The SST designs of the 1960’s are hardly unknown. But what’s generally not well understood is that designs such as the Boeing 2707 were *huge.* This was considered necessary because SSTs with fuselage lengths in line with existing jetliners – such as the Concorde – would have small passenger capacities due to the need for the fuselages to be *very* narrow compared to their lengths. This, as Concorde showed, was a great way to build an extremely cost-ineffective fuel hog.
So the 2707 would be terribly long and pointy, with a geometry quite a bit unlike regular jetliners. A practical concern is “how do we deal with these things at airports?” If nothing else, the long pointed nose of the SST would put the passenger door considerably further aft than for a conventional rounded-nose jetliners. So, like the 747 and the A380, it was assumed that the larger airports would have to make some infrastructure modifications in order to deal with these new beasts.
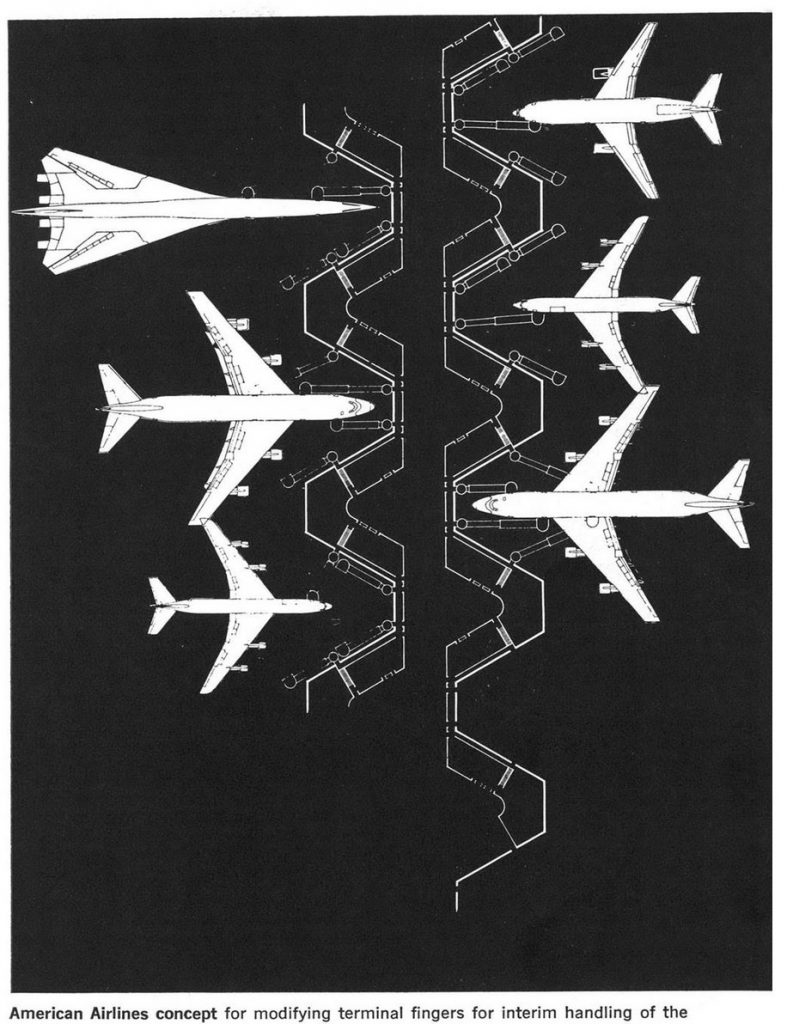
The illustration below, from a 1967 issue of Aviation Week, shows American Airlines thinking about the airports of the future. Note that the 2707 is pulled in far closer than the other craft, with the tip of t’s very pointed nose just a few feet away from the building while the others are notably further away. The SST is being serviced by two extendable jetways at maximum extension, while most of the other planes seem to be getting along with just one jetway… though one of the 747s is using four. Note that even though the 747 isn’t pulled in quite as far as the 2707, the SST nonetheless projects much further out into the airfield. For some airports this could well have meant that the taxiways would have been a cluttered mess.