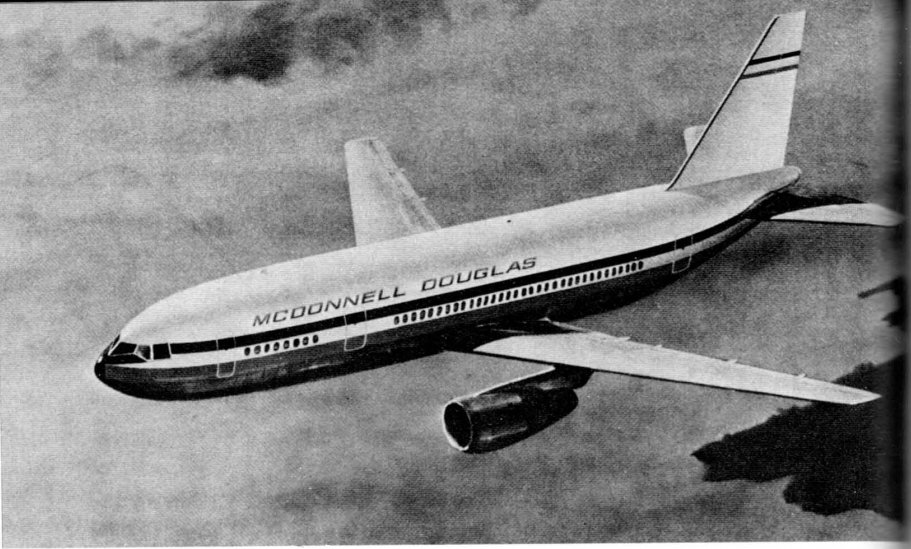
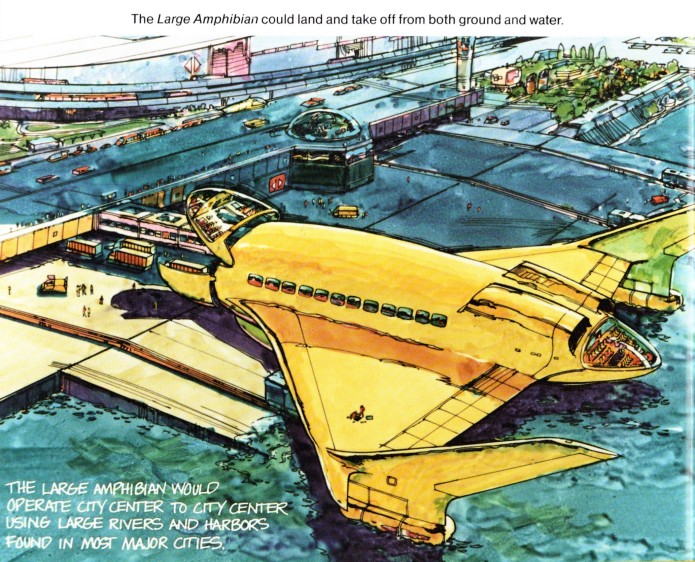
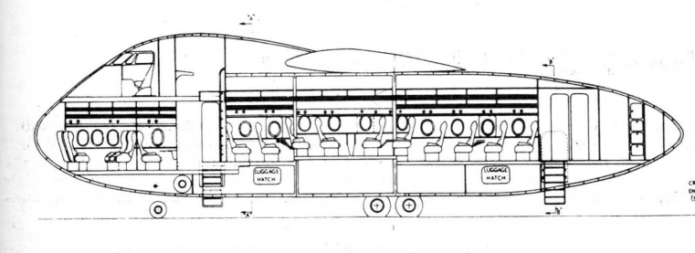
The 1970’s saw a lot of airlines and airline manufacturers going to great lengths to economize, thanks in no small part to the spike in fuel prices and general economic downturn caused by the OPEC oil embargo. Some of this economizing came in the form of new “air bus” concepts to jam as many people as possible into mid-sized jetliners. Wide-bodied configurations were popular for that. McDonnell-Douglas proposed a new airliner in the mid-70’s that was derived from their long-range high capacity DC-10. The fuselage was cut short and stubby; the third turbofan at the base of the vertical tail was deleted. The wings and tail surfaces were all-new. This made it slightly more economical on a passenger-mile basis than the trijet, but also made it inappropriate for trans-oceanic flight since airlines were not yet ready to accept twin-jets for such routes. Intercontinental flight in twinjets would have to wait for the 777. McDonnell-Douglas figured that up to 278 passengers could be wedged into the available space… and that even more seats could be installed in the below-deck cargo bay.
The full rez scan of the two-page article about this design has been made available at 300 DPI to all $4/month patrons/subscribers in the 2021-09 APR Extras folder at Dropbox. If you would like to help fund the acquisition and preservation of such things, along with getting high quality scans for yourself, please consider signing on either for the APR Patreon or the APR Monthly Historical Documents Program.
0