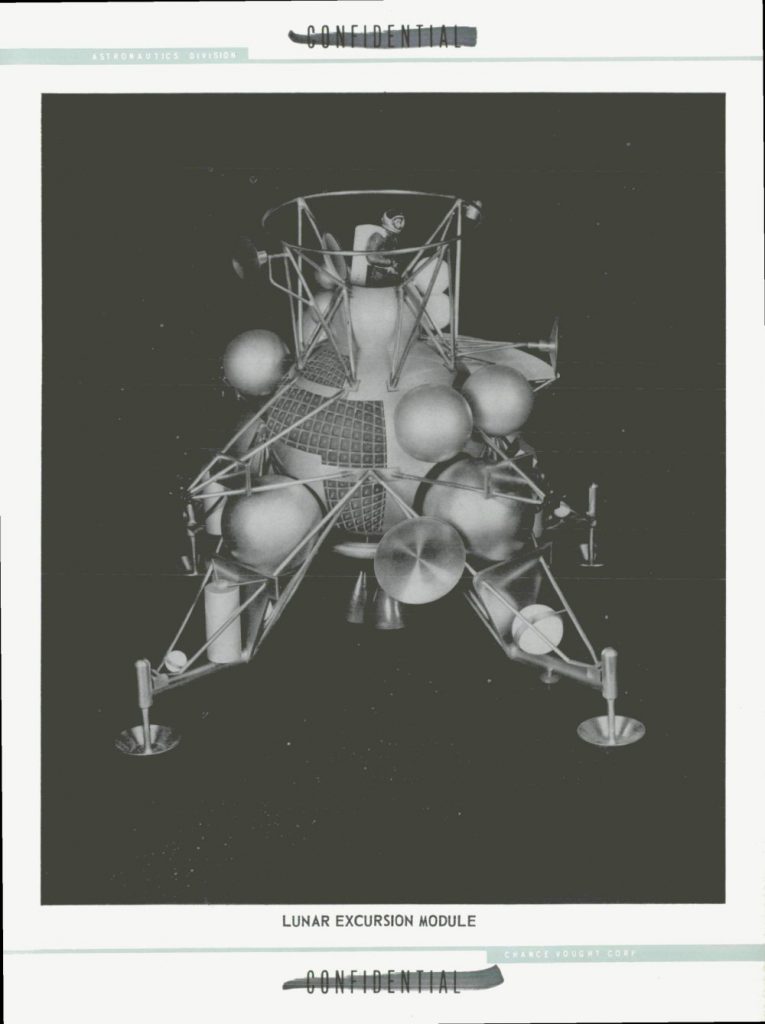
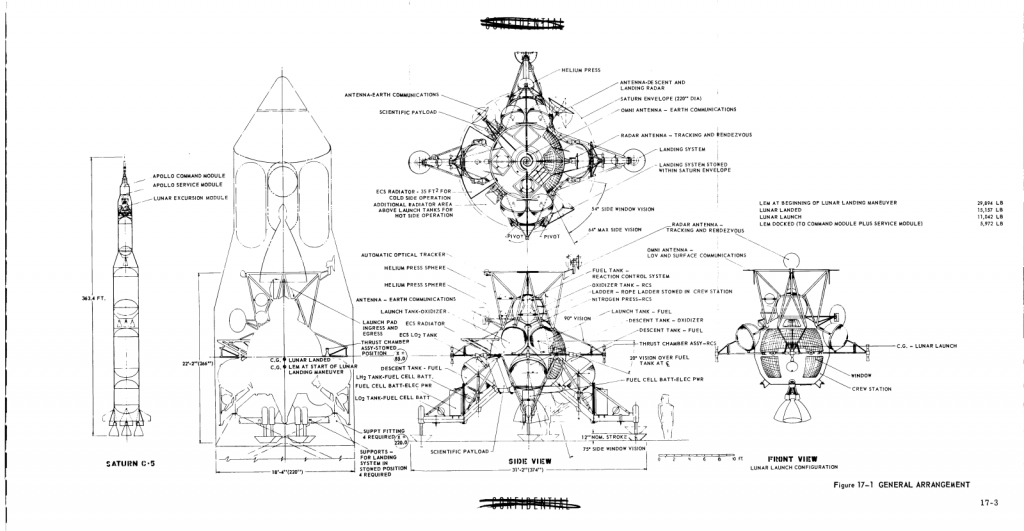
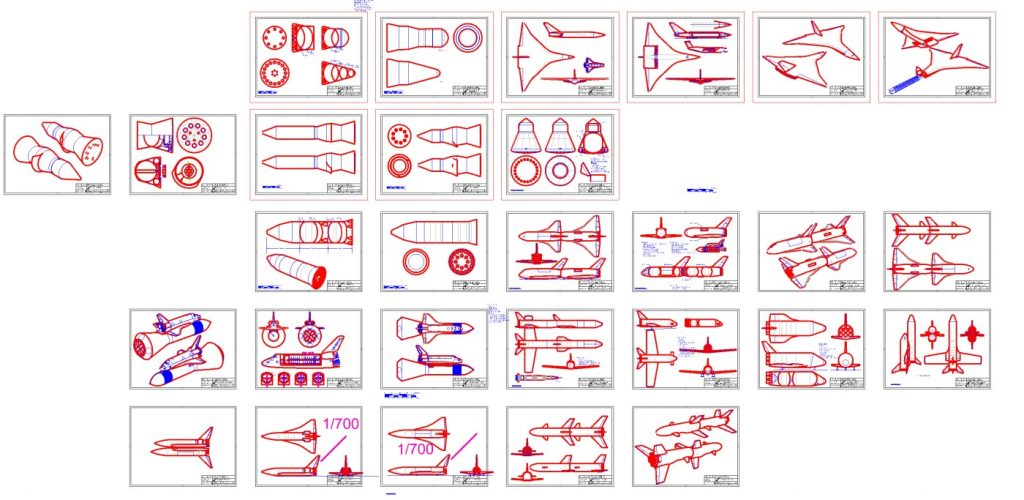
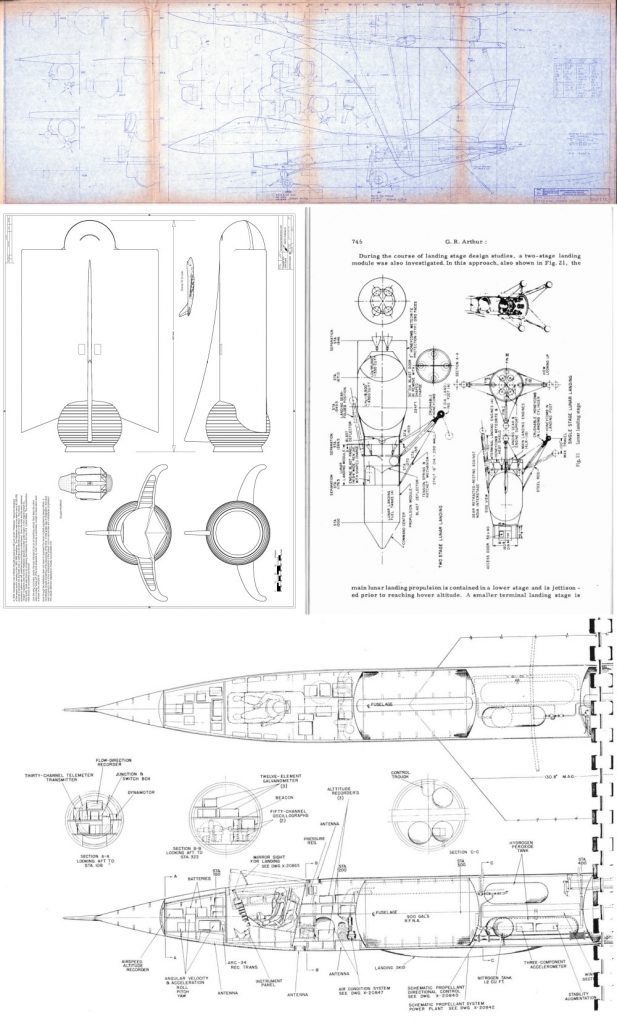
While these may be originally spacecraft-specific, they apply not only to other areas of aerospace engineering, but to all areas of life. The canonical list is kept HERE.
1. Engineering is done with numbers. Analysis without numbers is only an opinion.
2. To design a spacecraft right takes an infinite amount of effort. This is why it’s a good idea to design them to operate when some things are wrong .
3. Design is an iterative process. The necessary number of iterations is one more than the number you have currently done. This is true at any point in time.
4. Your best design efforts will inevitably wind up being useless in the final design. Learn to live with the disappointment.
5. (Miller’s Law) Three points determine a curve.
6. (Mar’s Law) Everything is linear if plotted log-log with a fat magic marker.
7. At the start of any design effort, the person who most wants to be team leader is least likely to be capable of it.
8. In nature, the optimum is almost always in the middle somewhere. Distrust assertions that the optimum is at an extreme point.
9. Not having all the information you need is never a satisfactory excuse for not starting the analysis.
10. When in doubt, estimate. In an emergency, guess. But be sure to go back and clean up the mess when the real numbers come along.
11. Sometimes, the fastest way to get to the end is to throw everything out and start over.
12. There is never a single right solution. There are always multiple wrong ones, though.
13. Design is based on requirements. There’s no justification for designing something one bit “better” than the requirements dictate.
14. (Edison’s Law) “Better” is the enemy of “good”.
15. (Shea’s Law) The ability to improve a design occurs primarily at the interfaces. This is also the prime location for screwing it up.
16. The previous people who did a similar analysis did not have a direct pipeline to the wisdom of the ages. There is therefore no reason to believe their analysis over yours. There is especially no reason to present their analysis as yours.
17. The fact that an analysis appears in print has no relationship to the likelihood of its being correct.
18. Past experience is excellent for providing a reality check. Too much reality can doom an otherwise worthwhile design, though.
19. The odds are greatly against you being immensely smarter than everyone else in the field. If your analysis says your terminal velocity is twice the speed of light, you may have invented warp drive, but the chances are a lot better that you’ve screwed up.
20. A bad design with a good presentation is doomed eventually. A good design with a bad presentation is doomed immediately.
21. (Larrabee’s Law) Half of everything you hear in a classroom is crap. Education is figuring out which half is which.
22. When in doubt, document. (Documentation requirements will reach a maximum shortly after the termination of a program.)
23. The schedule you develop will seem like a complete work of fiction up until the time your customer fires you for not meeting it.
24. It’s called a “Work Breakdown Structure” because the Work remaining will grow until you have a Breakdown, unless you enforce some Structure on it.
25. (Bowden’s Law) Following a testing failure, it’s always possible to refine the analysis to show that you really had negative margins all along.
26. (Montemerlo’s Law) Don’t do nuthin’ dumb.
27. (Varsi’s Law) Schedules only move in one direction.
28. (Ranger’s Law) There ain’t no such thing as a free launch.
29. (von Tiesenhausen’s Law of Program Management) To get an accurate estimate of final program requirements, multiply the initial time estimates by pi, and slide the decimal point on the cost estimates one place to the right.
30. (von Tiesenhausen’s Law of Engineering Design) If you want to have a maximum effect on the design of a new engineering system, learn to draw. Engineers always wind up designing the vehicle to look like the initial artist’s concept.
31. (Mo’s Law of Evolutionary Development) You can’t get to the moon by climbing successively taller trees.
32. (Atkin’s Law of Demonstrations) When the hardware is working perfectly, the really important visitors don’t show up.
33. (Patton’s Law of Program Planning) A good plan violently executed now is better than a perfect plan next week.
34. (Roosevelt’s Law of Task Planning) Do what you can, where you are, with what you have.
35. (de Saint-Exupery’s Law of Design) A designer knows that he has achieved perfection not when there is nothing left to add, but when there is nothing left to take away.
36. Any run-of-the-mill engineer can design something which is elegant. A good engineer designs systems to be efficient. A great engineer designs them to be effective.
37. (Henshaw’s Law) One key to success in a mission is establishing clear lines of blame.
38. Capabilities drive requirements, regardless of what the systems engineering textbooks say.
39. Any exploration program which “just happens” to include a new launch vehicle is, de facto, a launch vehicle program.
39. (alternate formulation) The three keys to keeping a new human space program affordable and on schedule:
1) No new launch vehicles.
2) No new launch vehicles.
3) Whatever you do, don’t develop any new launch vehicles.
40. (McBryan’s Law) You can’t make it better until you make it work.
41. There’s never enough time to do it right, but somehow, there’s always enough time to do it over.
42. Space is a completely unforgiving environment. If you screw up the engineering, somebody dies (and there’s no partial credit because most of the analysis was right…)