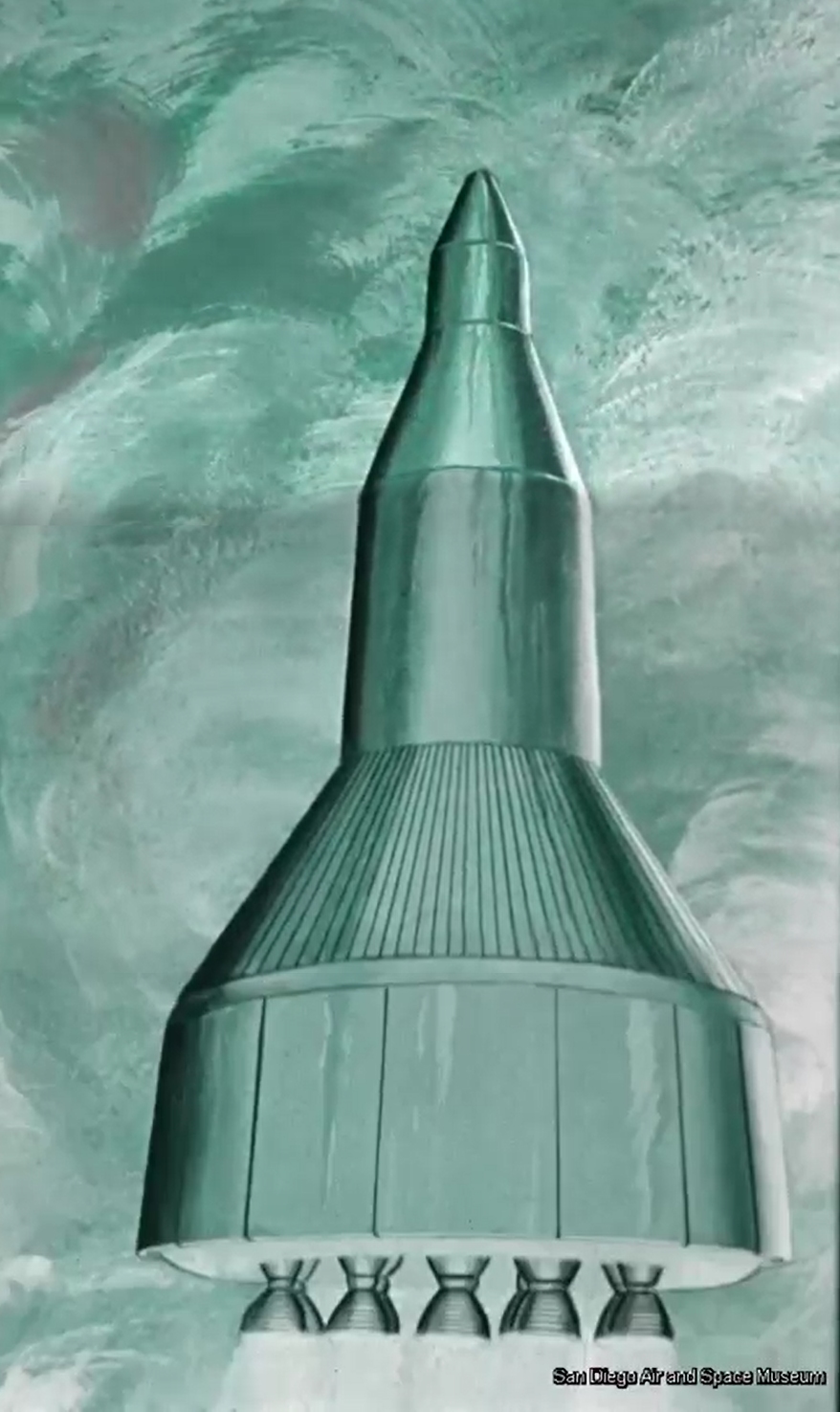
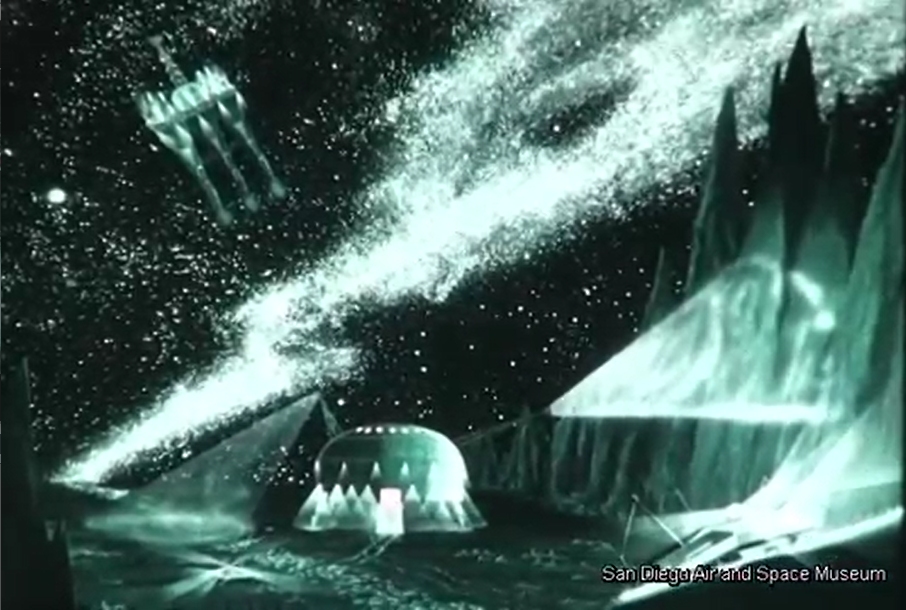
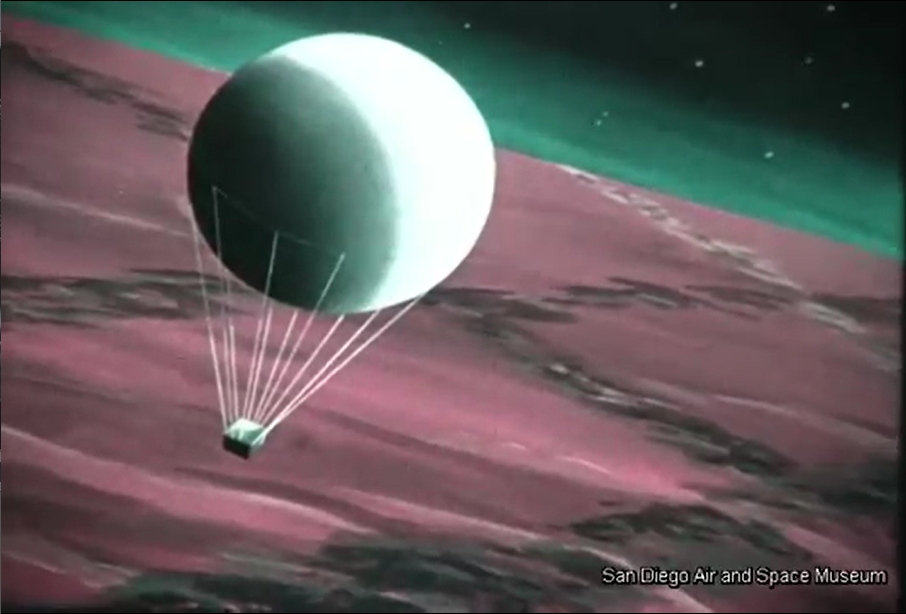
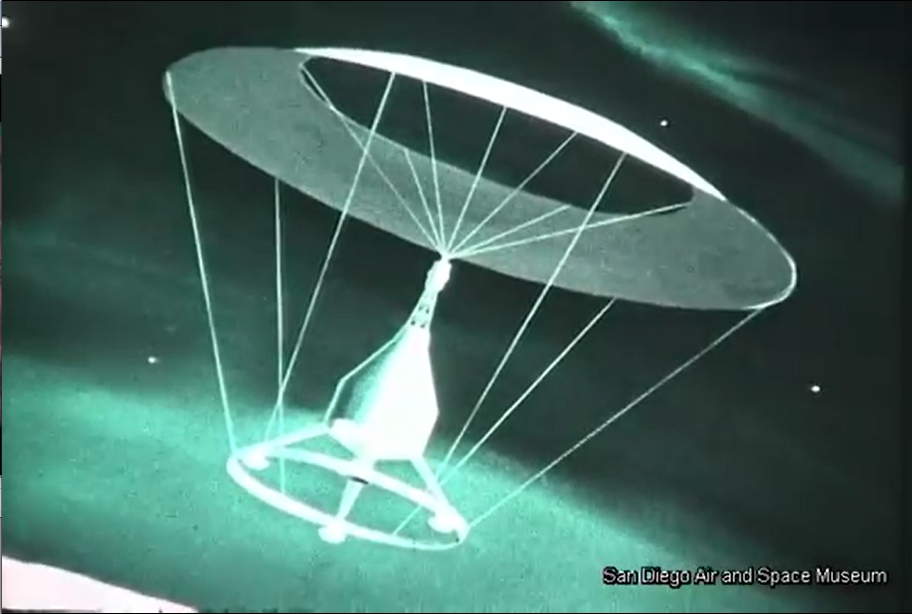
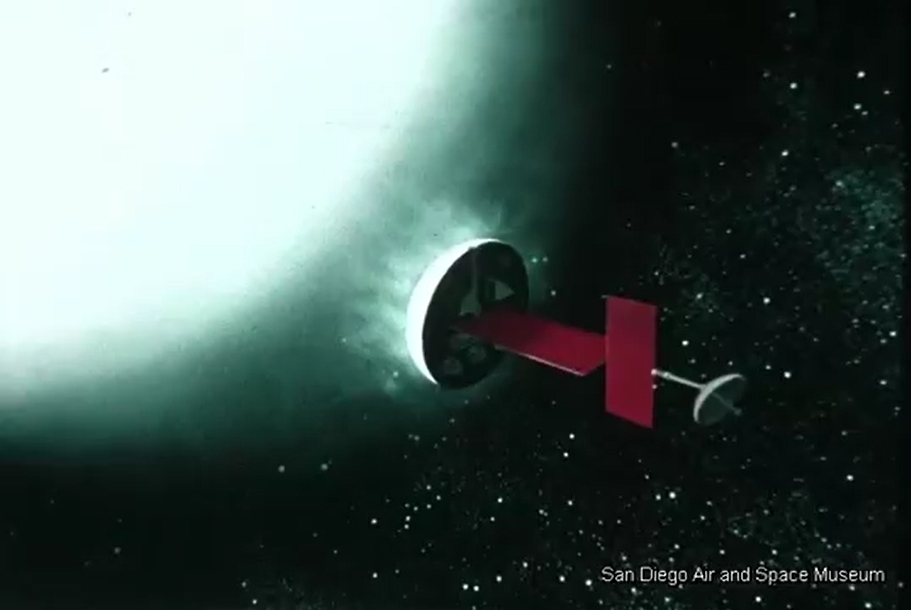
This video was posted on YouTube some six-ish years ago, but remains worthy of viewing and discussion. It’s a General Dynamics film to NASA from late 1962/early 1963 discussing the study of Early Manned Interplanetary Missions (EMPIRE), NAS8-5026. It describes the future as it should have been… and as how Krafft Ehricke, the presenter of the film and one of the driving forces behind the program, saw it:
1: Manned landing on the moon by the end of the 60’s.
2: Initial manned flights to (flybys and orbits) Venus and Mars in the early 70s
3: Entire solar system explored robotically by the end of the 1980’s
4: Manned mission to Pluto by 1995
Ehricke’s view of the future of space flight from the standpoint of the mid-1960’s was previously shown HERE.
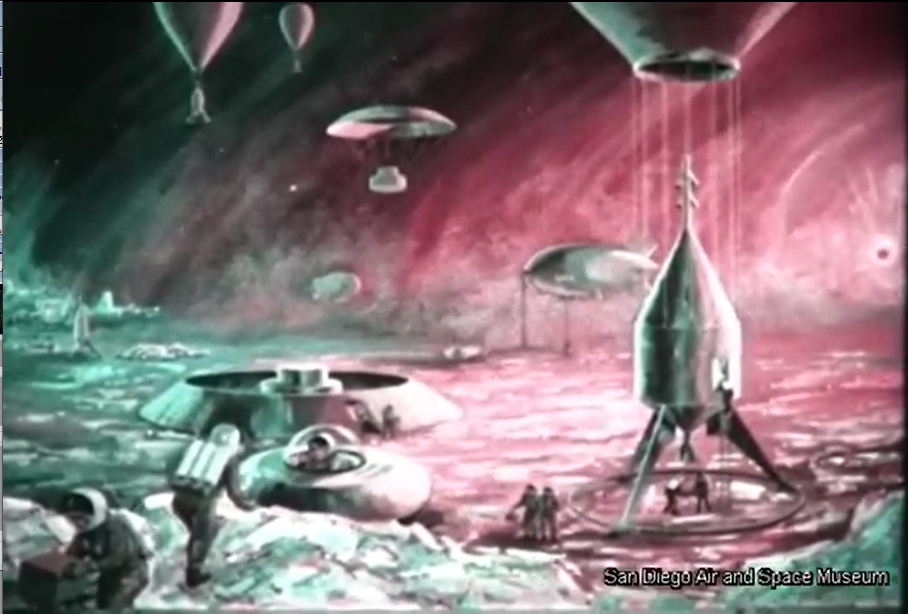
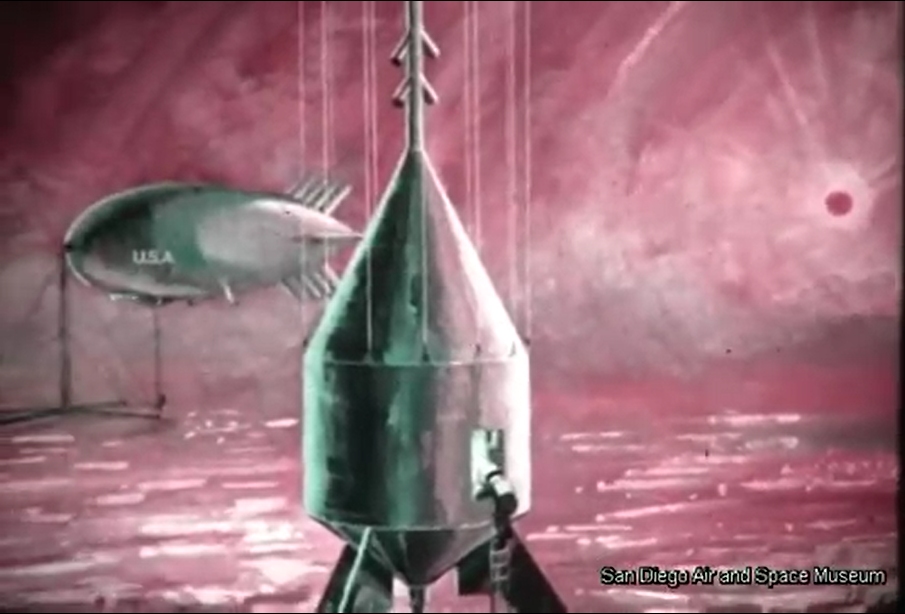
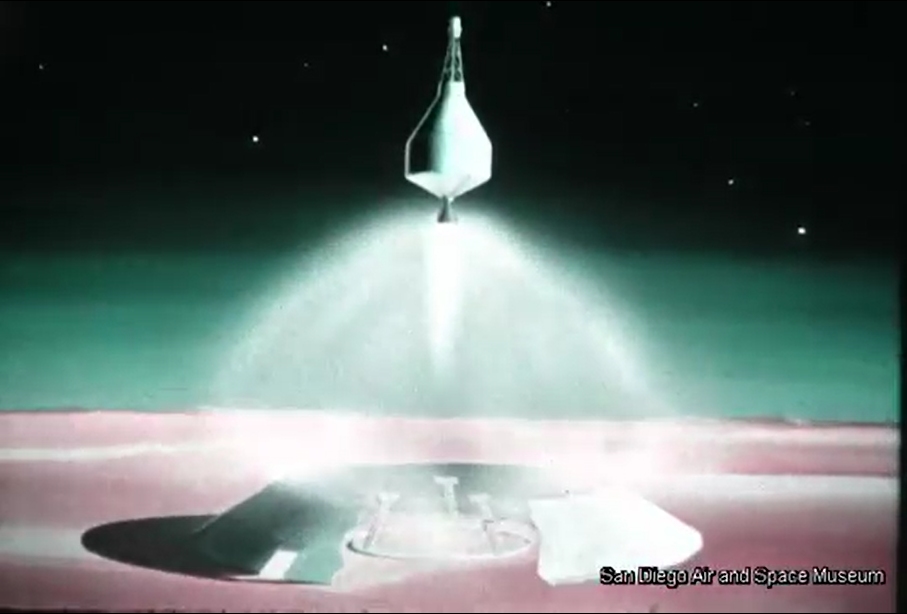
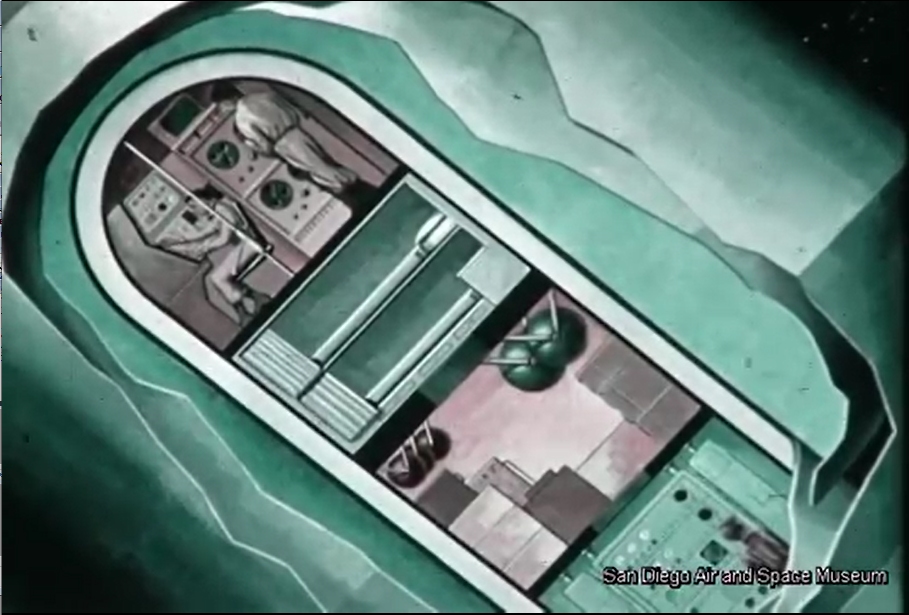
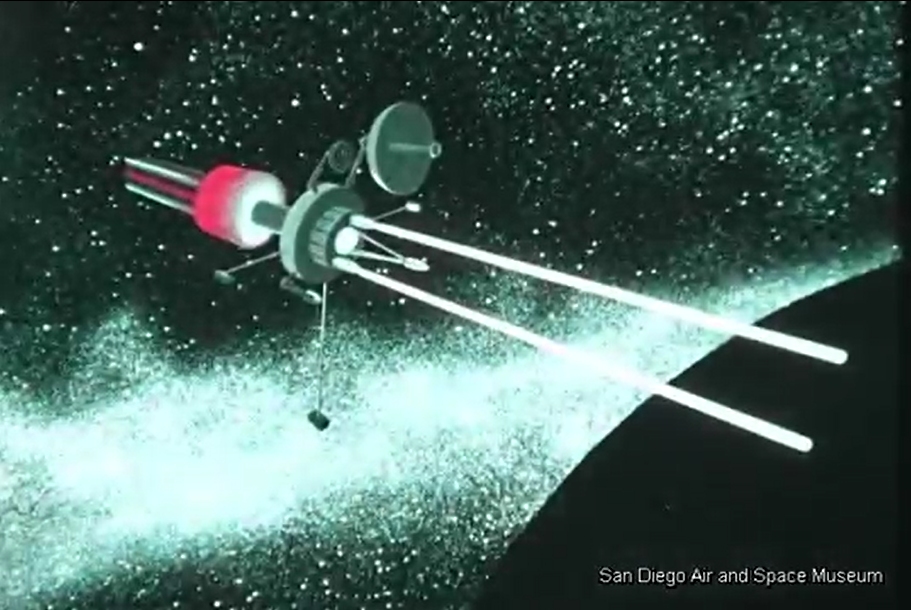
The original film included a number of bits of concept art of both manned and unmanned spacecraft. Sadly no Orion vehicles are on display (it is name-dropped), but the Mars lander/excursion module was of the kind originally proposed for Orion. This was pre-Mariner when the Martian atmosphere was *massively* over-estimated; these landers and their dinky parachutes would, with the real Martian atmosphere, have made impressive craters in the surface.