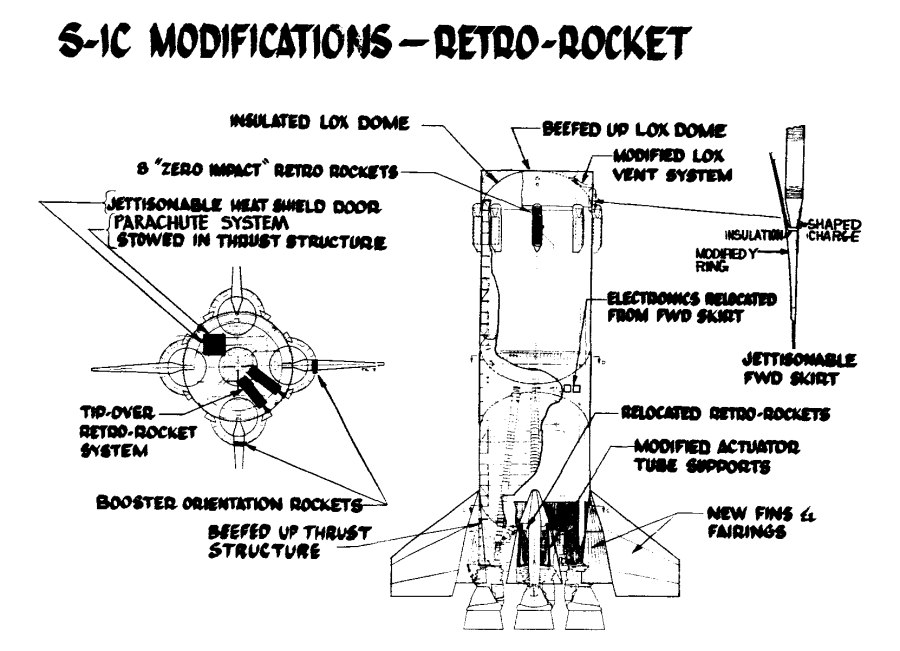
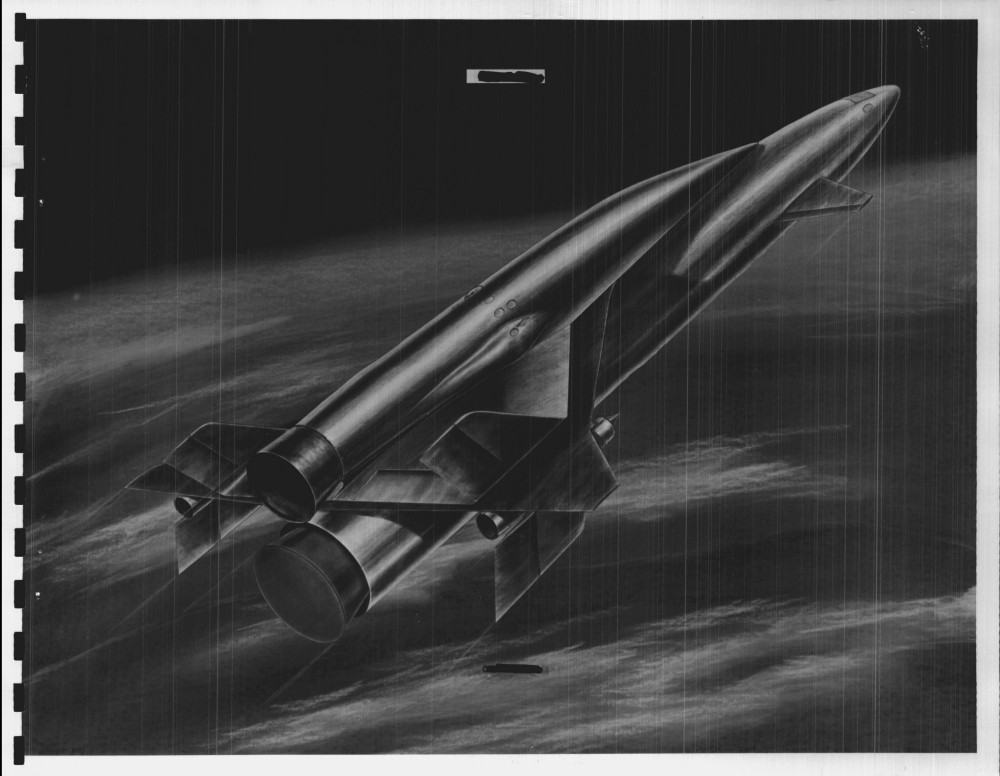
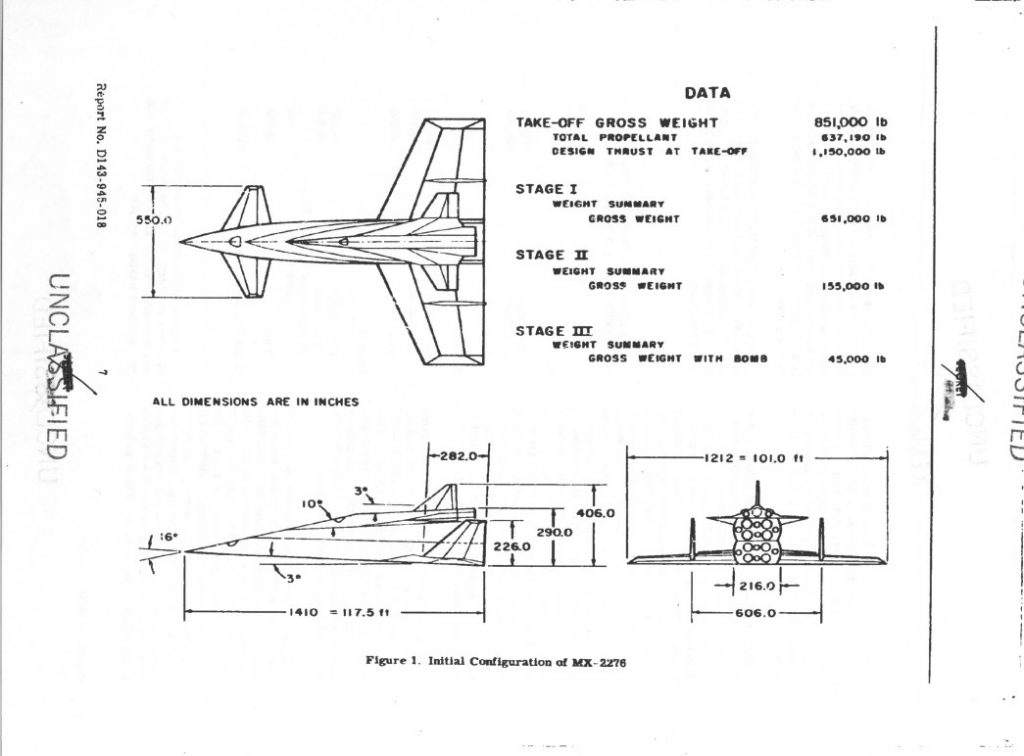
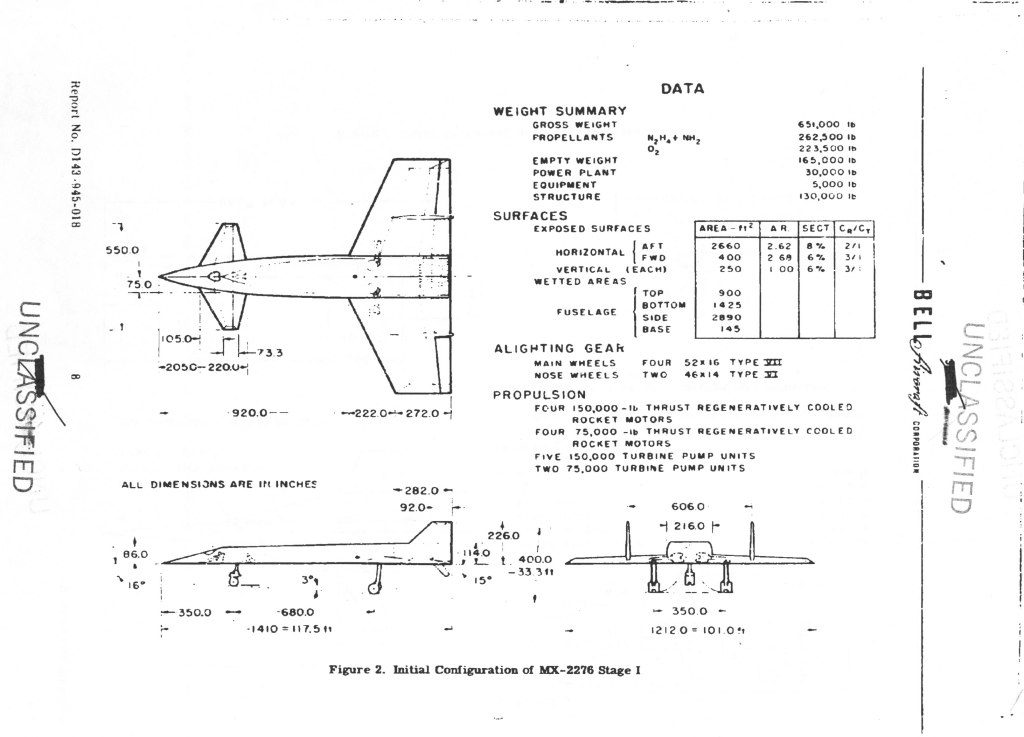
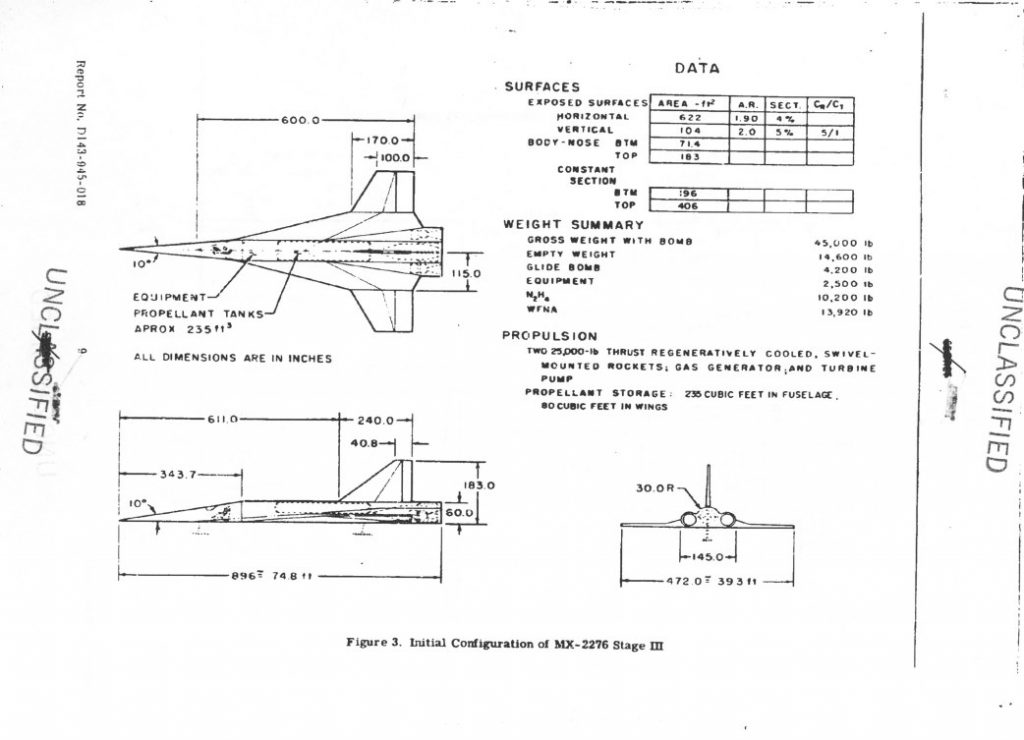
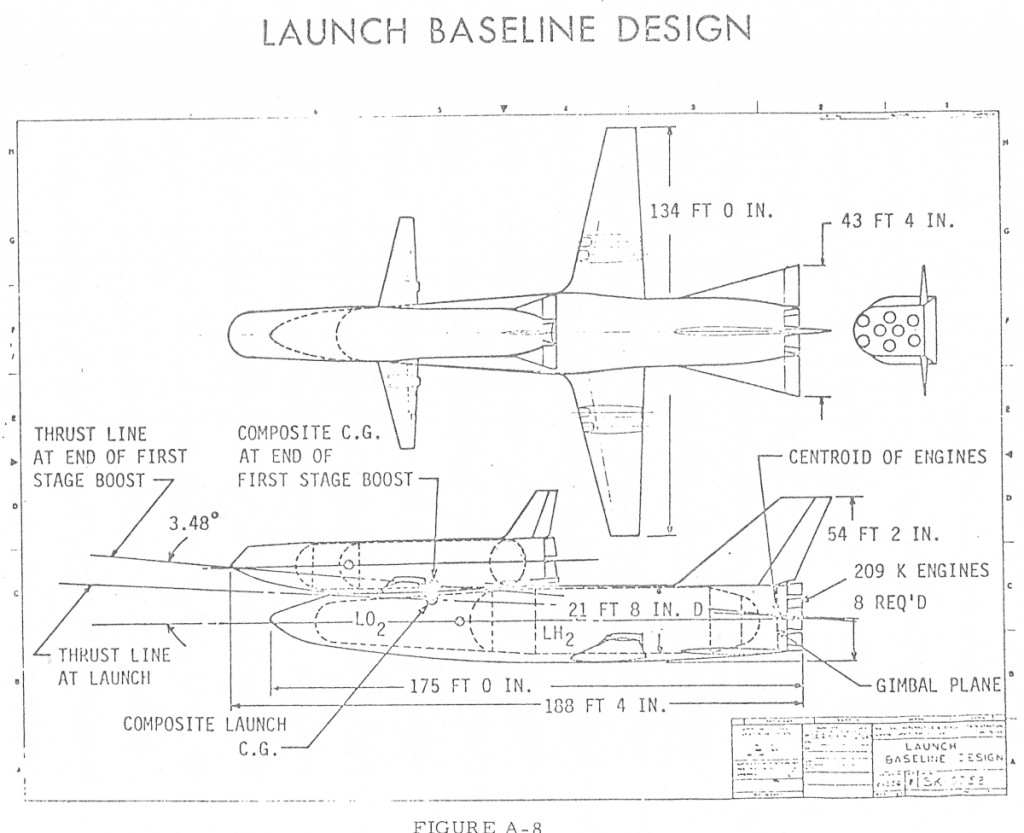
An illustration from a 1964 Boeing report on Saturn V first stage recovery and re-use. A number of concepts were studied, from balloons to parachutes. This particular one used parachutes to slow the stage and solid propellant retro-rockets in the nose for terminal braking, doing something akin to Falcon’s “hoverslam” just before splashdown. The forward LOX dome in the concept would be structurally strengthened to survive the impact. After the initial splash, rockets would be used to tip the stage over in a particular direction… and then more, bigger rockets would be used just before the stage fell over to keep it from hitting too hard.
Another concept was to use a design that would blow off the LOX tank forward dome before impact. The stage would thus hit the water like an inverted cup. As the water compressed the air within the LOX tank, blowout doors at the “bottom” of the tank would, well, blow out, giving the compressed air somewhere to go. This would serve as a pneumatic shock absorber for the stage, but it would pretty much trash the LOX tank.