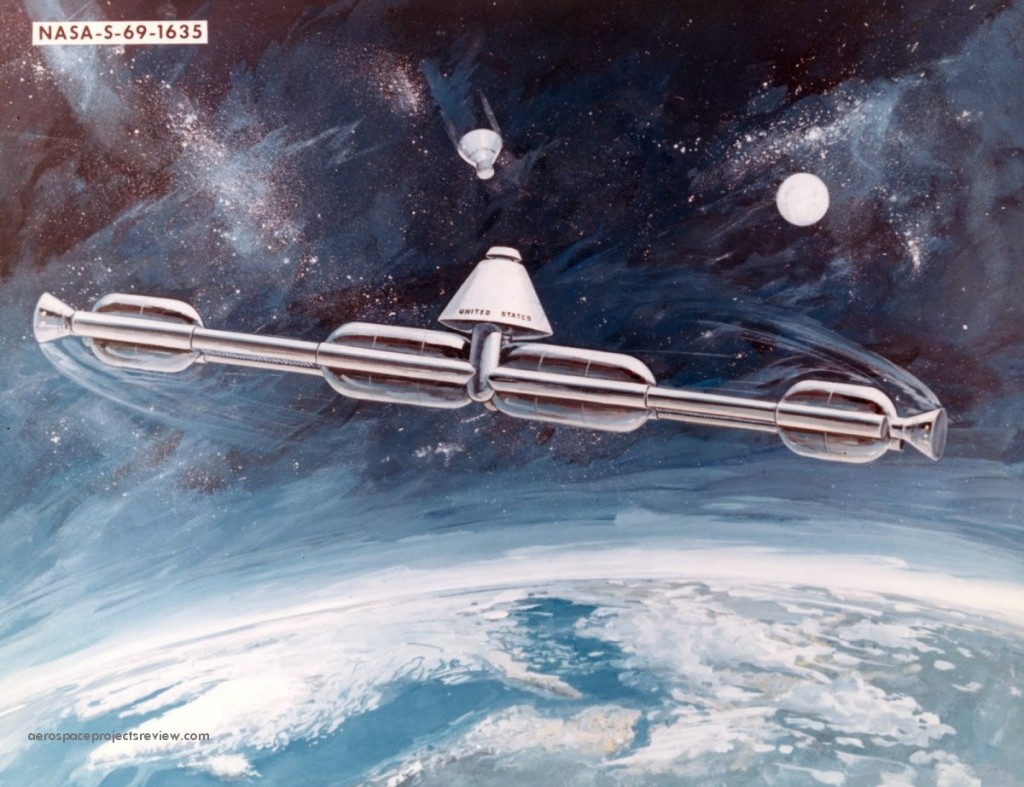
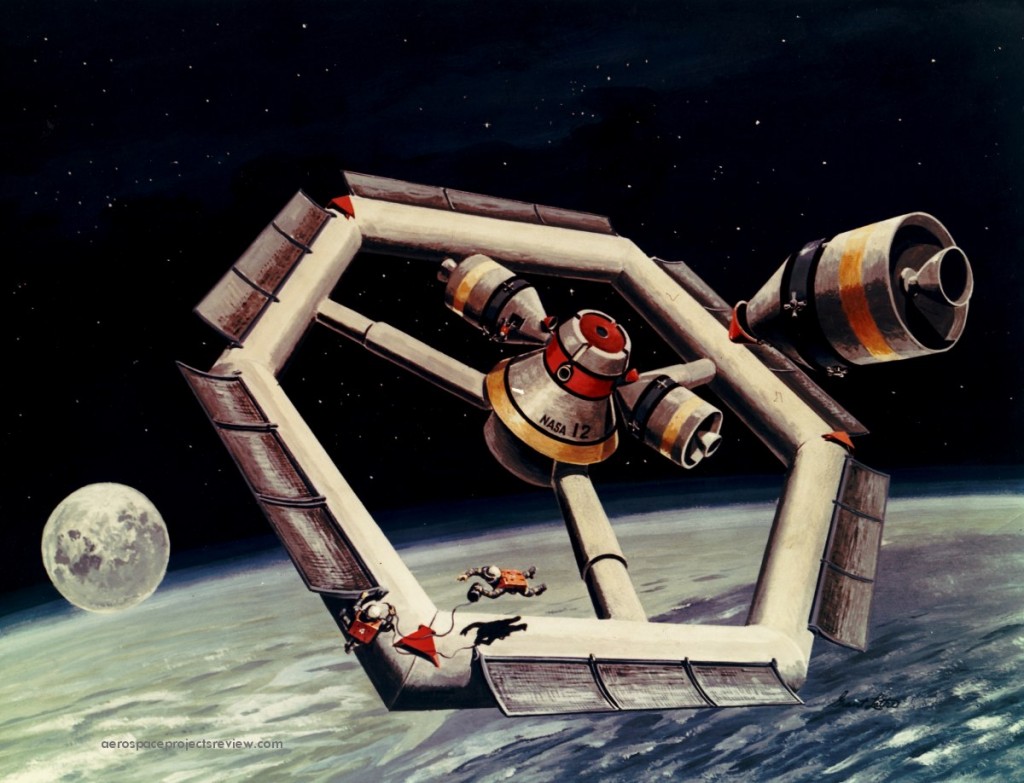
NASA artwork from 1962 depicting a single-launch space station. Launched by a Saturn V, this space station would be folded up, then would unfold once on orbit to form something of a torus. Rotation would then supply a measure of artificial gravity. With a design like this, much of the inner volume would not be very efficiently used… as the straight cylindrical segments diverge further from a circular centerline for a hypothetical truly circular torus, the more the inner surface of the segment would seem to slope “uphill.” Thus the interior would probably be stepped so that the floor would be “flat” from the acceleration vector point of view, to keep everything from rolling or sliding “downhill.” In this case the central hub appears to be rotationally decoupled.
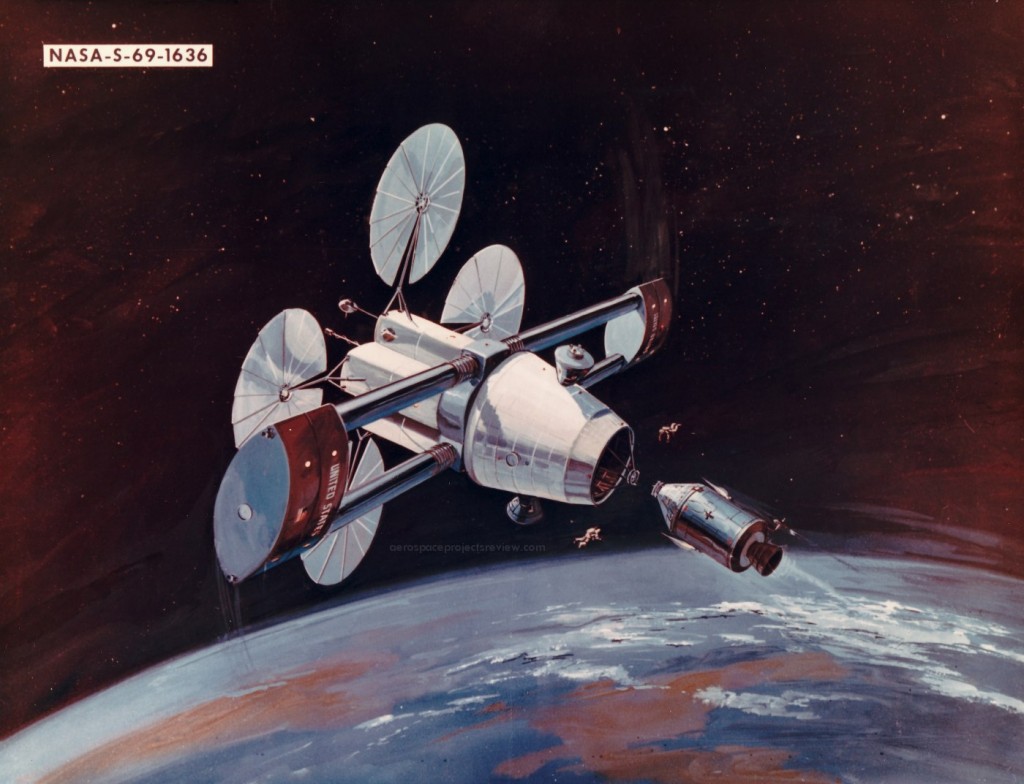
Image is related to this radial-arm concept, and was scanned at the NASA HQ history archive.