Here are two presumably wholly unrelated pieces of aerospace artwork. At least I *hope* they’re unrelated…
The first is an anonymous painting of a spaceplane. Doesn’t seem terribly realistic; most likely done for advertising purposes (I wonder if the “7-11” might indicate a relationship to the chain of the same name). The print arrived damaged, as you an see; the paper was thick and *really* brittle and really didn’t appreciate being rolled up. If anyone knows anything about it, feel free to comment.
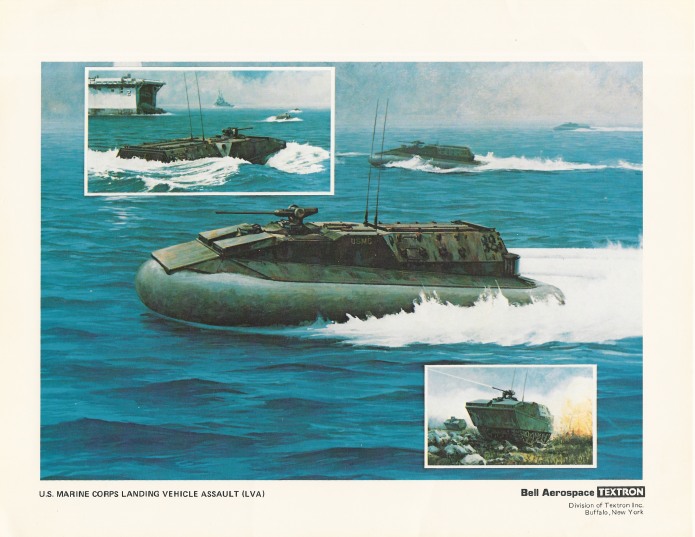
The second is concept art from Bell Aerospace illustrating an amphibious troop carrier for the Marine Corps. The design of the assault vehicle is fairly ordinary as such things go, except for one detail: it could turn into a hovercraft and float across the surface of the water, rather than plowing through it. No further details provided, so I don’t know if the hover-skirts were deployable and retractable, or if they were simply dropped when the vehicle got to shore. The latter would certainly seem more economical.
I’ve uploaded the full rez scans to the 2018-03 APR Extras Dropbox folder, available to all current APR Patrons at the $4 level and above. If you are interested in this and a great many other “extras” and monthly aerospace history rewards, please sign up for the APR Patreon. Chances are good that $4/month is far cheaper than your espresso/booze budget!