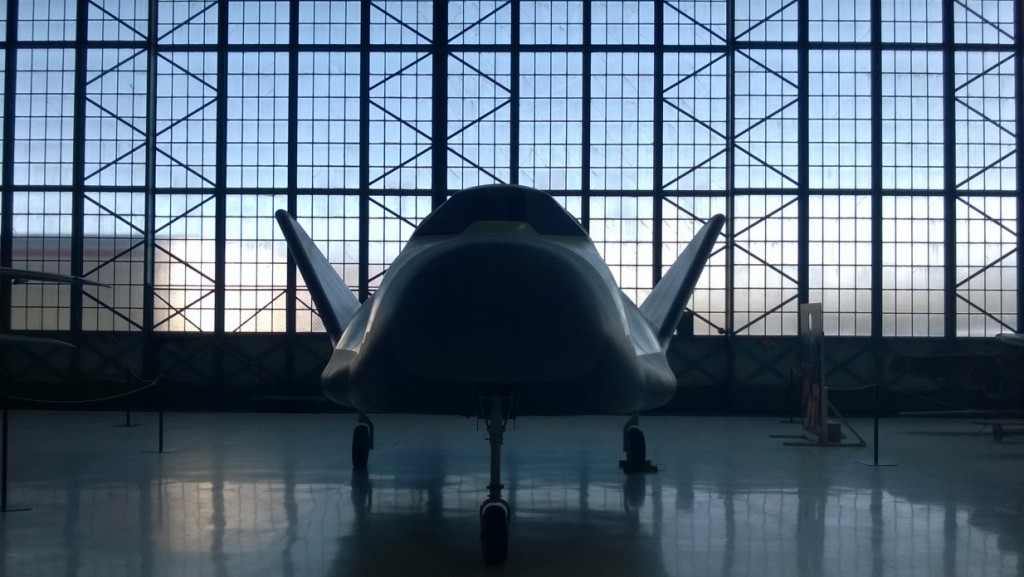
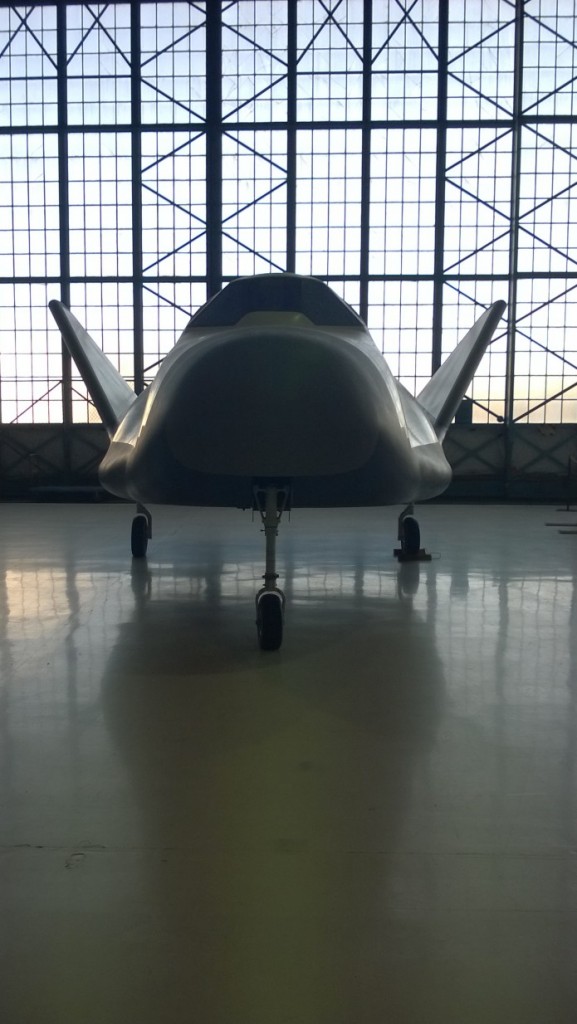
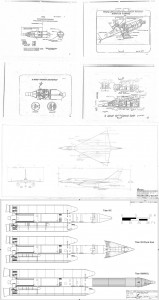
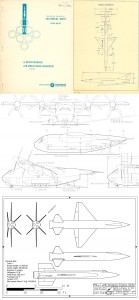
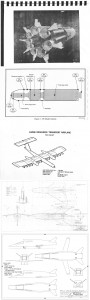
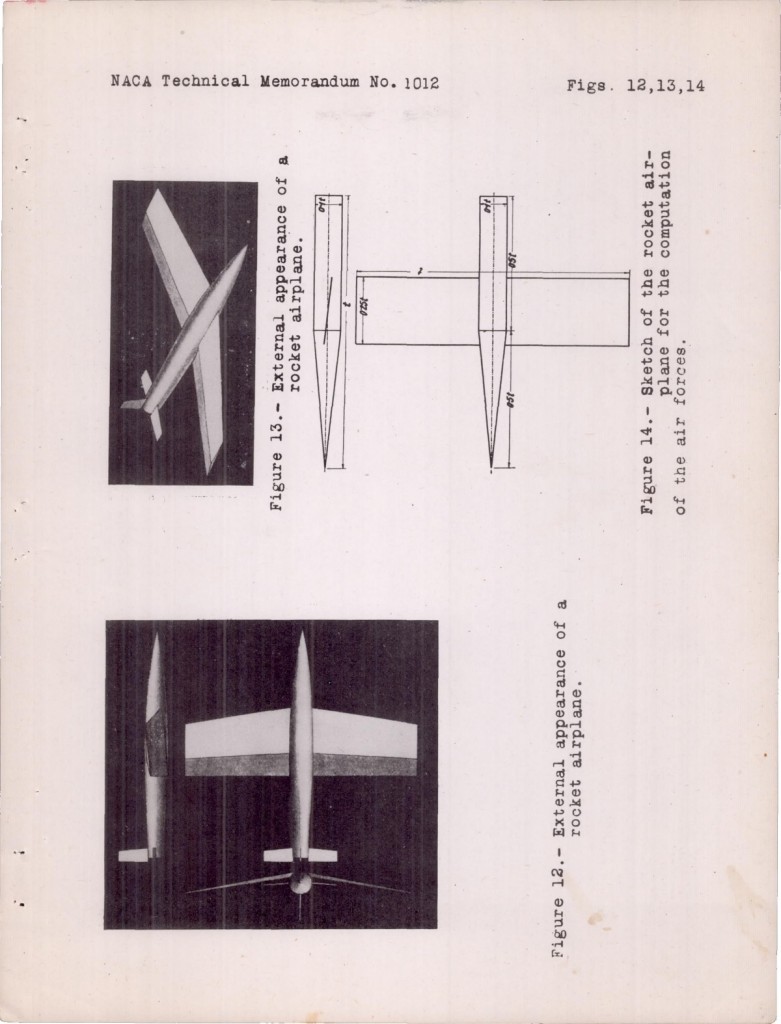
Recent photos of the HL-20 lifting body spaceplane mockup on display at the Wings Over the Rockies aviation museum near Denver. An attempt at art on the photographers part, I suppose.
Now available… two new additions to the US Aerospace Projects series.
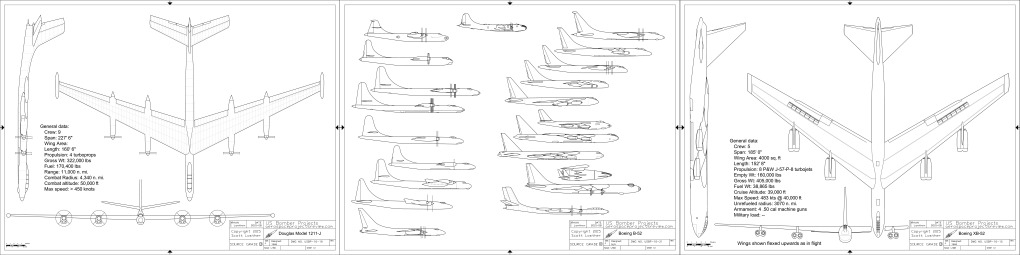
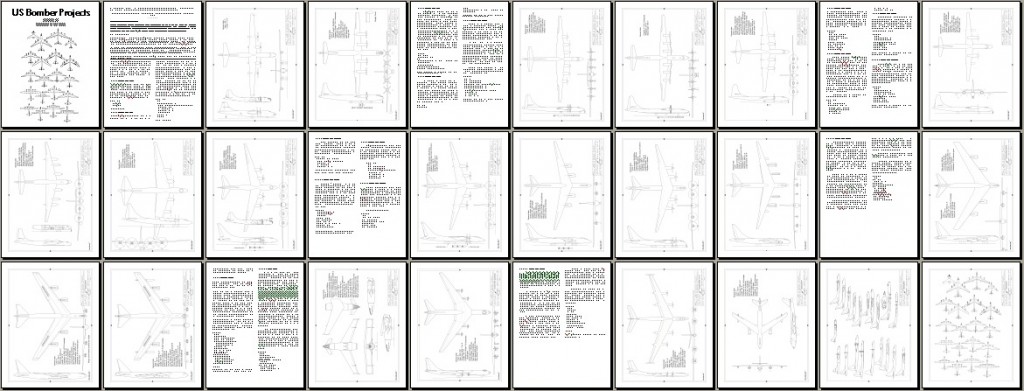
US Bomber Projects #16: The B-52 Evolution Special
Boeing Model 444 A: A late war turboprop heavy bomber
Boeing Model 461: An early postwar turboprop heavy bomber
Boeing Model 462: A large six-turboprop ancestor of the B-52
Boeing Model 462-5: A six-turboprop B-52 ancestor
Boeing Model 464-17: 1946 four-turboprop strategic bomber, a step toward the B-52
Boeing Model 464-18: a reduced-size version of the 464-17 turboprop strategic bomber
Boeing Model 464-25: a modification of the 464-17 turboprop bomber with slightly swept wings, among other changes
Boeing Model 464-27: a slightly-swept turboprop B-52 progenitor
Boeing Model 464-33-0: A turboprop B-52 predecessor
Boeing Model 464-34-3: A turboprop B-52 predecessor
Boeing Model 464-40: The first all-jet-powered design in the quest for the B-52
Boeing Model 464-40: The first all-jet-powered design in the quest for the B-52
Boeing Model 464-046: A six-engined B-52 predecessor
Boeing Model 464-49: The penultimate major design in the development of the B-52
Fairchild M-121:A highly unconventional canard-biplane
Convair B-60: A swept-wing turboprop-powered derivative of the B-36
Douglas Model 1211-J: An elegant turboprop alternative to the B-52
With additional diagrams of the B-47, XB-52 and B-52B
USBP#16 can be purchased for downloading for the low, low price of $6.25.
—
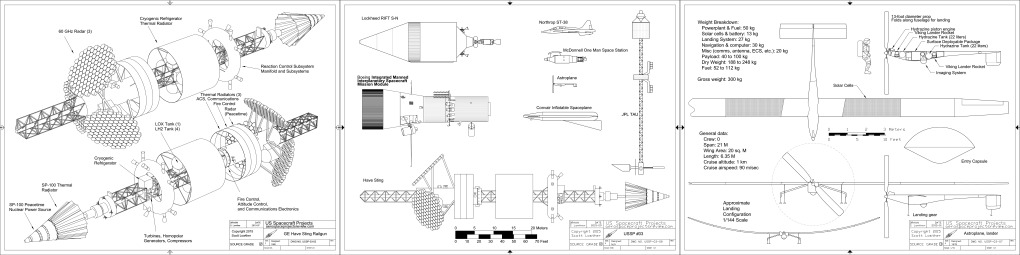
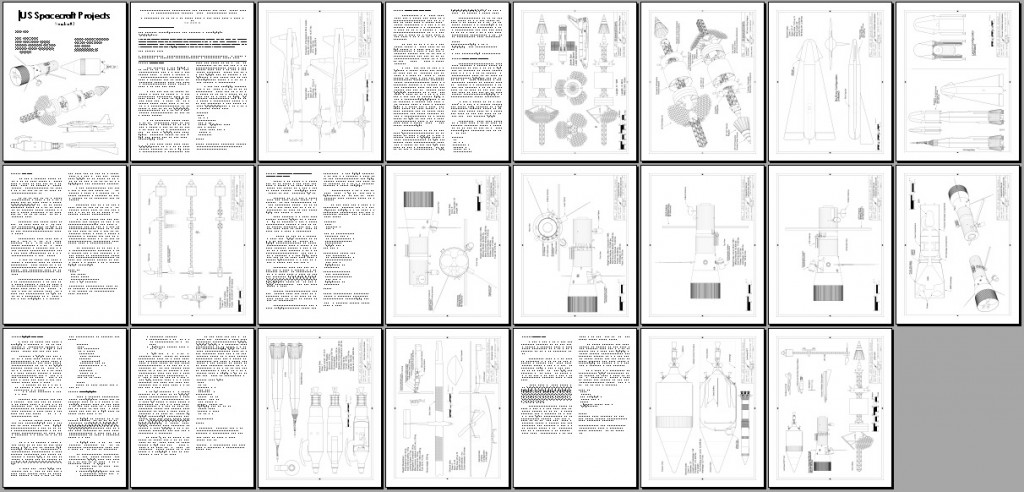
US Spacecraft Projects #03
Northrop ST-38 Space Trainer: a rocket-powered T-38 for trips to space
“Have Sting:” A General Electric design for a gigantic orbital railgun
JPL Thousand Astronomical Unit probe: A spacecraft into interstellar space
Integrated MannedInterplanetary Spacecraft: A Boeing concept for a giant spacecraft to Mars and Venus
Convair Inflatable Spacecraft: an early spaceplane concept
One Man Space Station: A 1960 McDonnell concept for a tiny space station
Astroplane: A lightweight aircraft for the exploration of Mars
Reactor-In-Flight Test: A Lockheed nuclear-powered stage for the Saturn V
USSP#03 can be purchased for downloading for the low, low price of $5.25.
—
Just released today… an official “History of the Manned Orbital Laboratory” by Carl Berger of the MOL Program Office, 1970. This originally Top Secret history still has a number of blacked-out text redactions and, sadly, no illustrations in its 356 pages. I’ve only skimmed through it, but it looks to be an interesting read.
Direct link to the “History of MOL” PDF file
The table of contents:
A Convair film about the NB-36H, a heavily modified B-36 bomber equipped with a nuclear reactor. The reactor was not hooked up to anything but instruments; all it did was sit there and give off radiation. Which was in fact the point of the exercise; the plane was an experiment in support of atomic powered aircraft, but the experiments were to see how crew, structure and instruments would stand up to the radiation environment produced by an airborne reactor.
If you’ve got a hankering to find out what the super-secret Lacrosse radar satellites look like, the Russians got you covered. A Russian satellite tracking facility in Siberia used telescopes to take photos of several of these satellites, and then, rather unconventionally, released the images. The images were collected and analyzed, and posted in a PDF album:
An Album of Images of LACROSSE Radar Reconnaissance Satellites
Made by a 60 cm Adaptive Optics System
at the
G.S. Titov Altai Optical-Laser Center
The images are not spectacular… nobody will be making details models based off them. But you can get a sense of the overall configurations(s), as well as the size of the antennae; from that, an analyst could give you a good idea what the capabilities of the sensor systems are.
Much more aerospace stuff is available via the APR Patreon.
Eugen Sanger was an Austrian engineer from the early/mid 20th century. While largely forgotten by the vast majority of everybody today, he is remembered, at least in aerospace circles, as the originator of the Silbervogel (“Silverbird”) rocket-powered suborbital bomber. This work was performed during WWII for the German government, and included some substantial rocket testing; the odd thing – though wholly in character for the Nazi regime – was that this work was entirely separate from the development work on the V-2 rocket. Had the efforts been brought together, chances are that German rocketry would have been further advanced by the end of the war.
In 1934, Sanger published a paper on advancement in liquid propellant rocketry, work that would later feed into his Silverbird effort. “Recent Results in Rocket Flight Technique” not only reported upon work done in developing a gas-oil and liquid oxygen burning rocket engine, but also proposals for manned rocket powered aircraft. The paper was originally written in German and granted the catchy title “Neuer Ergebnisse der Raketenflugtechnik,” but it was translated into English by the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in April of 1942. Why was it was translated just then? Depending on the speed of the translators, the work may have begun just after the American entry into WWII, which might indicate a bit more interest in German rocketry in certain portions of the US Government than has generally been understood.
The abstract & such for the report can be seen on the NASA Technical Report Server HERE. Or it can be directly downloaded as a 33 meg PDF HERE.
Note: my original plan for this writeup was to include verbiage along the lines of “Sorry that the two-bit black-and-white scan quality is so poor, but whatcha gonna do.” But in looking it up, I found that the original bleah-quality scan has been replaced with a higher quality full-color scan. This is a good thing!
Much more aerospace stuff is available via the APR Patreon.
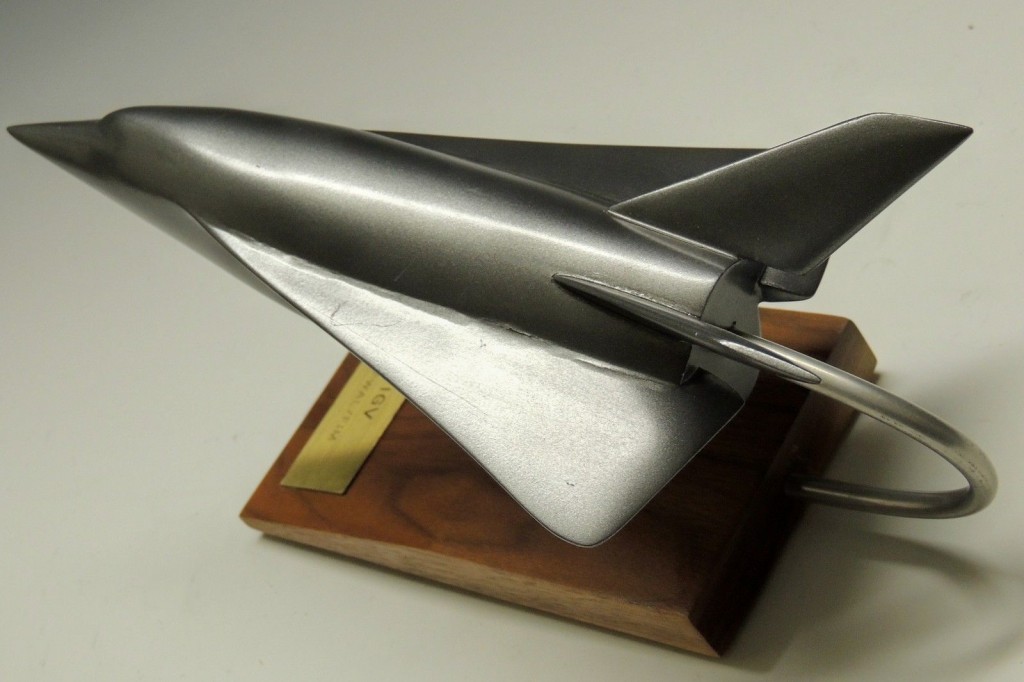
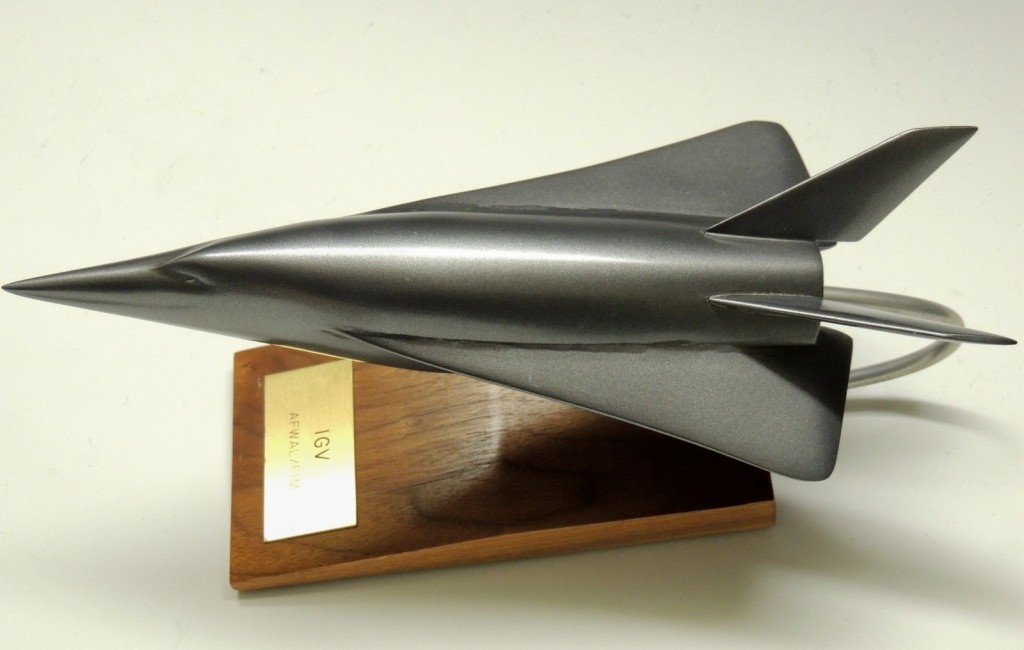
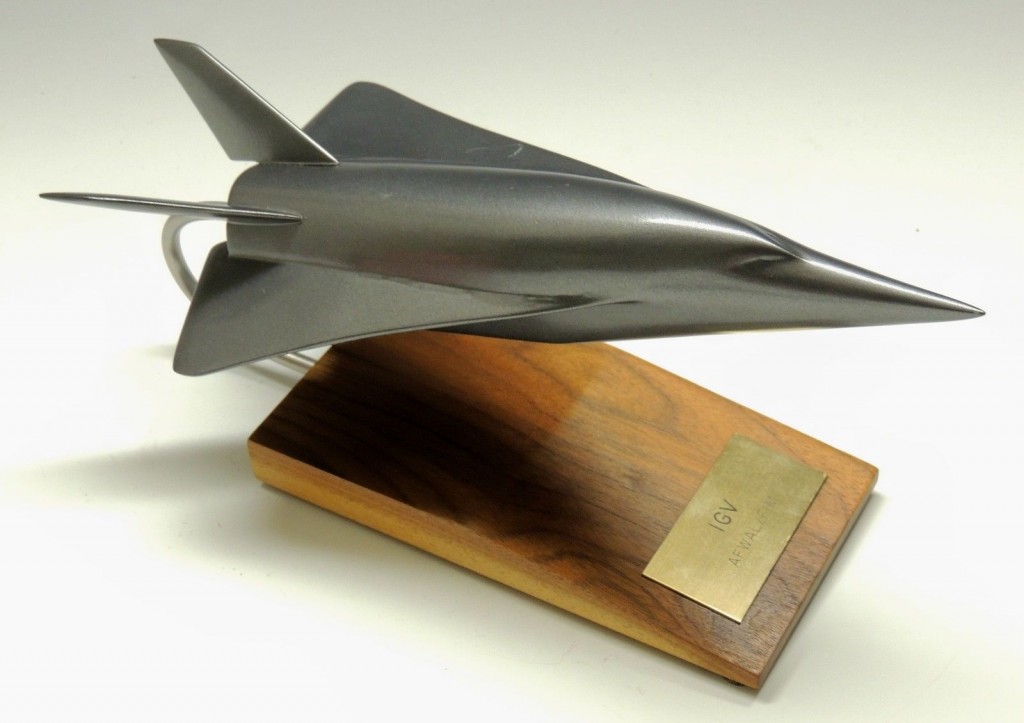
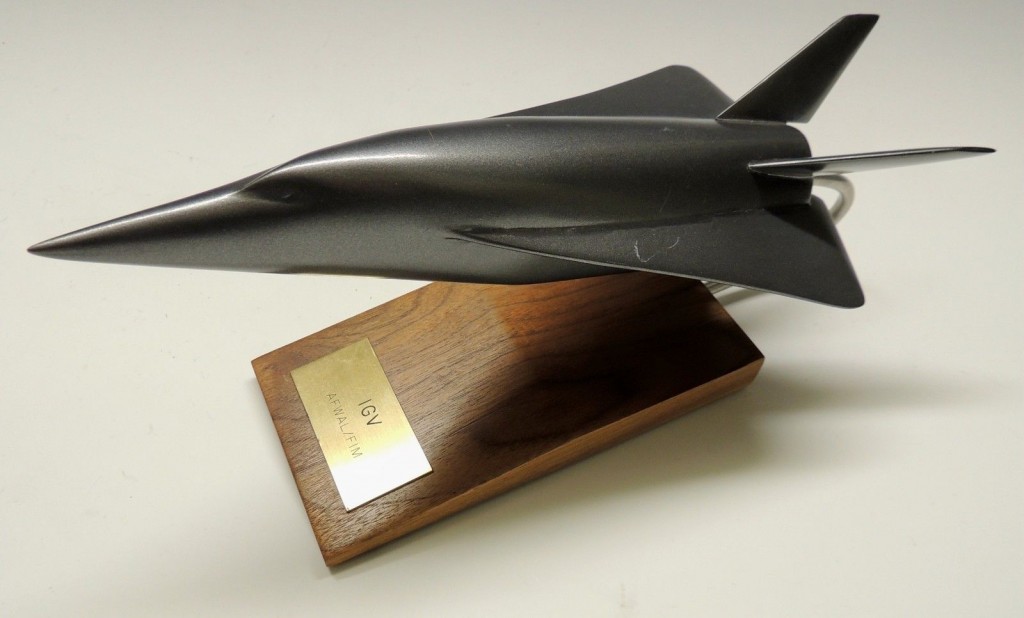
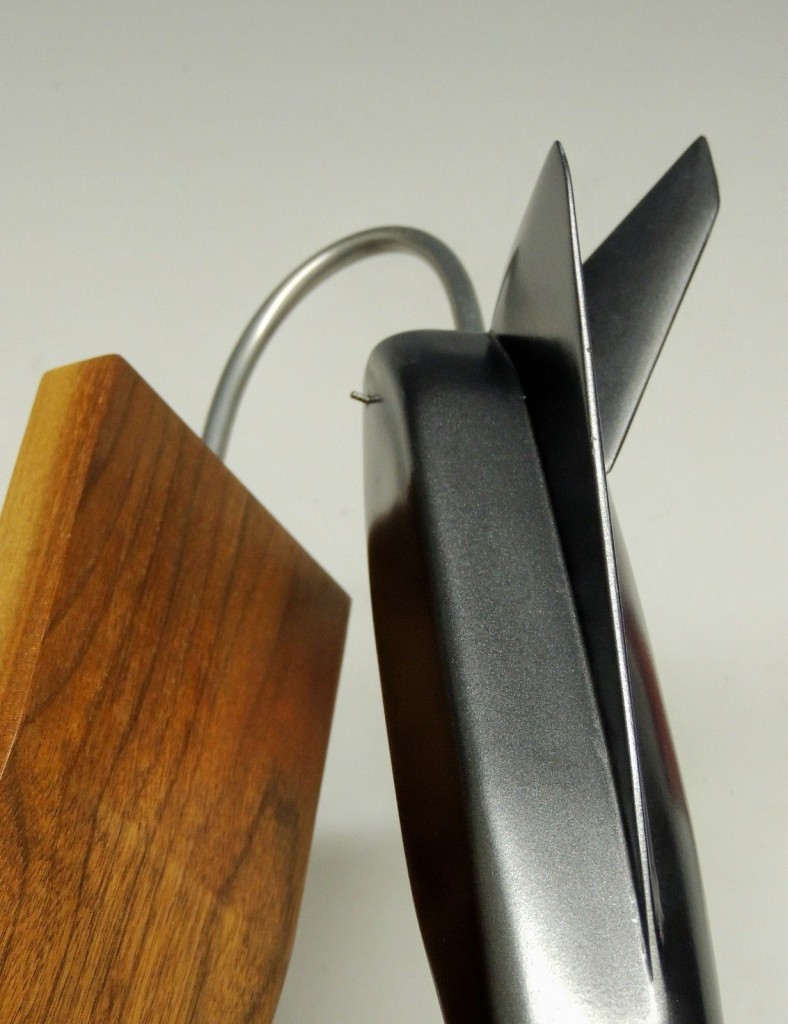
A recent ebay auction was for a display model of the early 1970’s McDonnell-Douglas Incremental Growth Vehicle. This was a proposed manned hypersonic “X-Plane,” designed from the ground up to be capable of having major components replaced. This would allow a simple rocket vehicle to be tested first, and then the fuselage could stretch, or new rocket engines tested, or new wings, or new wings, a fuselage stretch and airbreathing engines, whatever the experiment called for.
Illustrations of a Martin concept from 1961 called “DEIMOS” (Development and Investigation of a Military Orbital System). Pitched to the Air Force, this entailed a modified Titan II launch vehicle, a standard cargo hauler and a scaled-up two-man Mercury capsule (this was before Gemini was finalized). The result was something akin to a smaller version of the later MOL (Manned Orbiting Laboratory). The Titan II described here (modifications unknown) could put a 10,000 pound payload into a 300 nautical mile orbit.
Capabilities and roles of DEIMOS were not provided, but it would presumably serve much the same role as MOL, though simpler and lighter weight: basic science as well as reconnaissance and intelligence gathering. The claim as of August 1961 was that if work began soon DEIMOS could begin flying in 1963.
A wind tunnel model of the Saturn I, checking specifically for base heating (i.e. heating of the base of the vehicle, between the engines, due to radiant heat from the plumes and convection/conduction from hot exhaust gases recirculating between the engines). This model is odd in that it depicts the clustered booster stage as a straight cylinder; further, there appears to be at least one long fairing up the side (although that could be an artifact of reflections & shadows). I suspect this *may* be a repurposed Atlas model.