This is the third of four “PDF Reviews” I plan to have in October, to make up for the lack of any in September. The idea is to present interesting online resources for those interested in the sort of aerospace oddities that you can find in the pages of Aerospace Projects Review. This little project is supported through my Patreon campaign; at current levels, I’ll post two such reviews per month. If you’d like to see more, or just want to contribute to help me along, please consider becoming a patron.
One of the odder American aircraft in the immediate post-war period was the McDonnell XP-85 “Goblin.” This was essentially the smallest jet fighter possible to build with the technology of the time… small so that it could be carried within the bomb bay of the Convair B-36. The B-36 could reach far, far beyond the range of any conceivable escort fighter, leaving it at the mercy of defending Soviet fighters; if it could carry a fighter jet with it, it might stand a chance. of course the idea was fairly ridiculous; the Goblin was the biggest plane that could be carried internally, yet would almost certainly stand little chance against a conventional fighter.
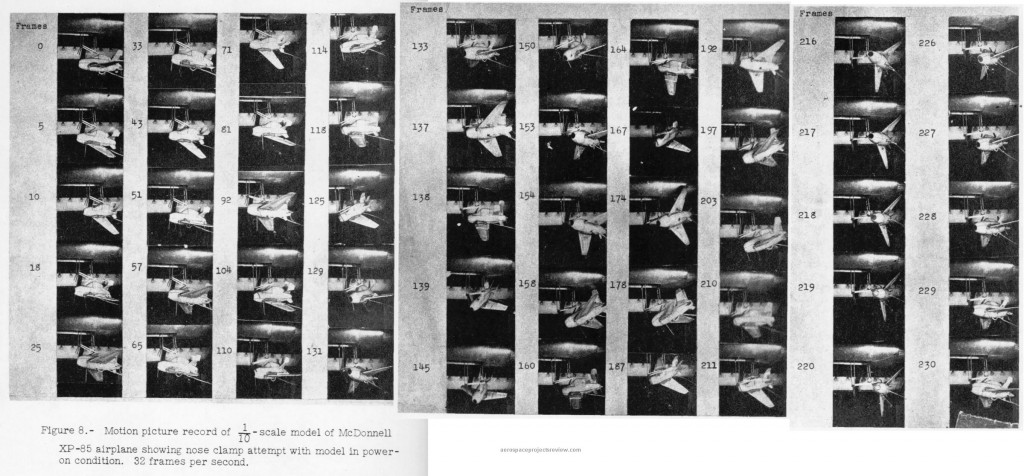
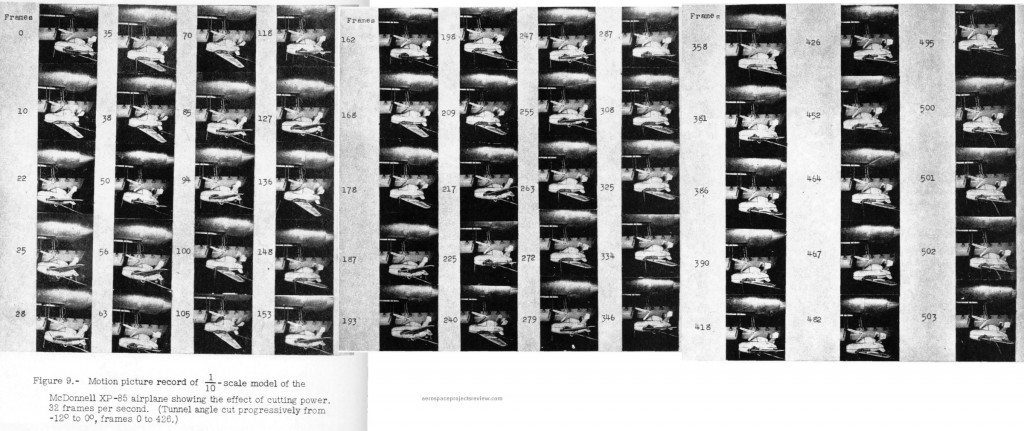
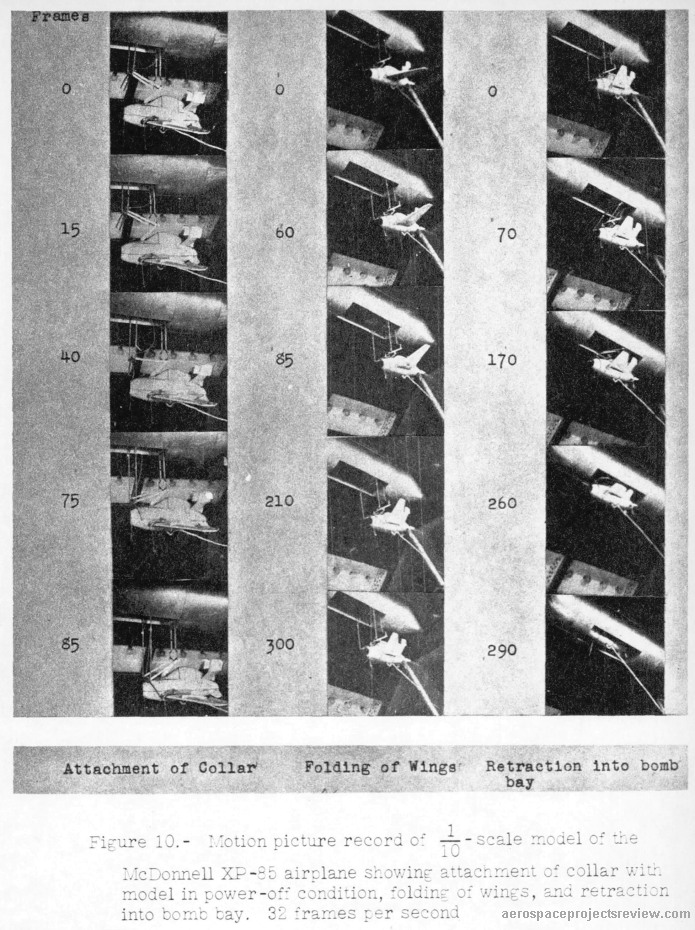
Dropping the fighter from the bomb bay would be fairly easy and straightforward. But getting it back was understood to be a challenge. The Goblin would rendezvous with a “trapeze” projected well below the bomb bay, outside of the turbulent airflow around the bombers fuselage. Once docked to the trapeze, it would be mechanically stabilized, the wings would fold up and the trapeze would retract, safely drawing the fighter into the bomb bay. That, at least, was the plan; actual testing with a B-29 showed that the docking rendezvous was far more difficult than envisioned.
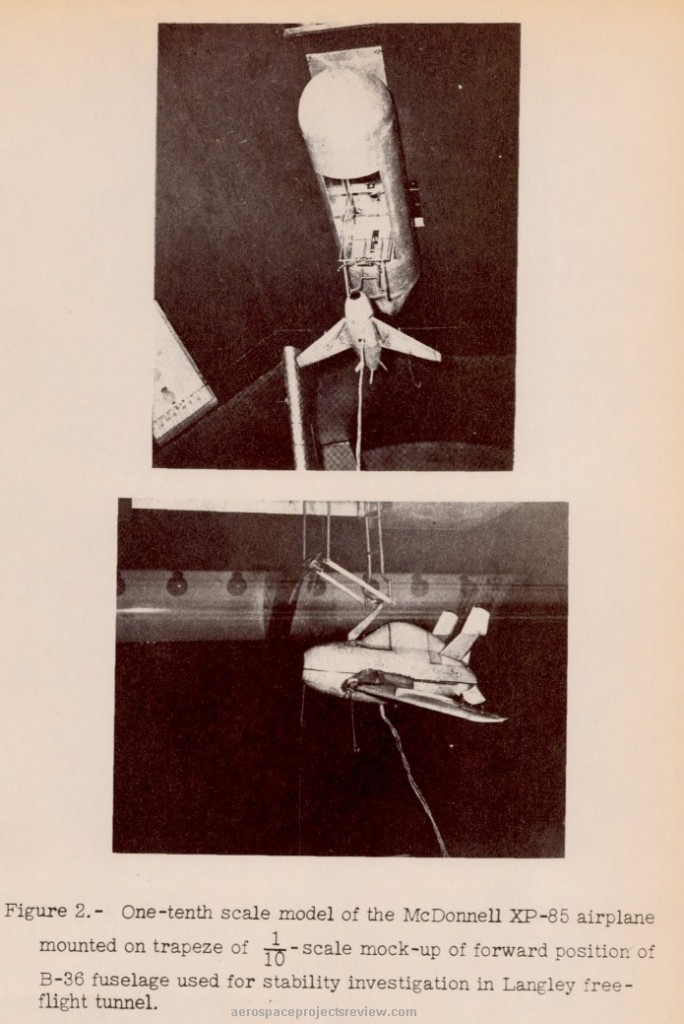
This difficulty was not wholly unforeseen. In 1947, the Langley Aeronautical Lab ran a series of wind tunnel tests of a 1/10 scale model of the Goblin and the forward fuselage of a B-36. Tests were conducted with both “power off” and “power on” models; the power off models were well behaved when docked to the trapeze, but the power on models quickly underwent violent flailing. The tests were filmed, with small still images included in the test report; the power-on model response is dramatic, to say the least.
Stability and Control Characteristics of a 1/10-Scale Model of the McDonnell XP-85 Airplane While Attached to the Trapeze
Here’s the link to the NASA-NTRS abstract of the report.
And here’s the DIRECT LINK TO THE PDF.

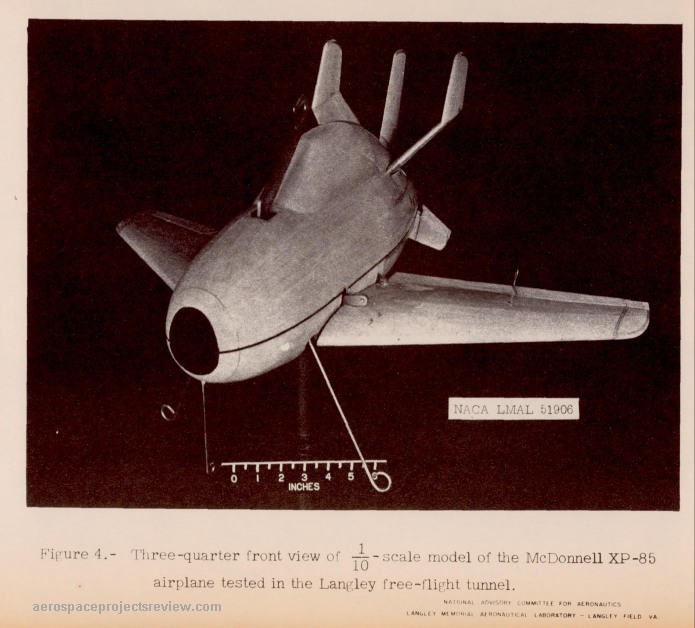
The wooden model of the FP-85 used. Note the hinged wings and the rudimentary landing gear, used to protect the model if it falls free.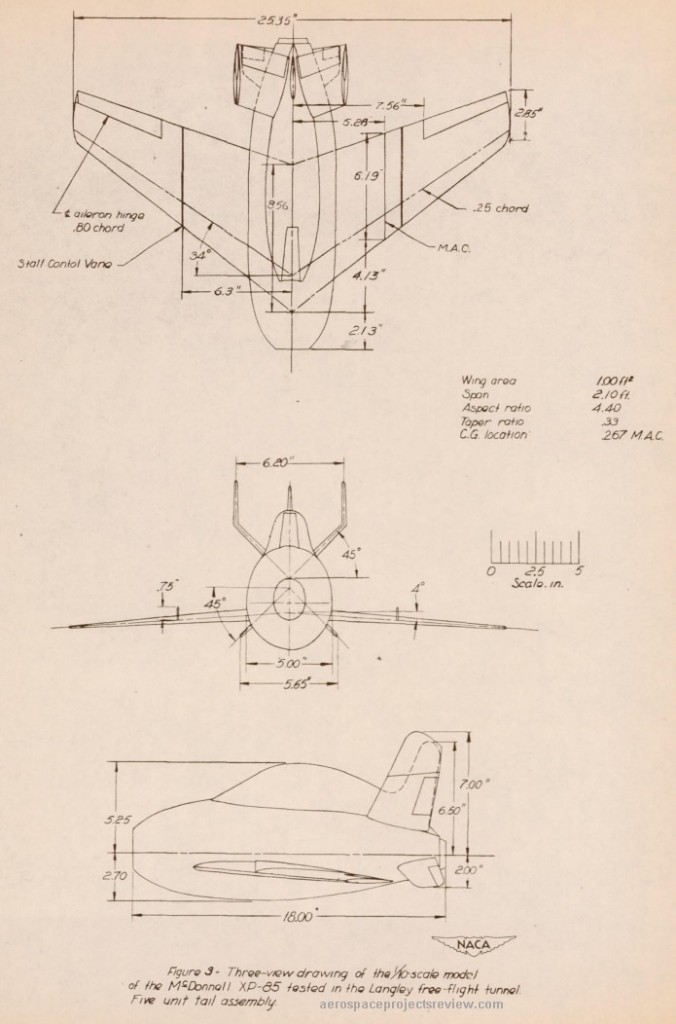
Diagram of the XP-85 model.