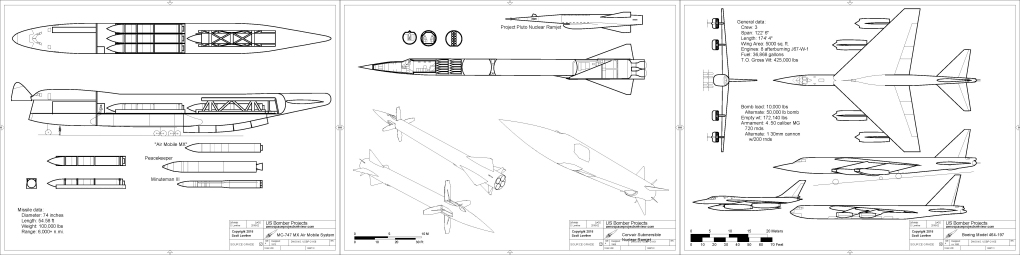
…for extracting water from rocks on the moon. This dates from 1963-65 and was part of a North American Aviation study relate to post-Apollo lunar exploration… which at the time was fully expected. The LESA (Lunar exploration Systems for Apollo) program would land habitats on the moon for extended exploration; the later phases of the LESA program were expected to occur in the late 1970.s The conclusion was that solar was preferred for the earliest phases, transitioning to nuclear. Basically, either system would cook rocks till the water came out as a thin vapor, which would be collected.
In the more than fifty years since this came out, the technologies involved haven’t changed a whole lot, especially solar: it remains a mirror and sunlight. Nukes should – hopefully – have improved. So it might still be a bit of a tossup on the moon; of course, any long-term lunar exploration is going to need nukes anyway for the simple reason that two weeks of night is a *real* long time if your base is solar powered. Going further out – asteroids, outer planet moons, comets and such – the math increasingly works in nuclears favor. But then, what’s needed is power, and mirrors in microgravity can be made extremely large.
It’s an interesting report. If not for the technology and techniques described, then for the basic worldview that suggested to engineers more than half a century ago that they’d soon have to crack water out of lunar rocks.
A Study of the Feasibility of Using Nuclear Versus Solar Power in Water Extraction from Rocks.
Direct PDF download link.
Help support the APR Patreon.