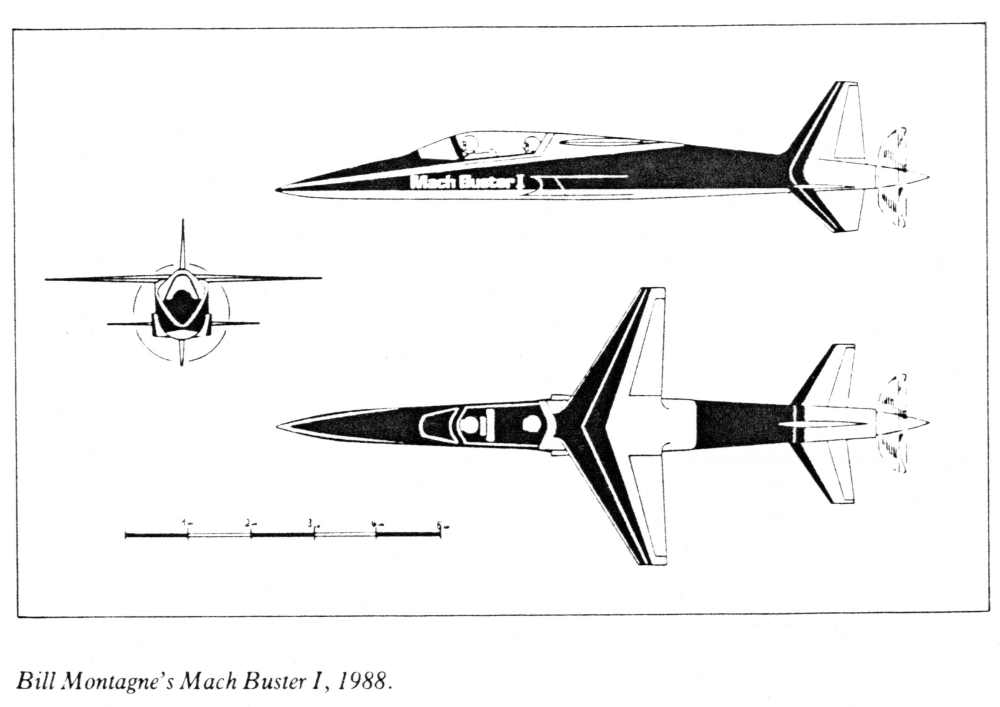
The “Mach Buster” was an unfinished amateur-built prop plane that was optimistically planned (in the late 1980’s) to exceed the speed of sound. Sadly, I’ve long since lost the reference for where the below image came from, existing in my collection solely as a single photocopy.
A brief article on the Mach Buster was in the August, 1989, issue of Popular Mechanics.
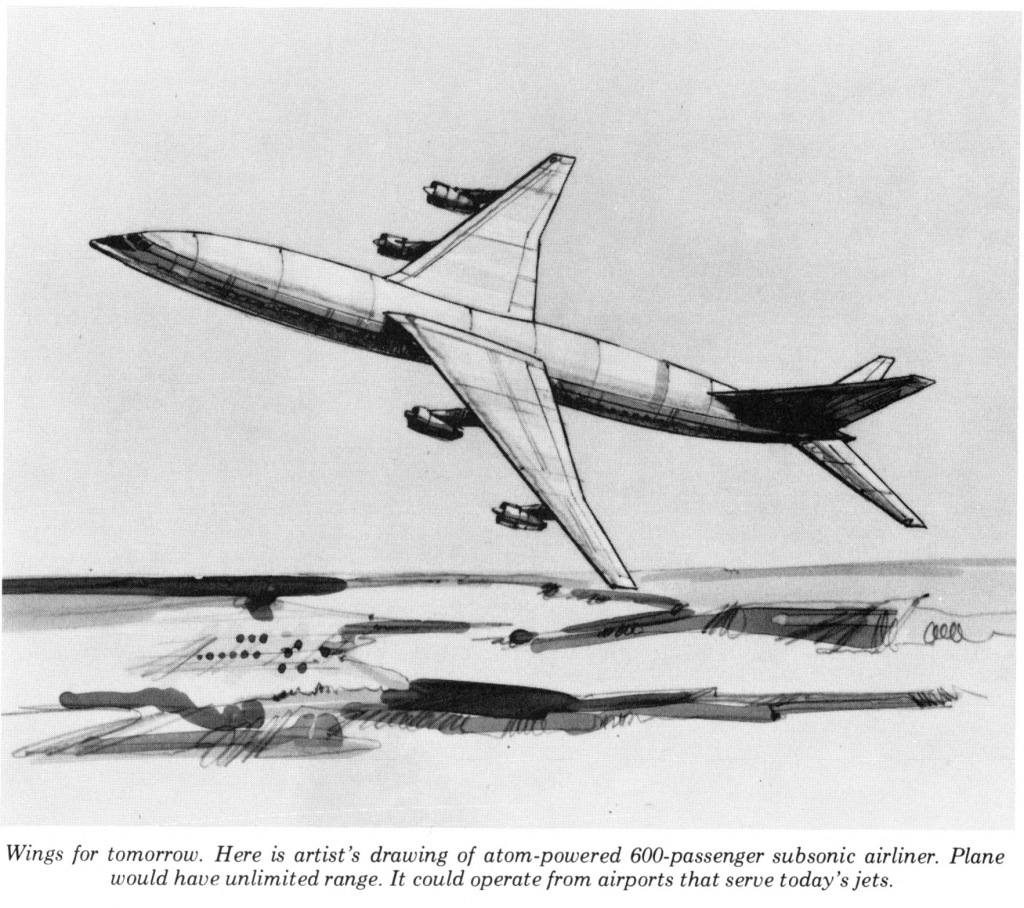
The heyday of the “atomic powered airplane” was the late 50’s-early 60’s. By the mid ’60’s it was done. But there was a brief, kinda sad and halfhearted revival in the seventies when the price of fuel spiked. An atomic airplane would be able to fly without all that pesky and overpriced petroleum; it could fly without producing pollution; and it could fly really, really far. Whether it could fly without irradiating the passengers, and whether it could fly at all, are questions largely left unanswered. The art below depicts a Lockheed concept for an atomic jetliner. It has the wasp-waisted configuration favored in the ’70’s for transonic jetliner designs, but where the reactor was supposed to go is not clear. *Presumably* it was to be fitted in the fuselage under the wings, as that’s the only place where no passenger windows are visible.
Once again Patreon seems to be becoming unstable. So I’ve got an alternate: The APR Monthly Historical Documents Program
For some years I have been operating the “Aerospace Projects Review Patreon” which provides monthly rewards in the form of high resolution scans of vintage aerospace diagrams, art and documents. This has worked pretty well, but it seems that perhaps some people might prefer to sign on more directly. Fortunately, PayPal provides the option not only for one-time purchases but also monthly subscriptions. By subscribing using the drop-down menu below, you will receive the same benefits as APR Patrons, but without going through Patreon itself.
The HC-130H is the designation of the Hercules cargo aircraft modified for Coast Guard search and rescue. The first one, shown in the diagram below, was given a number of modifications from the standard C-130. Most obvious was the radome fairing above the fuselage and the Fulton device on the nose. This meant that the aircraft was capable of snagging a balloon-lifted cable, and then snatching a payload – possibly a person – from the ground. See “The Dark Knight” for a demonstration…
Given the craziness going on, I decided that what the world clearly needs is something consistent. Like, say, me posting one piece of aerospace diagram or art every day for a month or so. So I’m going to do that. But in order to keep people from getting too complacent, I’m posting some of them on this blog, some on the other blog. Why? Because why not, that’s why. I’m slapping the posts together now and scheduling them to show up one at a time, one a day. Given the pandemic… who knows, this little project might well outlive *me.*
So, check back in (on this blog or the other) on a daily basis. Might be something interesting.