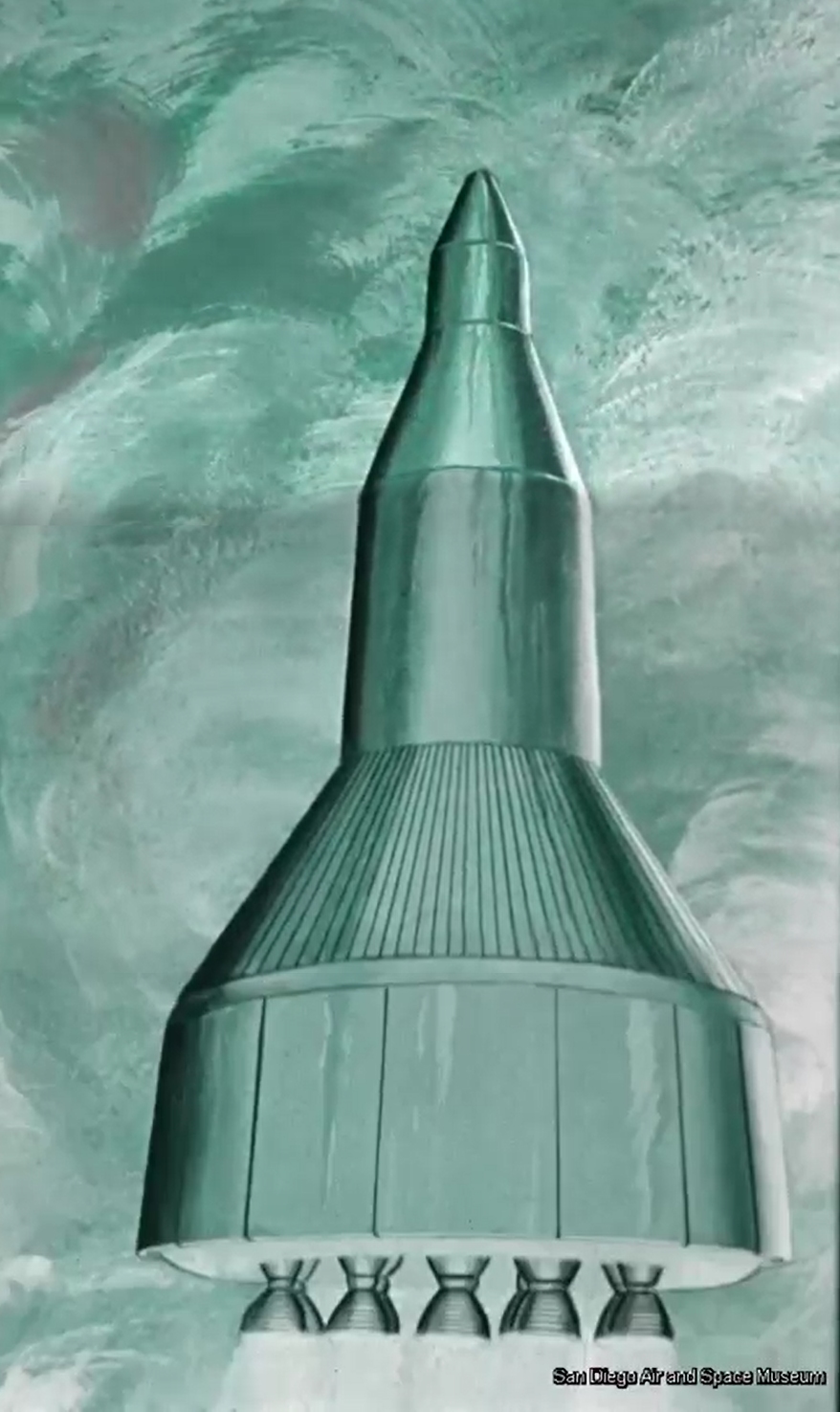
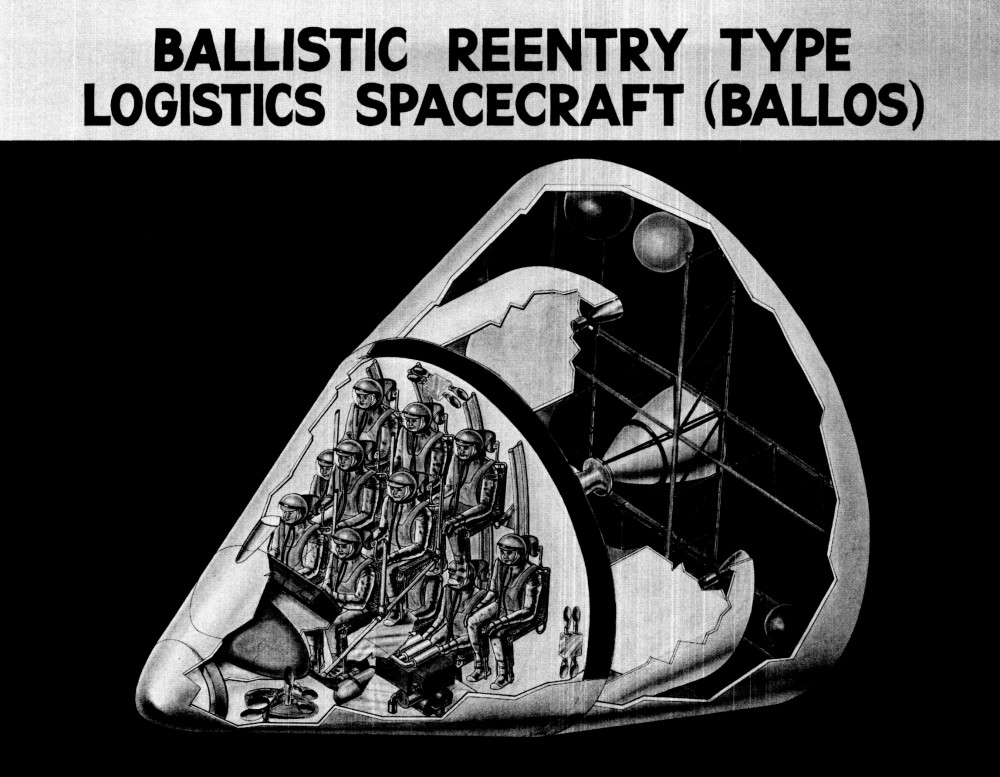
Artwork circa 1964 depicting the Lockheed BALlistic LOgistics Spacecraft (BALLOS), a sort of super-sized Apollo capsule meant for the transportation of a dozen astronauts (10 passengers, 2 crew) at once to and from any one of the doubtless dozens of space stations that the United States would surely have in orbit by the mid 1970’s. Launch vehicle would be a Saturn Ib.
A piece of art from Hughes Research Labs from the late 70’s depicting an Orion nuclear pulse vehicle in flight. Sadly low rez, but whatareyagonnado.
It’s an interesting piece, but it seems likely to be quite inaccurate. in deep space when the system operates in a pretty hard vacuum, the fireballs resulting from each blast would expand outwards at a speed of many hundreds or thousands of kilometers per second.
Once again Patreon seems to be becoming unstable. So I’ve got an alternate: The APR Monthly Historical Documents Program
For some years I have been operating the “Aerospace Projects Review Patreon” which provides monthly rewards in the form of high resolution scans of vintage aerospace diagrams, art and documents. This has worked pretty well, but it seems that perhaps some people might prefer to sign on more directly. Fortunately, PayPal provides the option not only for one-time purchases but also monthly subscriptions. By subscribing using the drop-down menu below, you will receive the same benefits as APR Patrons, but without going through Patreon itself.
Given the craziness going on, I decided that what the world clearly needs is something consistent. Like, say, me posting one piece of aerospace diagram or art every day for a month or so. So I’m going to do that. But in order to keep people from getting too complacent, I’m posting some of them on this blog, some on the other blog. Why? Because why not, that’s why. I’m slapping the posts together now and scheduling them to show up one at a time, one a day. Given the pandemic… who knows, this little project might well outlive *me.*
So, check back in (on this blog or the other) on a daily basis. Might be something interesting.
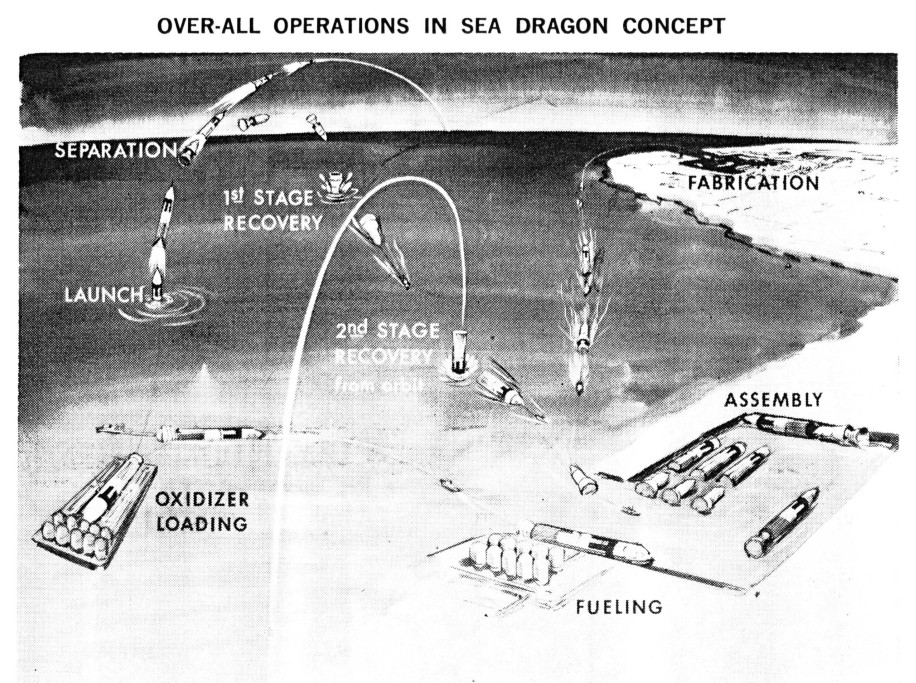
Sea Dragon was, as is doubtless news to few around here, an early 1960’s idea at Aerojet for an extremely large, very simply two-stage pressure-fed space booster. It was meant to be as cheap to build and operate as possible with 1960’s tech, relying on scale to make it all work. Would it have worked? Maybe. Physics supports it. Would it have been cheap to operate? Hard to tell. “Simple as possible” does not equate to “simple,” and anything the size of Sea Dragon, especially screaming out of the sky to smack into the ocean while blisteringly hot… well, there are always risks.
In 1963 the idea of a pinpoint vertical landing a la the Falcon 9 would have been ridiculous, so splashdown was really the only way to go for a booster designed for simplicity. But as NASA and Thiokol found with dropping Shuttle boosters into the drink, recovery and refurbishment after salt water immersion can be a bit of a headache. The way to make a Sea Dragon truly economically competitive would be, as with Falcon 9, flight after flight after flight, often enough that it ceases to be an Amazing News Story and becomes, like the Falcon 9, seemingly dull and monotonous. But given the million-pound payload of the Sea Dragon it’s difficult to envision a space program following on the footsteps of Apollo that would have required a Sea Dragon every few weeks. It would certainly have been *nice* to have had such a program (and if the current pandemic takes down western civ it will turn out that the lack of such a program was criminally negligent) but the existence of a timeline with such a program seems a little difficult to envision.
The article, written by sea Dragon advocate Robert Truax, that the above illustration came from has been scanned and made available to above-$10 APR subscribers and Patrons.
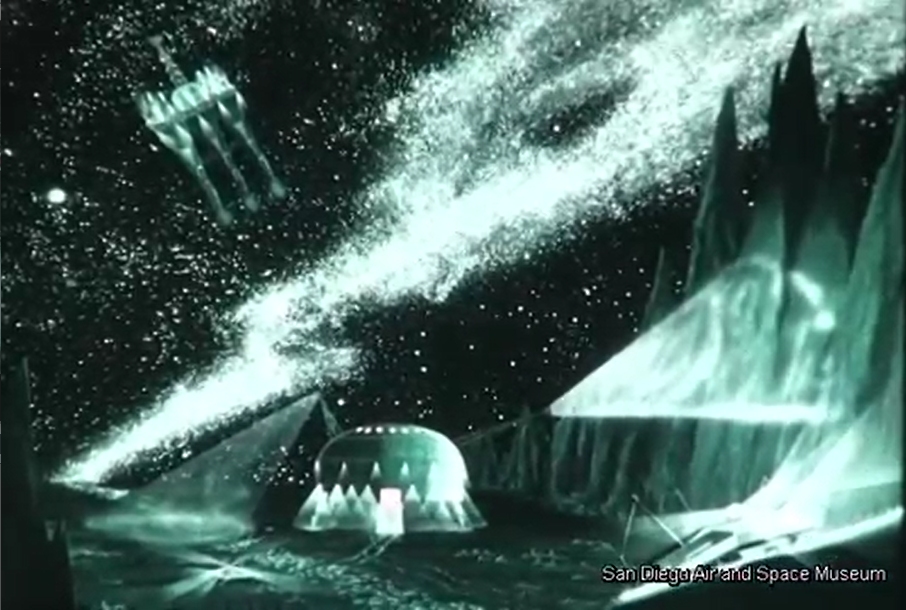
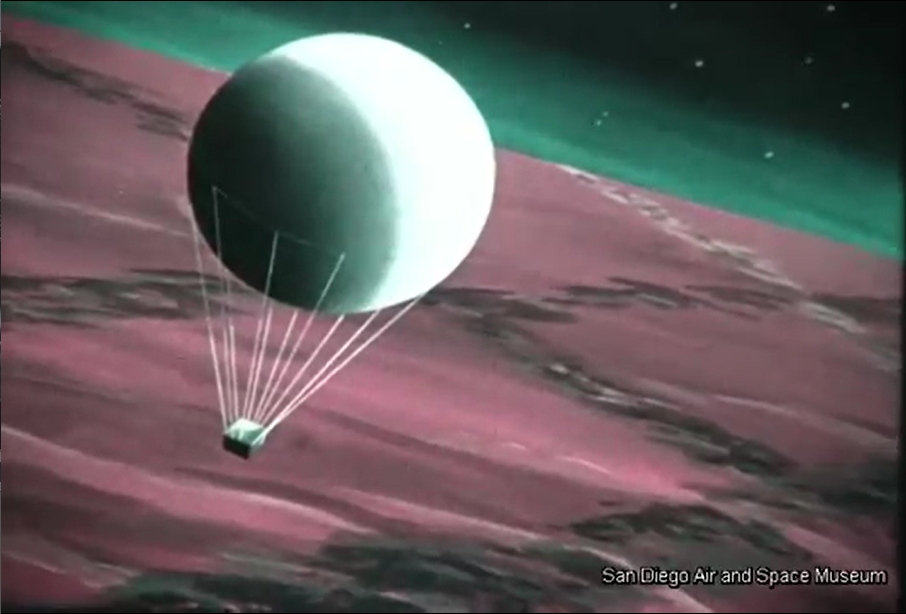
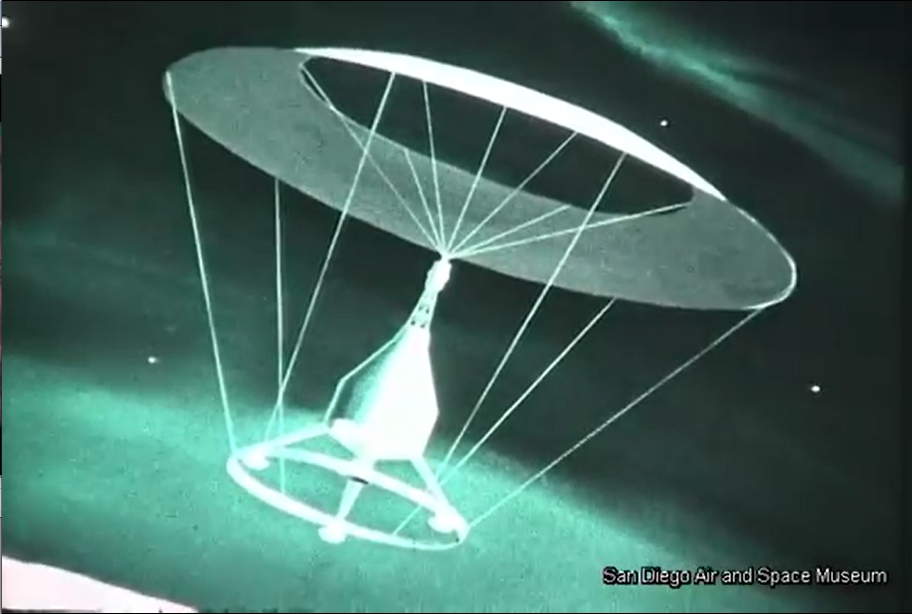
This video was posted on YouTube some six-ish years ago, but remains worthy of viewing and discussion. It’s a General Dynamics film to NASA from late 1962/early 1963 discussing the study of Early Manned Interplanetary Missions (EMPIRE), NAS8-5026. It describes the future as it should have been… and as how Krafft Ehricke, the presenter of the film and one of the driving forces behind the program, saw it:
1: Manned landing on the moon by the end of the 60’s.
2: Initial manned flights to (flybys and orbits) Venus and Mars in the early 70s
3: Entire solar system explored robotically by the end of the 1980’s
4: Manned mission to Pluto by 1995
Ehricke’s view of the future of space flight from the standpoint of the mid-1960’s was previously shown HERE.
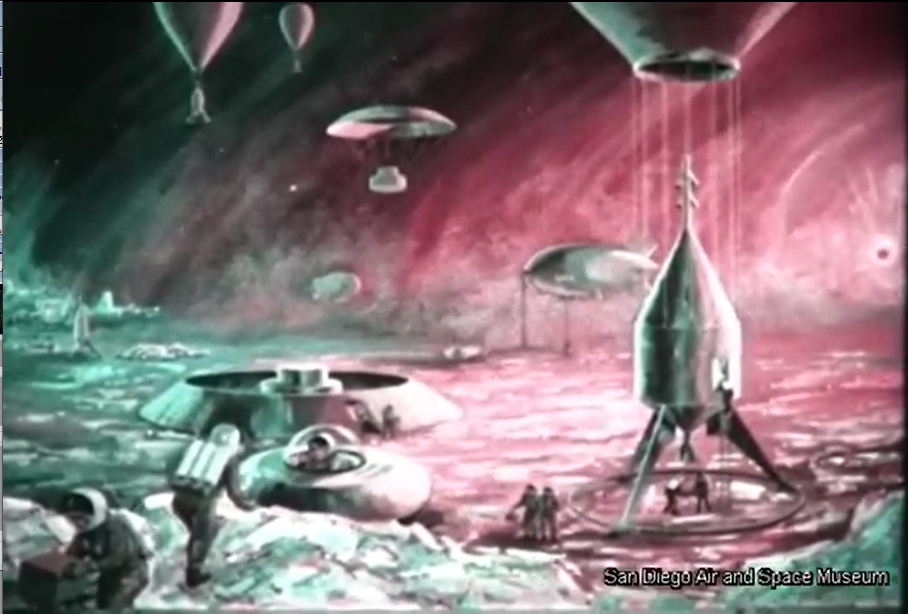
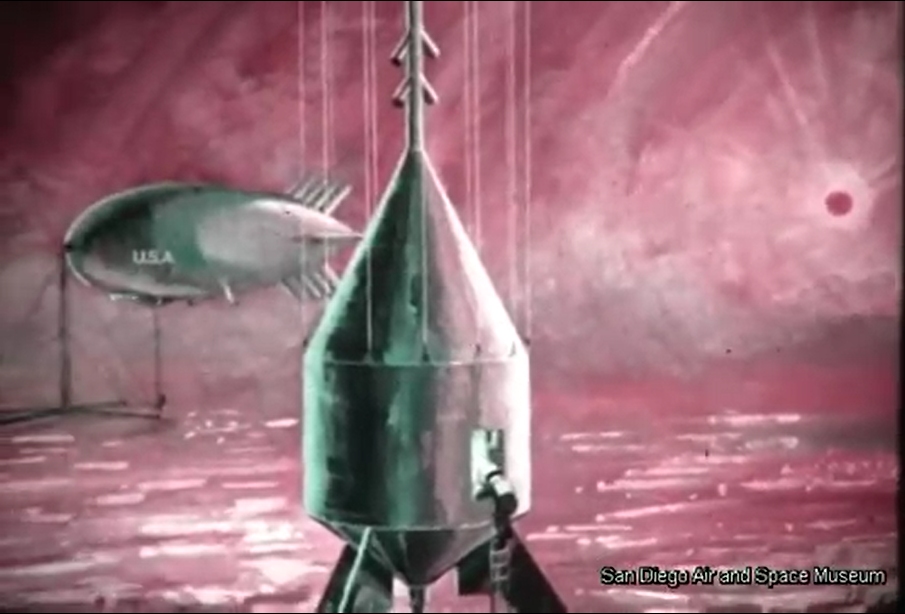
The original film included a number of bits of concept art of both manned and unmanned spacecraft. Sadly no Orion vehicles are on display (it is name-dropped), but the Mars lander/excursion module was of the kind originally proposed for Orion. This was pre-Mariner when the Martian atmosphere was *massively* over-estimated; these landers and their dinky parachutes would, with the real Martian atmosphere, have made impressive craters in the surface.
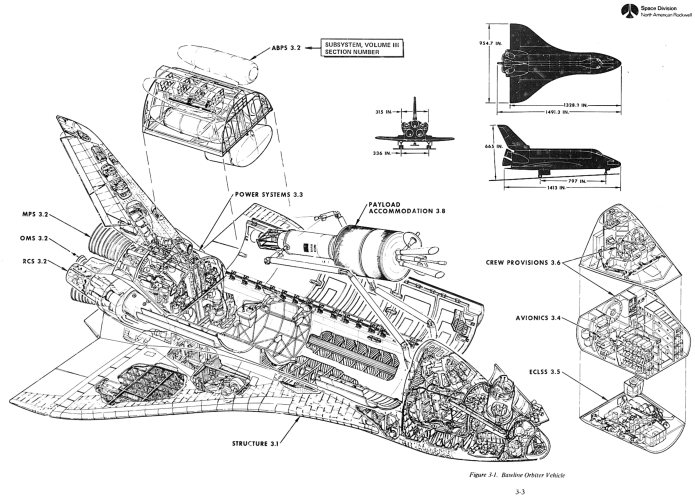
The North American Rockwell proposal for the Space Shuttle Orbiter. It is clearly *close* to what actually got built, but there are important differences. The airlock is in the nose and the OMS pods are lower on the sides of the rear fuselage and the rear portion of the cargo bay could be fitted with a pod that includes flip-out turbofan engines for range extension and landing assistance.
The full-rez scan of this diagram has been made available to all $4 and up APR Patreons and Monthly Historical Document Program subscribers. It has been uploaded to the 2020-02 APR Extras folder on Dropbox for Patreons and subscribers. If interested in this piece or if you are interested in helping to fund the preservation of this sort of thing, please consider becoming a patron, either through the APR Patreon or the Monthly Historical Document Program.