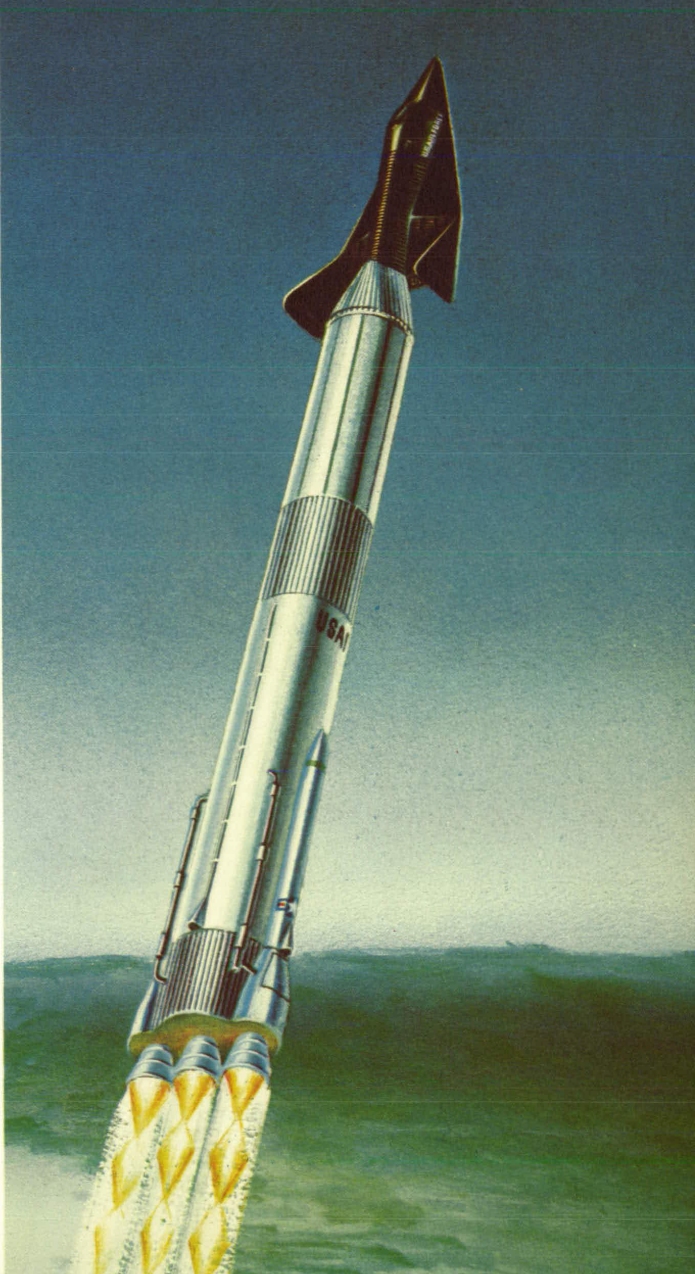
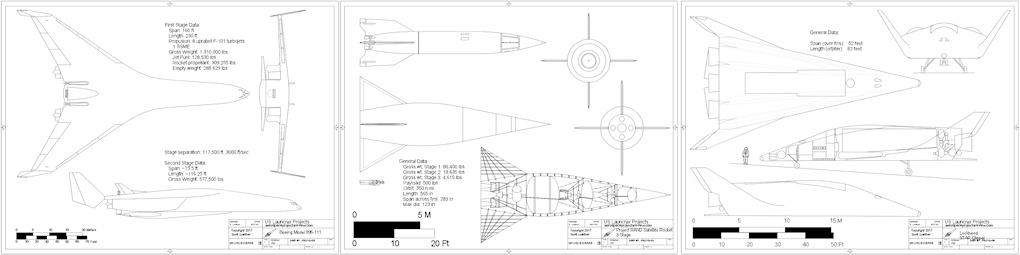
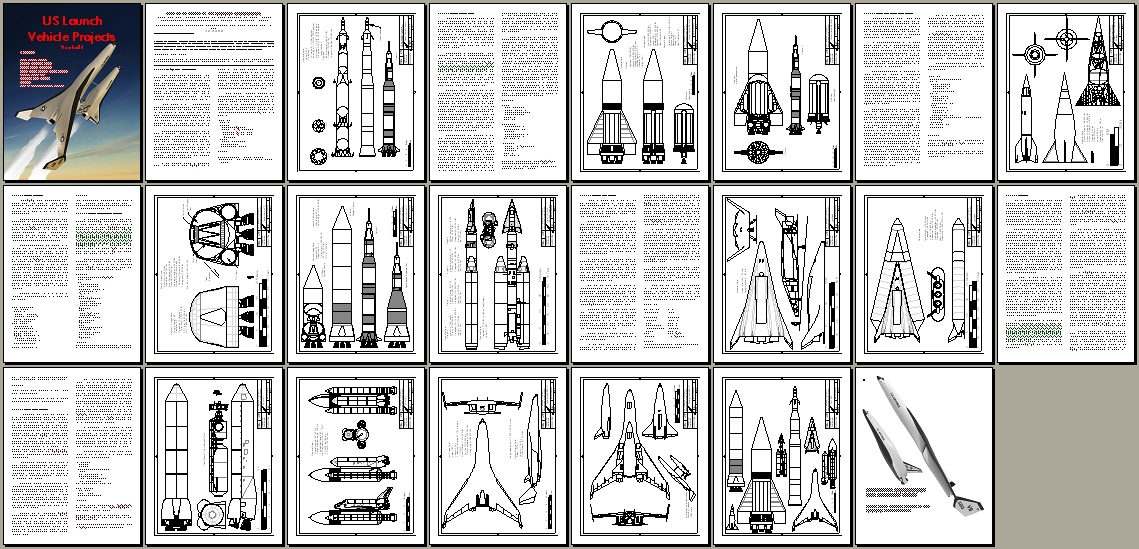
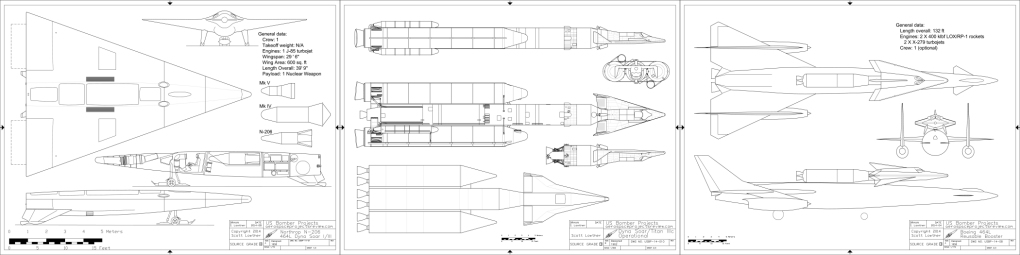
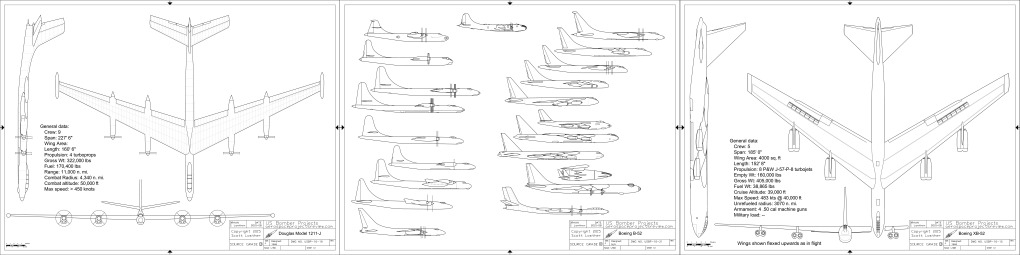
Every now and then something of aerospace history interest and importance shows up on EBay that is too expensive for easy acquisition, and so I will run a “crowdfunding campaign” to procure the funds to purchase the item. In these cases, the item – almost always a document of some kind – is scanned, the funders get complete copies, and the original is then sent to a relevant archive. Another such item has popped up.
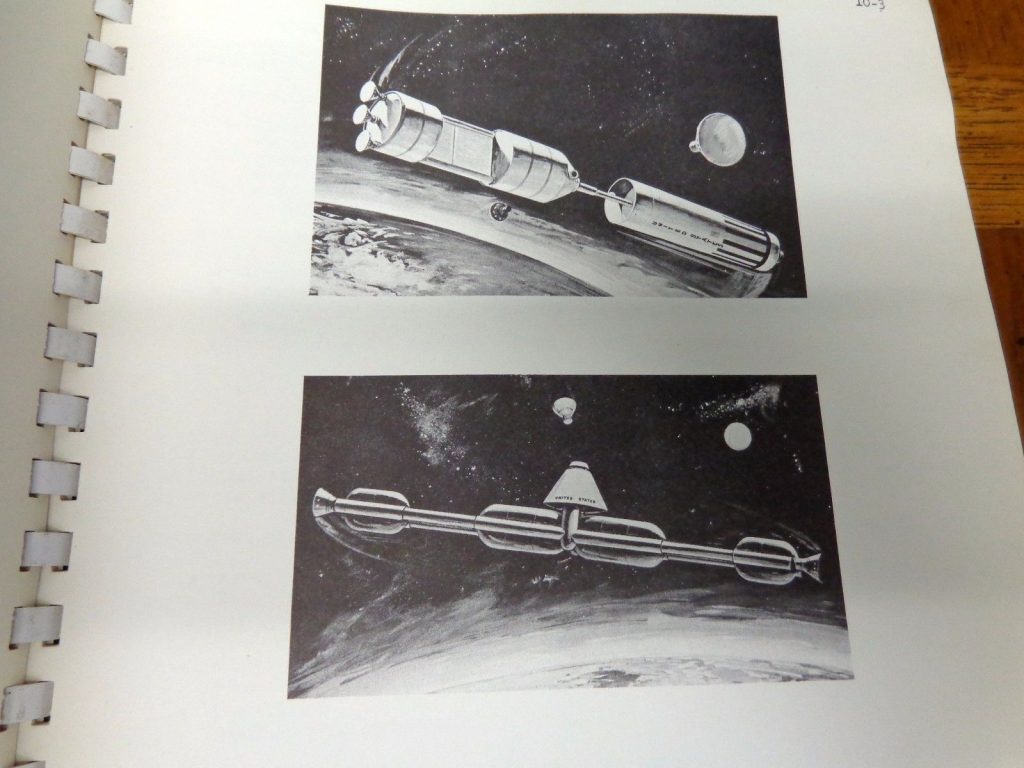
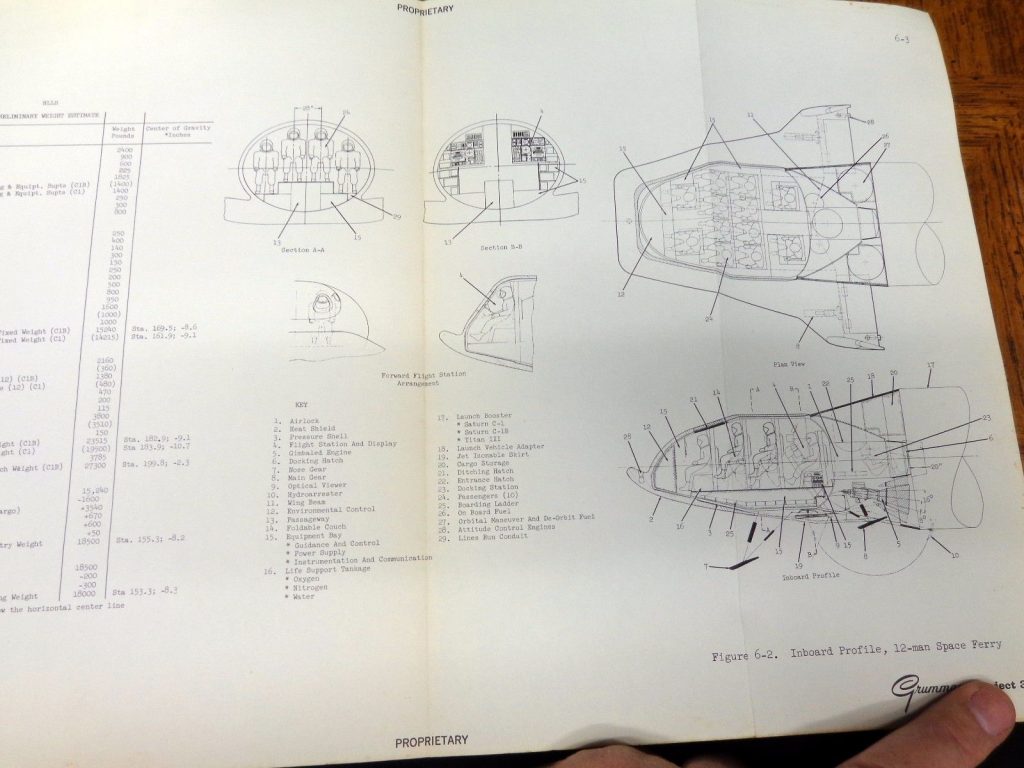
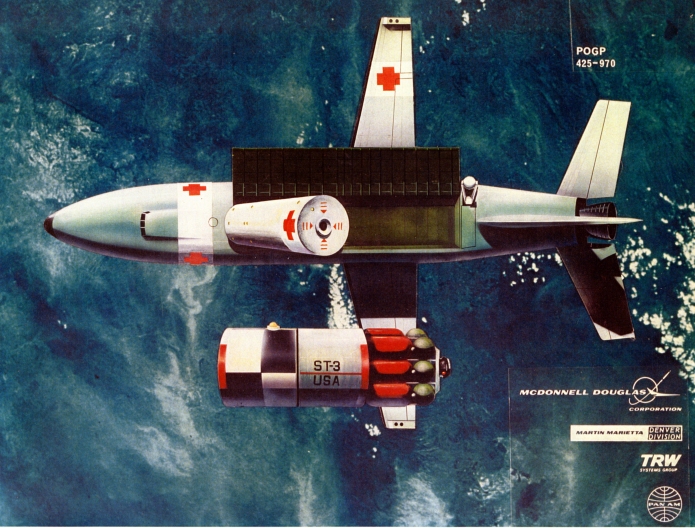
In this case, the item is expensive because the seller has put a stupid-high Buy It Now price on it. What they have is a pair of early-1960’s Grumman documents abut manned lifting body logistics spacecraft. Very interesting-looking stuff, the sort of item I’d snap up in a heartbeat for Aerospace Projects Review… if they didn’t cost $800.
So, I’m looking for people willing to join in on purchasing this. I currently have six people lined up, but the minimum this time is fifteen: this would drop the price per person to about $53.50. That’s still a pretty good chunk of change, but the more people who sign on, the lower the price will be.
So if you’d like to sign on, just send me an email  or comment below. You won’t be asked to put up money unless the documents are purchased, and that won’t happen until at least 15 people sign up. Check back here for updates.
or comment below. You won’t be asked to put up money unless the documents are purchased, and that won’t happen until at least 15 people sign up. Check back here for updates.
UPDATE, 11/15/2017-9:37PM mountain time: 10 people signed up. 2/3 of the way there…
UPDATE, 11:17 PM: 12 people.
UPDATE, 11/16/2017-8:29 AM: 14 people signed up. One more and I’ll pull the trigger on this, but I’ll keep availability open for a little while longer in order to hopefully bring in more funders and reduce the per-person cost. Can’t keep it open *too* long, because… sheesh, 800 bucks. My mortgage payment comes due *tomorrow.*
UPDATE, 7:54 PM: Now at 17 funders. The seller is currently away for a few days and it seems unlikely that anyone else will plunk down the $802 for this, so I’ll risk it and leave things open for a few more days to get more funders on board. With 17, the price per person is now $47.17. If it gets to 20, that’ll be $40.10, and so on.
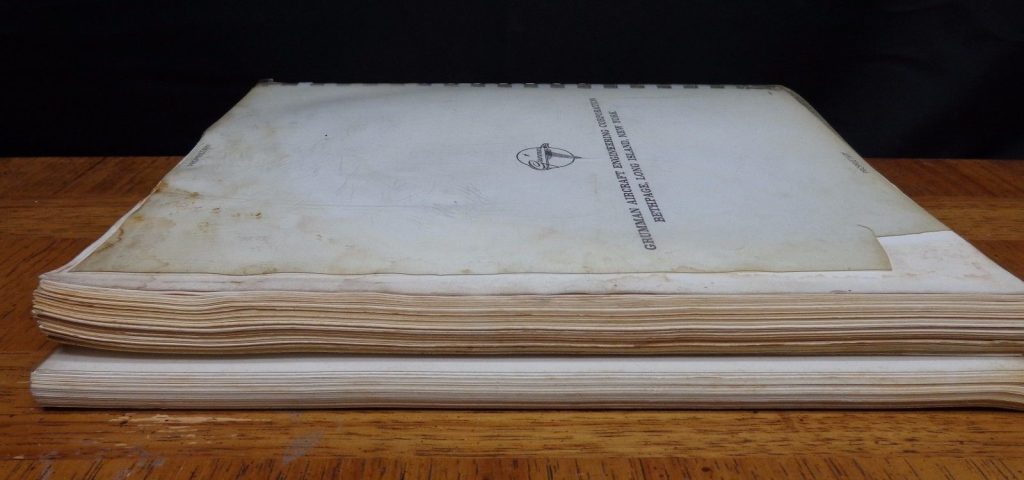
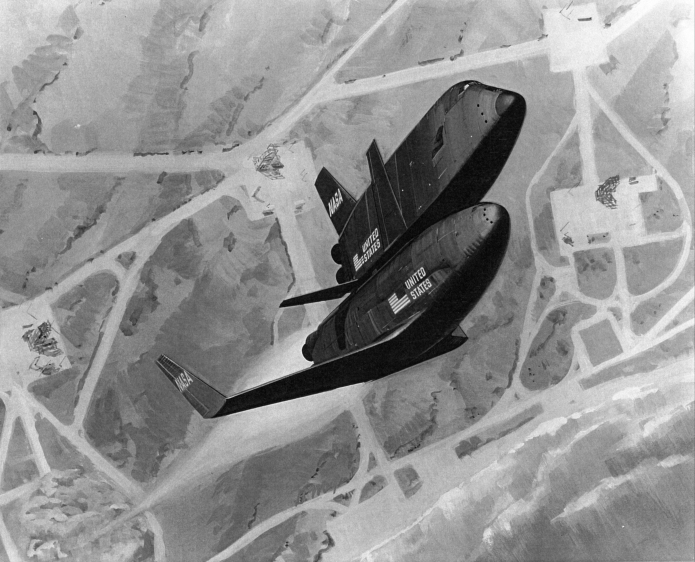







 or comment below. You won’t be asked to put up money unless the documents are purchased, and that won’t happen until at least 15 people sign up. Check back here for updates.
or comment below. You won’t be asked to put up money unless the documents are purchased, and that won’t happen until at least 15 people sign up. Check back here for updates.