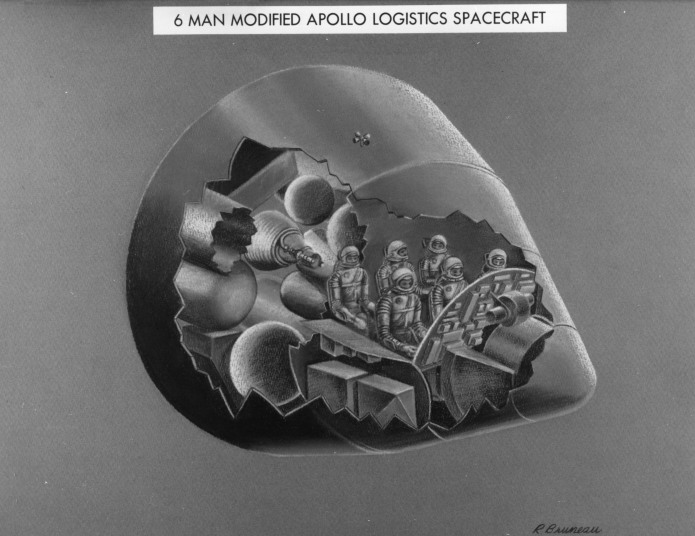
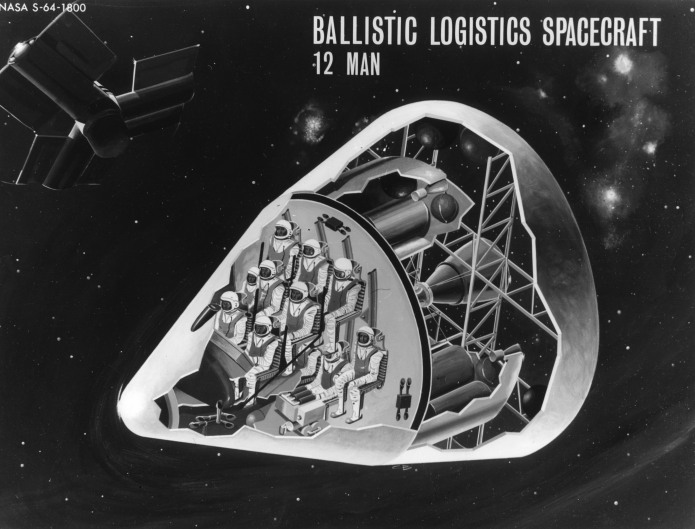
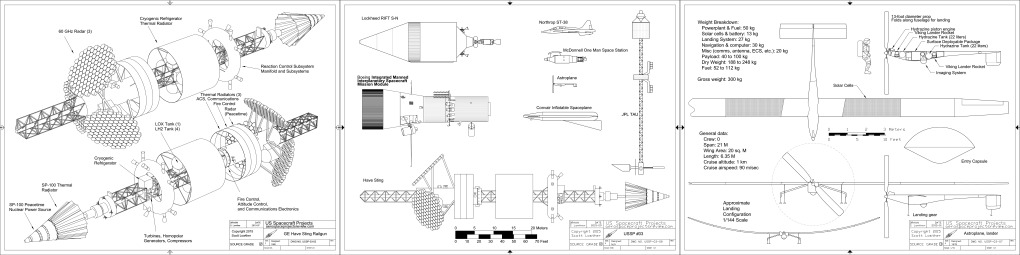
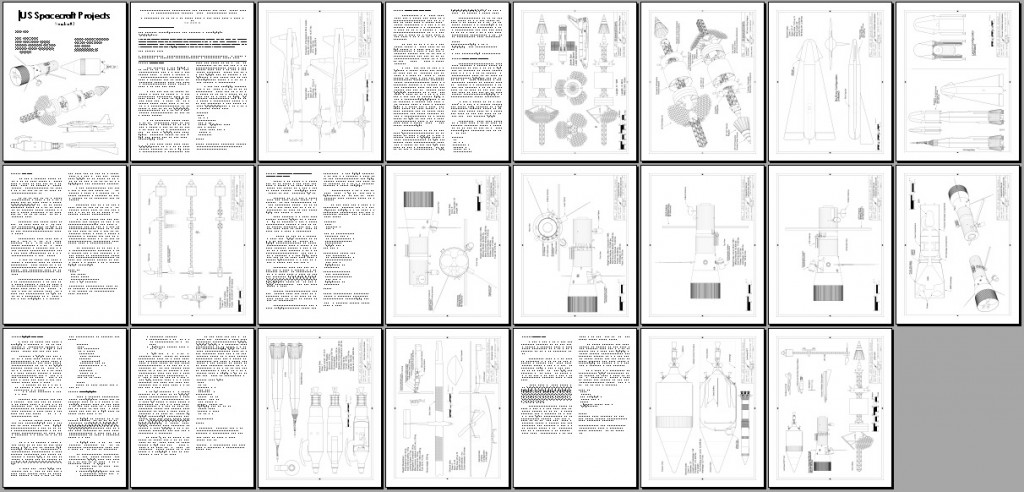
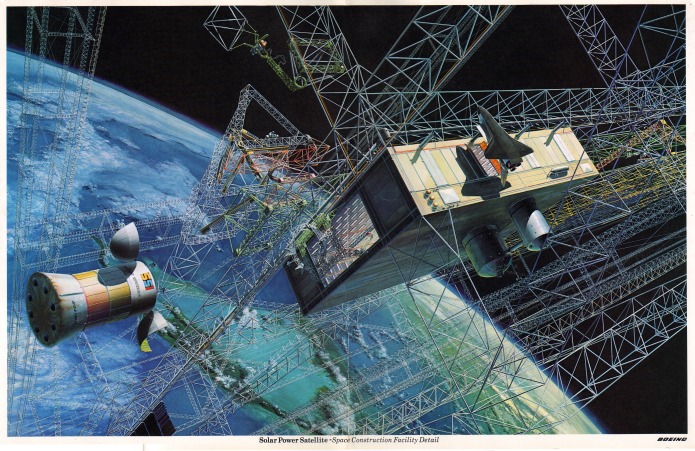
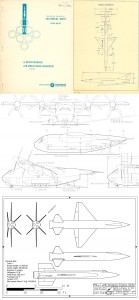
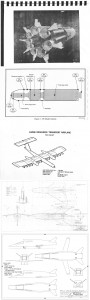
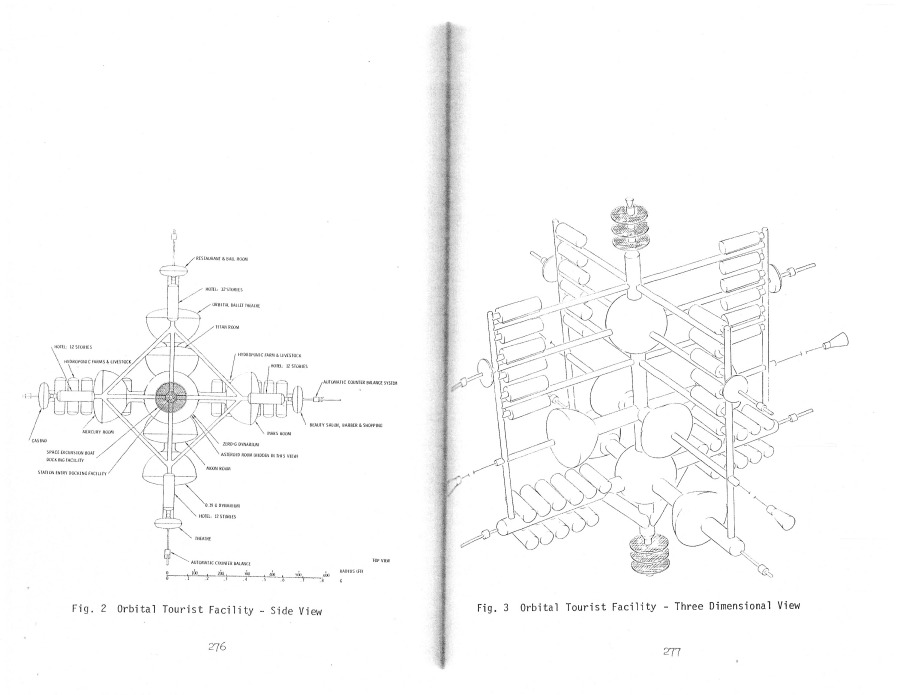
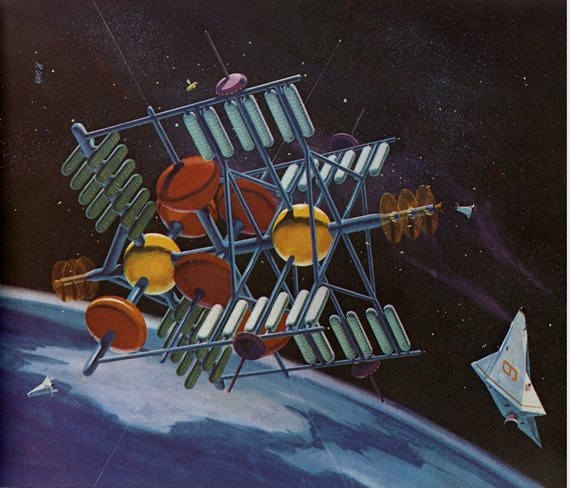
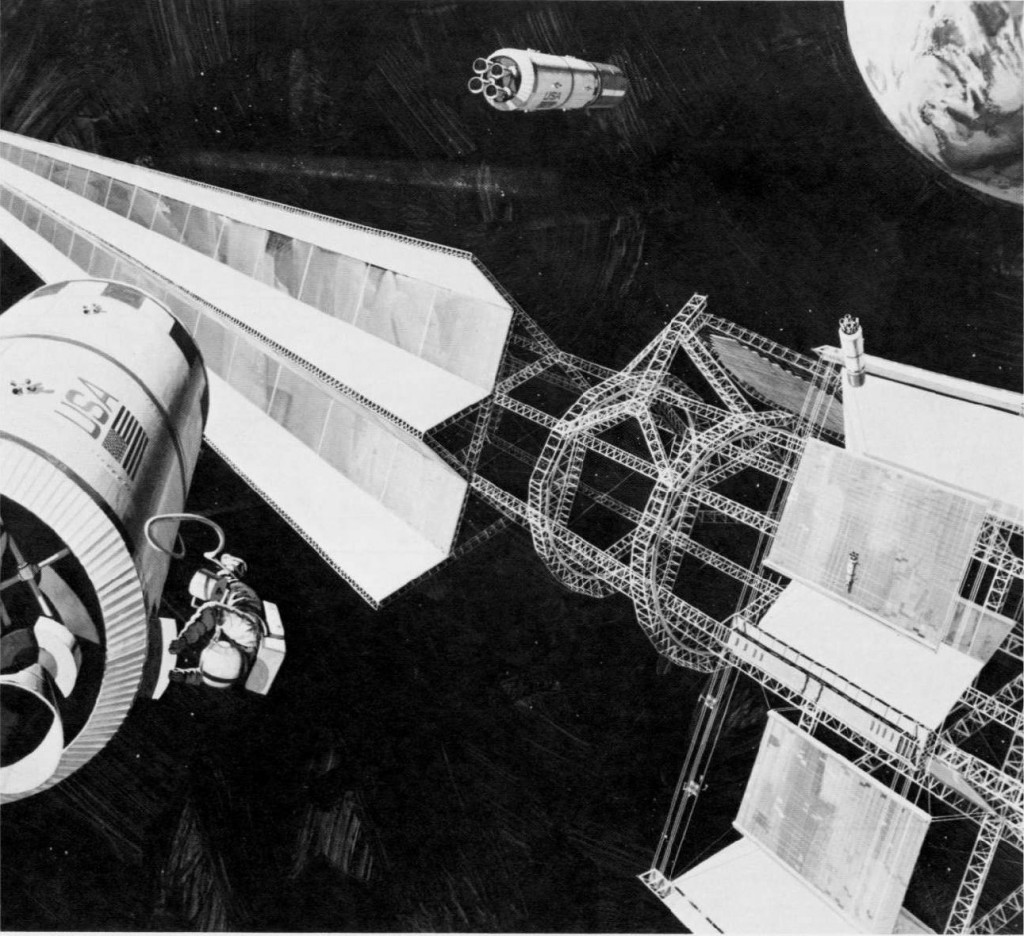
All through the 1960’s – or at least up until the last few years, when “Great Society” spending ate into NASA’s budget – the assumption was that NASA would soon have numerous space stations in orbit and some preliminary lunar bases, with Mars missions soon to follow. In order to support those, NASA would have to have a cost effective means to launch sizable crews into orbit. A number of approaches were proposed, including Big Gemini and, in the end, the Space Shuttle. One approach that probably would have been quite workable was to simply scale up the Apollo capsule into something capable of holding more than three; a slight scaleup seats six, a further scaleup seats twelve. These would have been launched atop the Saturn Ib and/or Saturn V boosters, and would come with their own basic orbital maneuvering systems, and could carry up some amount of cargo in the conical transition/propulsion sections. At the end of the mission, the capsule would return to Earth for recovery, refurbishment and reuse; the propulsion module would be allowed to burn up.
Of course, none of these were ever built.
The full resolution versions of these artworks have been posted into the 2015-10 folder in the APR Extras Dropbox. Please check out the APR Patreon!