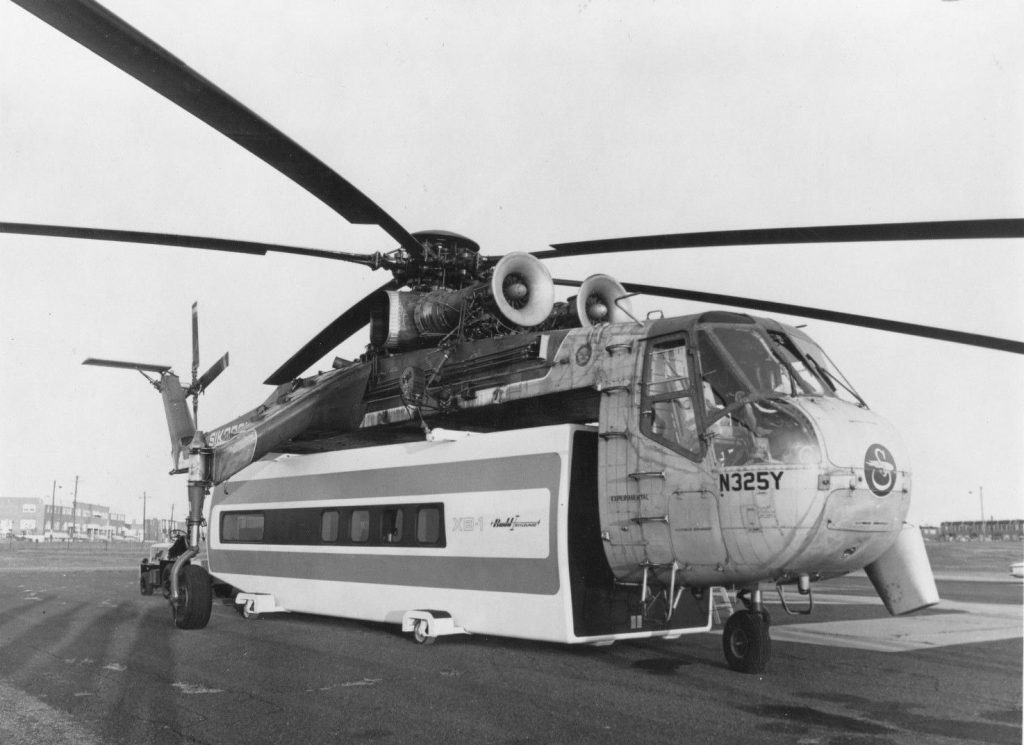
Throughout the 1960’s Sikorsky tried to sell a civilian passenger transport helicopter to airlines. The helicopter in question was the “S-65,” not to be confused with the CH-53 Sea Stallion which also bore the S-65 designation. The civilian S-65 design effort dragged on into the early 1970s and involved a very wide range of designs. One of the earliest configurations (1962) was a more or less civilianized version of the military S-65/CH-53.

The design quickly changed, diverging far from the CH-53 basis and beginning to incorporate unconventional elements. By the end of 1962 the CH-53 elements were almost gone (the cockpit and engine/rotor system are visually somewhat similar, but clearly different), and the tail incorporated an unusual dual-torque rotor configuration, one rotor on the end of two butterfly tails.

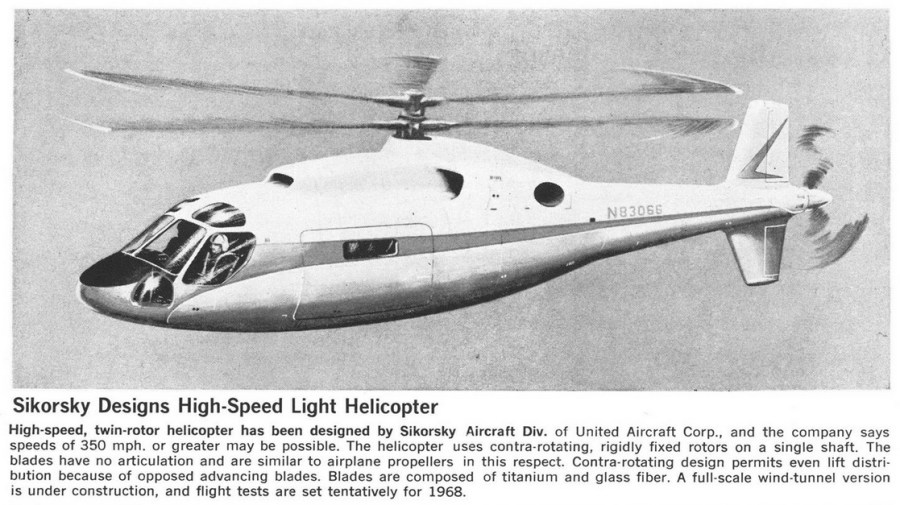
By 1965 the tail had reverted to a more normal layout; the fuselage was now circular in cross section and visually rotund.

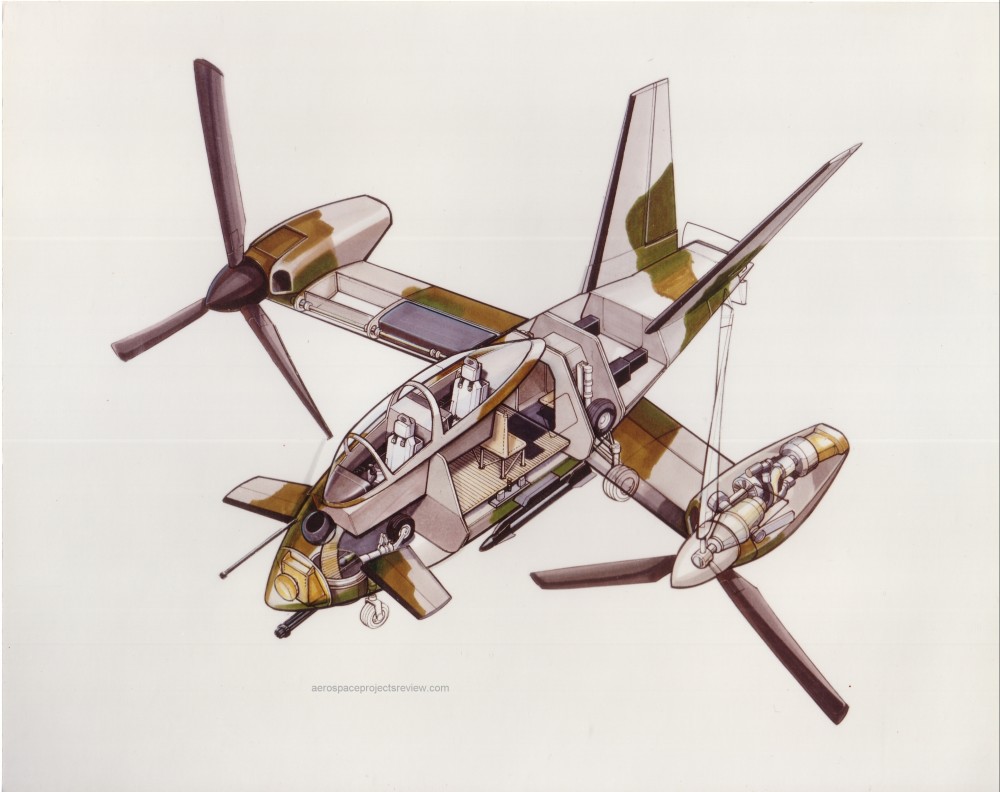
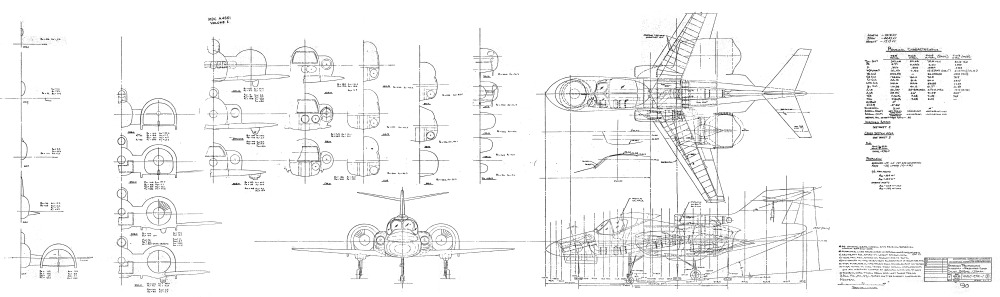
By 1968 the S-65 had transformed from a pure helicopter into a compound helicopter, adding two turboprops under two stub wings. These would greatly increase forward speed and cruise fuel efficiency, at of course added weight and cost. The tail reverted to the earlier butterfly configuration, but with a single torque rotor.

By 1969 the 1968 design was modestly refined and proposed to the USAF as a search and recovery aircraft, which a compound helicopter should theoretically be good at. This was more or less the end of the line for design development. Throughout the project, a number of varitions on each configuration were proposed, including a version using more or less the last design but with telescoping main rotor blades that would shrink in diameter during high speed flight, reducing drag.