A clearer view of the jet engine pod…
You can now purchase a printed version of Aerospace Projects Review issue V3N3 through MagCloud. Two options: just the printed version, and the printed version with a digital download (PDF).
See:
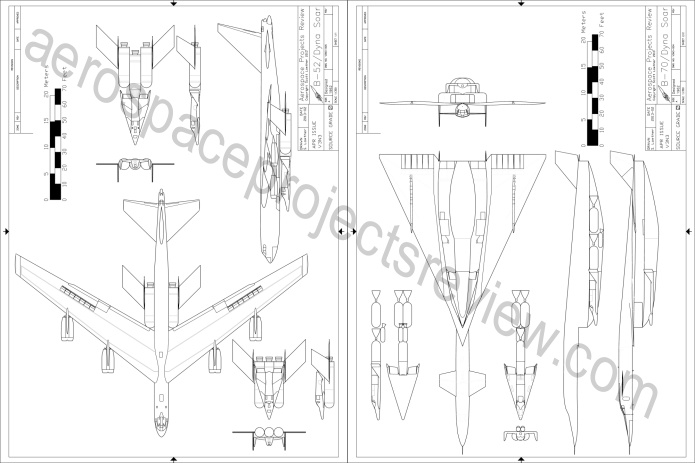
At last: issue V3N3 of APR is now available. The first article covers the proposed use of bombers, specifically the B-52 and B-70, as launch platforms for the Dyna Soar manned military spaceplane.
The second article is on the Martin Astrorocket, a series of early-sixties design studies of reusable low-cost manned launch systems for the USAF.
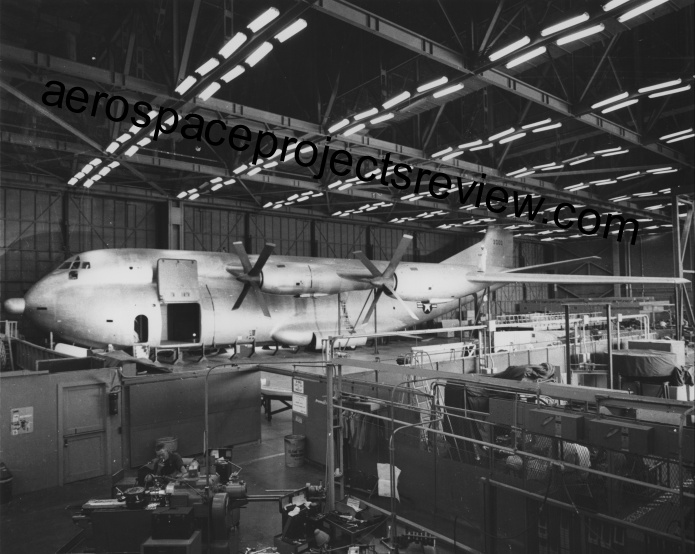
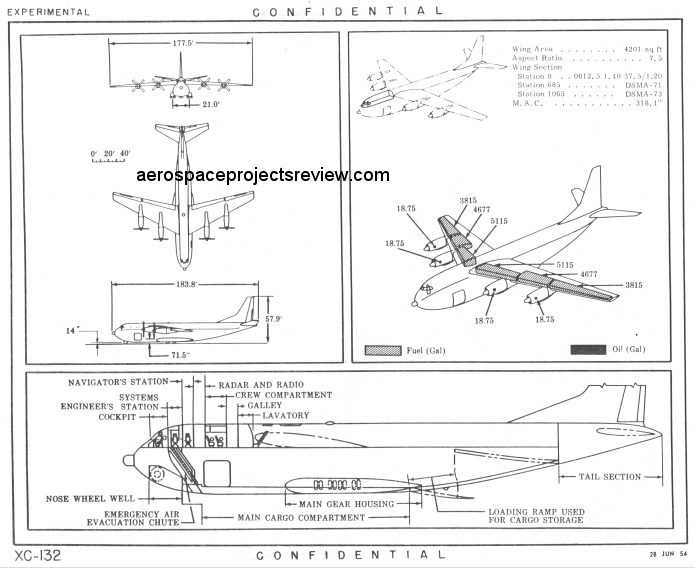
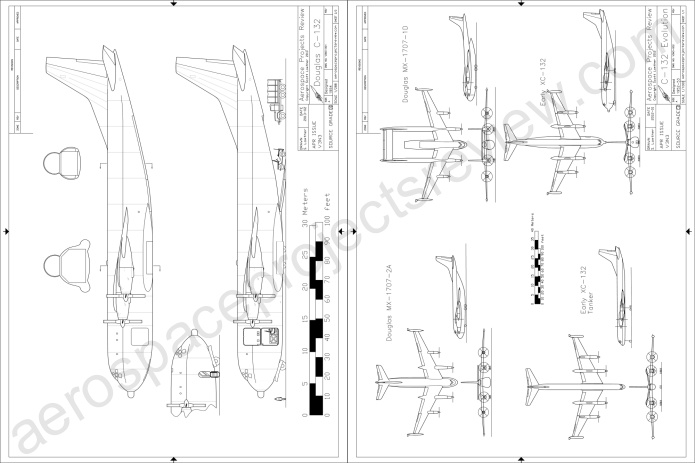
The next article covers the development of the Douglas XC-132 turboprop transport/tanker plane throughout much of the 1950’s. This would have been by far the biggest turboprop plane the us would have built… had it been built. Article contains a number of good photos of the full-scale mockup.
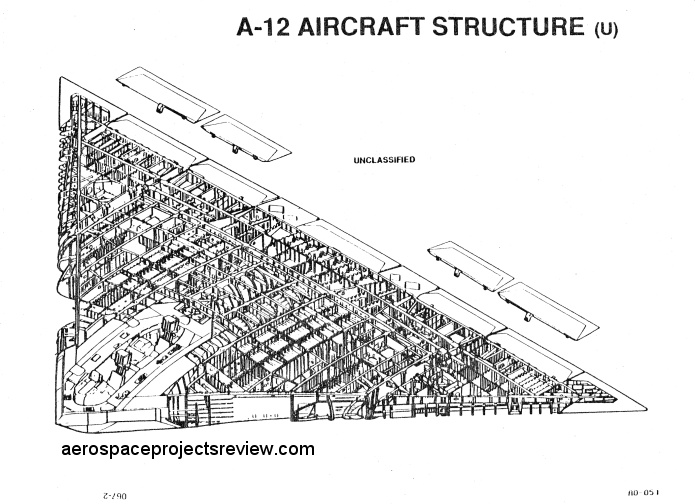
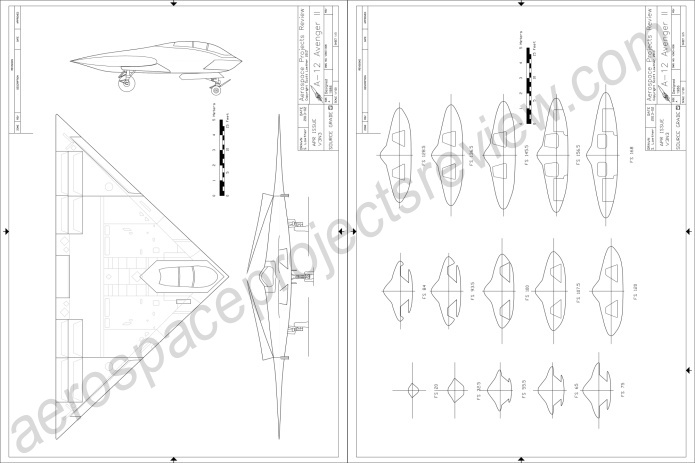
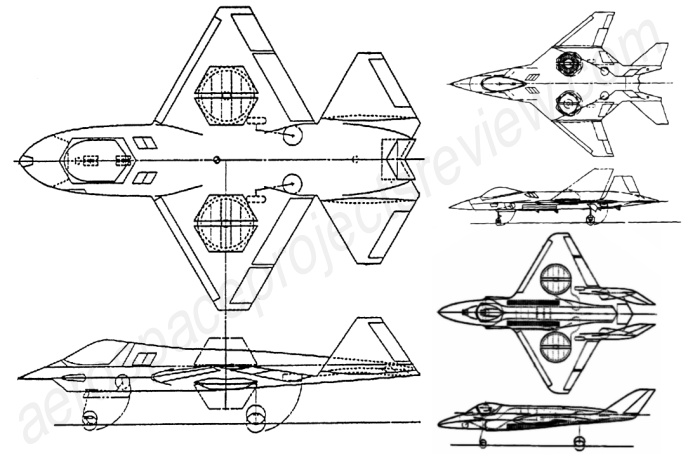
Next is an article on the A-12 Avenger II stealthy strike plane for the US Navy. This article includes info and drawings on the Northrop competitor, as well as a number of rarely seen and all-new detailed diagrams of the A-12.
A brief article on a trio of Grumman designs from the 1989-1993 time period, VTOL lift-fan combat aircraft, including the Future Attack Air Vehicle (FAAV).
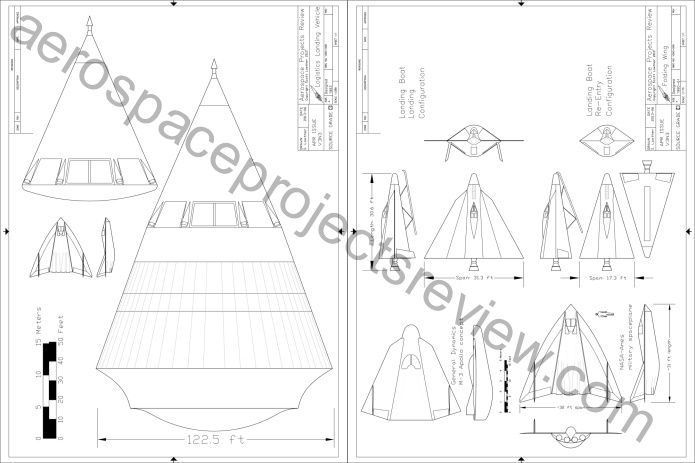
Last but not least, an article describing a trio of seemingly unrelated – yet possibly related – designs: a “landing boat” for Project Orion, a lifting body design for the Apollo program, and a fighter jet designed to be launched via booster rockets. Included is information on the logistics Landing Vehicle, General Dynamics’ equivalent of the Douglas ICARUS/Ithacus troop transport rocket.
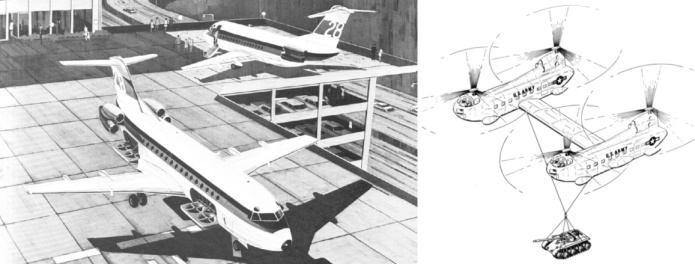
And two “Aerospace History Nuggets,” a Ryan concept for a VTOL jetliner and a concept from Bell for linking two helicopters together to forma single heavy lifter.
Here’s the complete issue V3N3 layout:
It is available in three formats. Firstly, it can be downloaded directly from me for the low, low price of $8.50. Second, it can be purchased as a professionally printed volume through Magcloud; third, it can be procured in both formats. To get the download, simply pay for it here through paypal.
——–
———
To get the printed version (or print + PDF version), visit my MagCloud page:
http://scottlowther.magcloud.com/
——————
Also available: the V3N3 Addendum. This contains 30 pages formatted for 11X17. Includes larger and improved versions of all the CAD diagrams produced for V3N3, including:
- 1/72 versions of the A-12 diagrams
- Scans of the original A-12 diagrams
- 1/144 versions of the XC-132 diagrams
- 1/288 versions of the XC-132 antecedents
- 1/250 versions of the Dyna Soar/bomber launchers
- 1/72 versions of the Landing Boat, “Space fighter” and Apollo lifting body
- 1/200 version of the Nova/LLV
The V3N3 Addendum can be downloaded for only $3.00!
——–
———
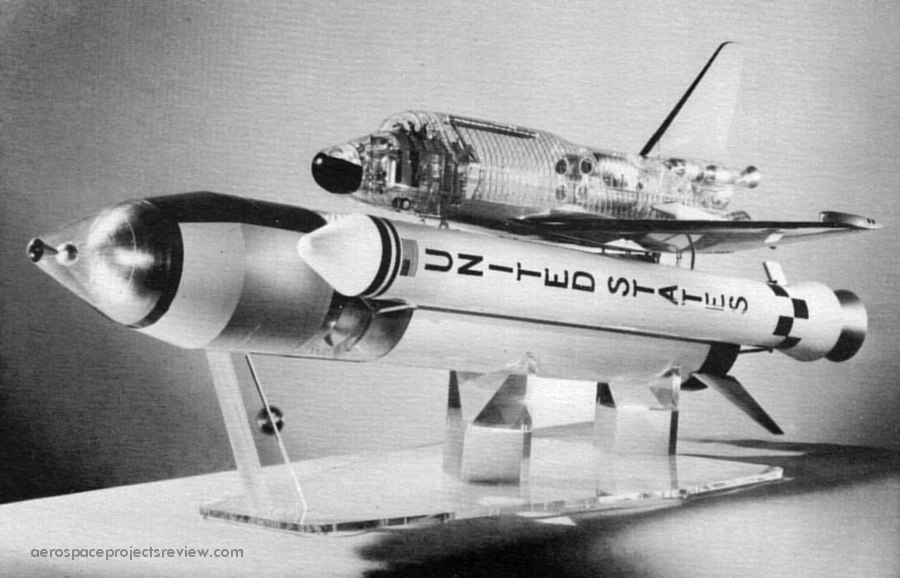
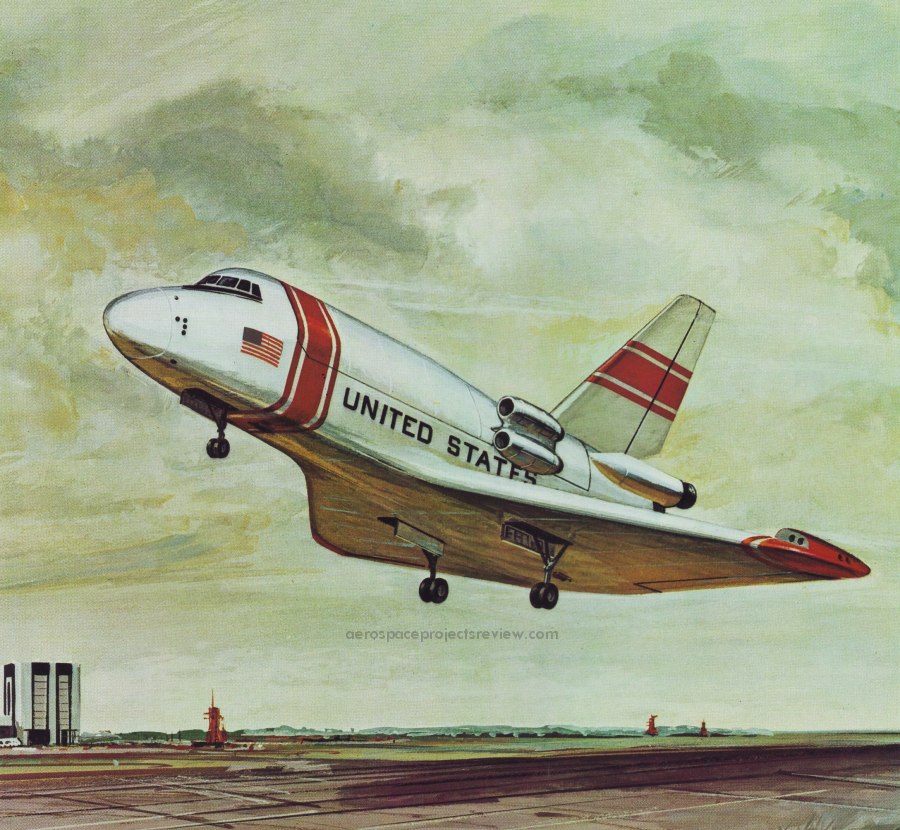
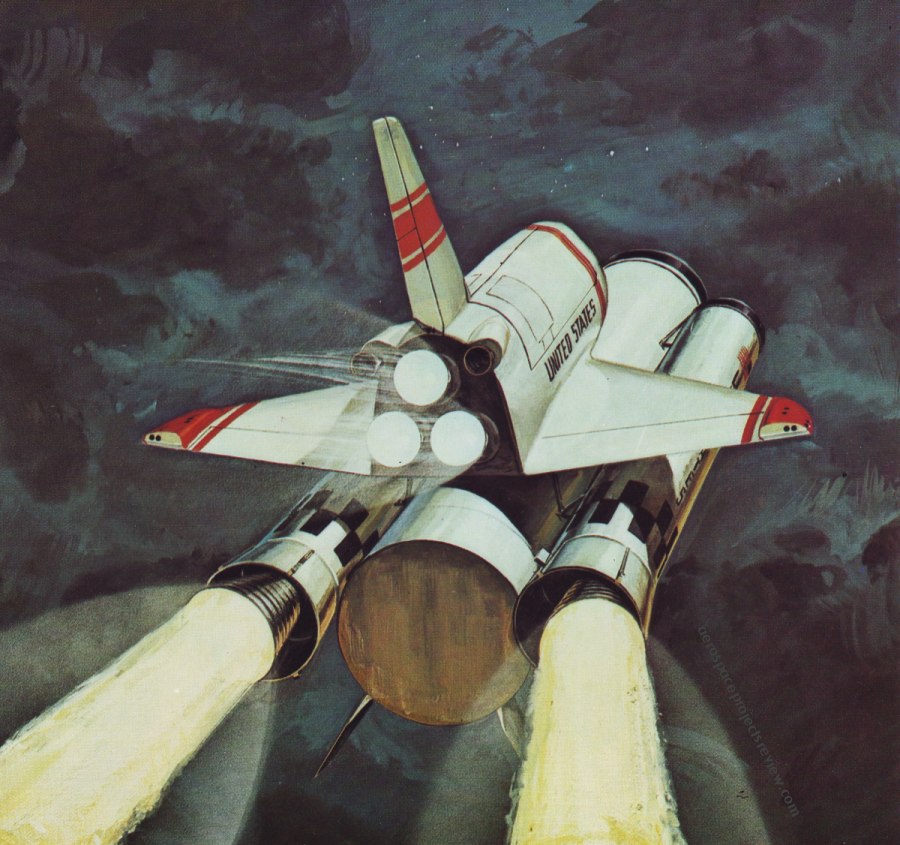
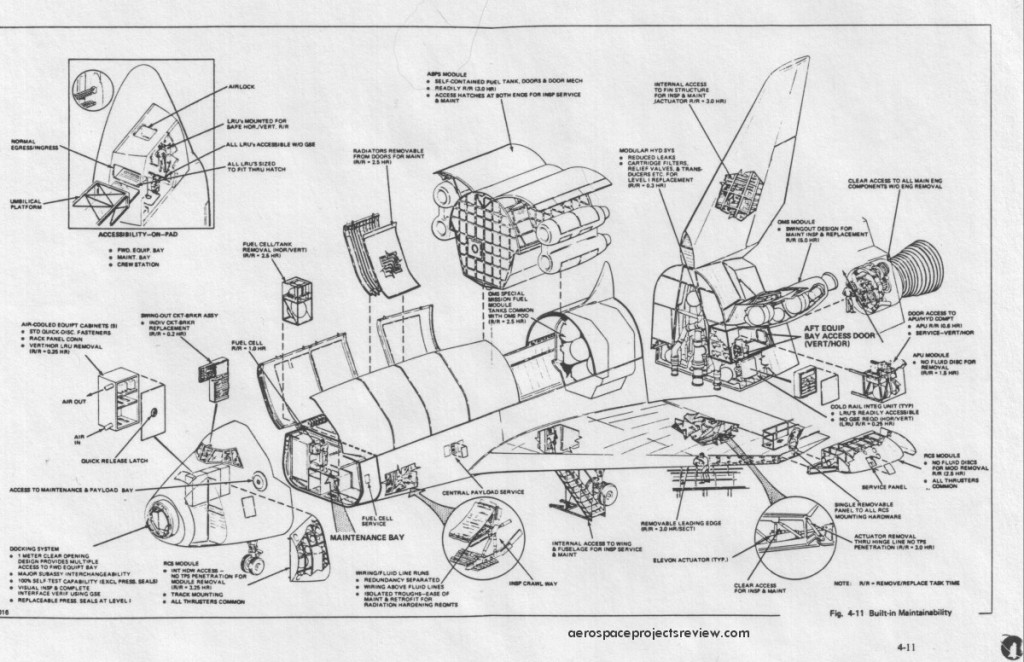
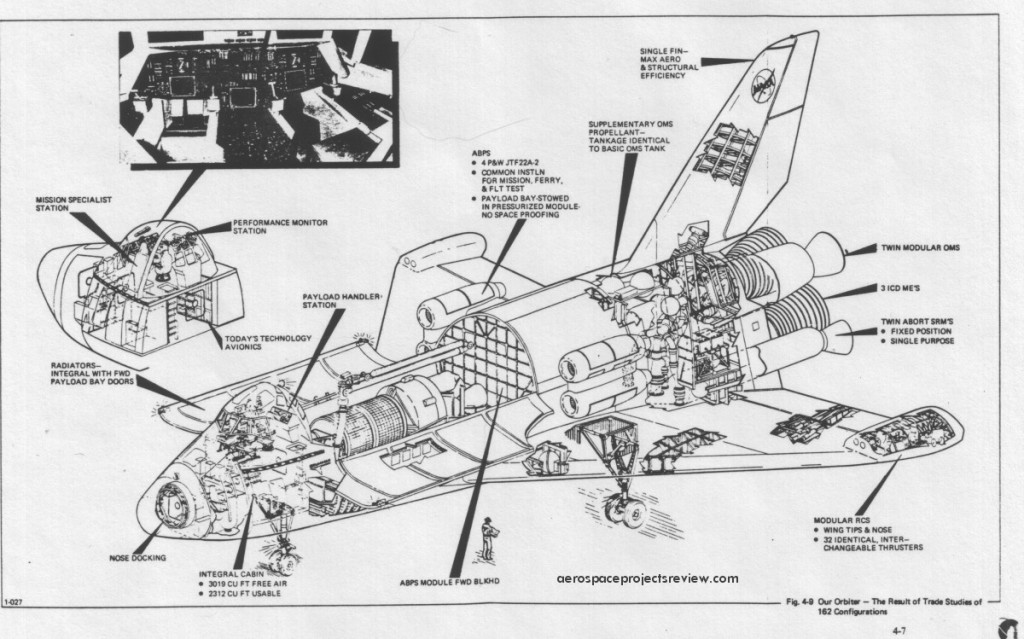
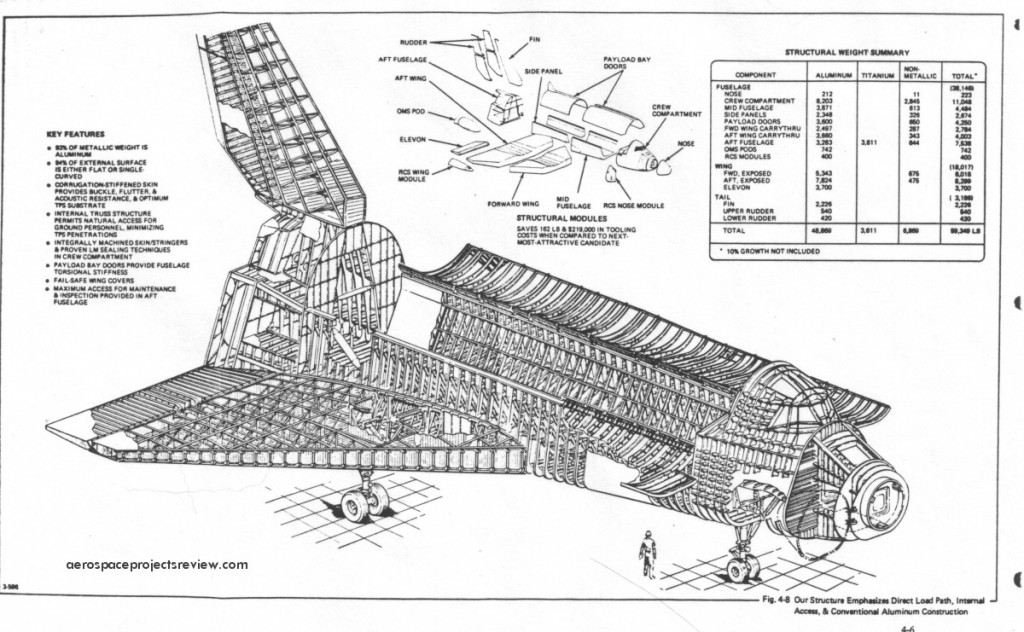
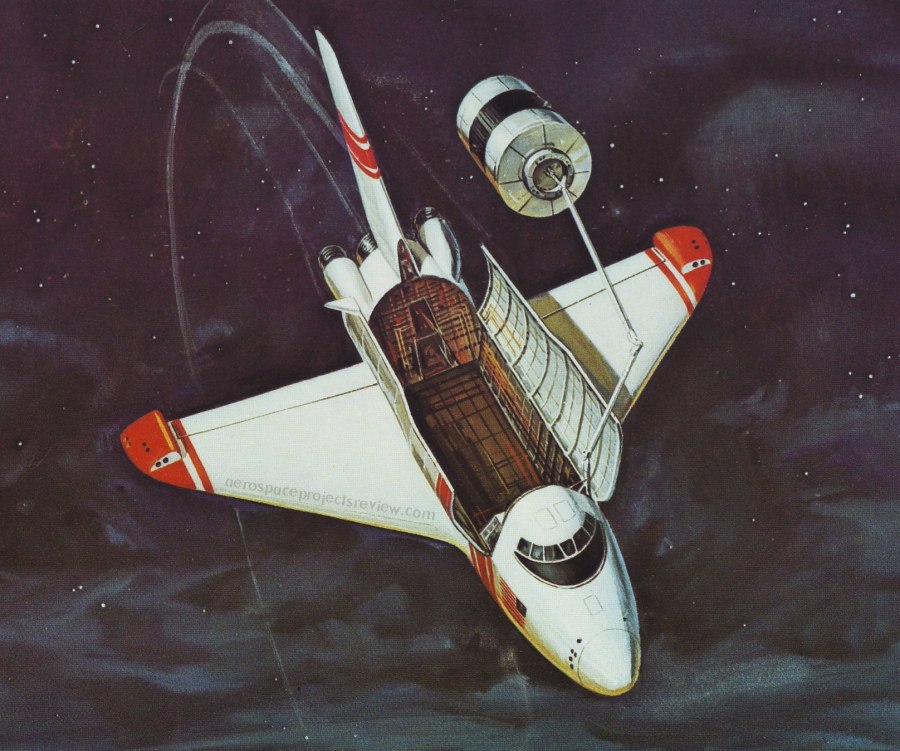
Some of the design features of the Grumman Design 619. Compared to the Shuttle Orbiter as actually built, the most obvious difference is the inclusion of the air breathing propulsion system model that consumes about 1/3 of the payload bay. Also note the RCS modules on the wingtips, the outward-bowing payload handlers station, nose airlock and the solid abort rockets along the aft fuselage.
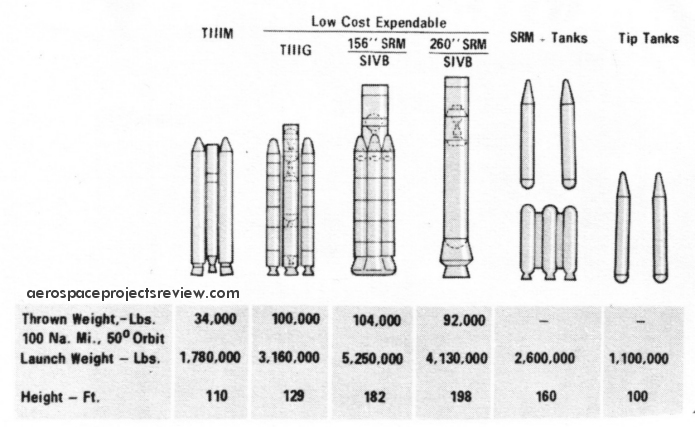
A little-known and poorly-documented proposed variant of the Titan family of launch vehicles, the Titan IIIG used an increased-diameter core with 156-inch diameter solid rocket boosters. The late-1960’s Titan IIIG would have been capable of launching 100,000 pounds, and seems to have been focused on USAF missions. McDonnell Douglas appears to have considered it for use in launching the Big Gemini logistics capsule. Beyond that, not much is known. The McD illustration below is one of the few I’ve come across, and does not seem likely to be terribly accurate. Also depicted here are the Titan IIIM, a launch vehicle composed of a cluster of four 156-inch solids topped by an S-IVb stage (a McD product), a 260-inch solid topped by an S-IVb, and external tank arrangements for reusable launch vehicles such as the ILRV (integral Launch and Recovery Vehicle), a predecessor to the Space Shuttle. McD’s entry to the ILRV study was a derivative of their generic Model 176 concept.
An illustration of Grumman’s 619 Space Shuttle – the final competitor for the competition that North American Rockwell won – lifting off. This design from 1972 was laid out pretty much as the final Space Transportation System was, but with some notable differences:
1) Stabilizing fins on the external tank
2) A “humped” back
3) four turbojet engines could be stored in the rear of the cargo bay, used for landing range extension, go-around capability and self-ferrying
4) Smaller OMS pods
5) Separate reaction control pods on the wingtips