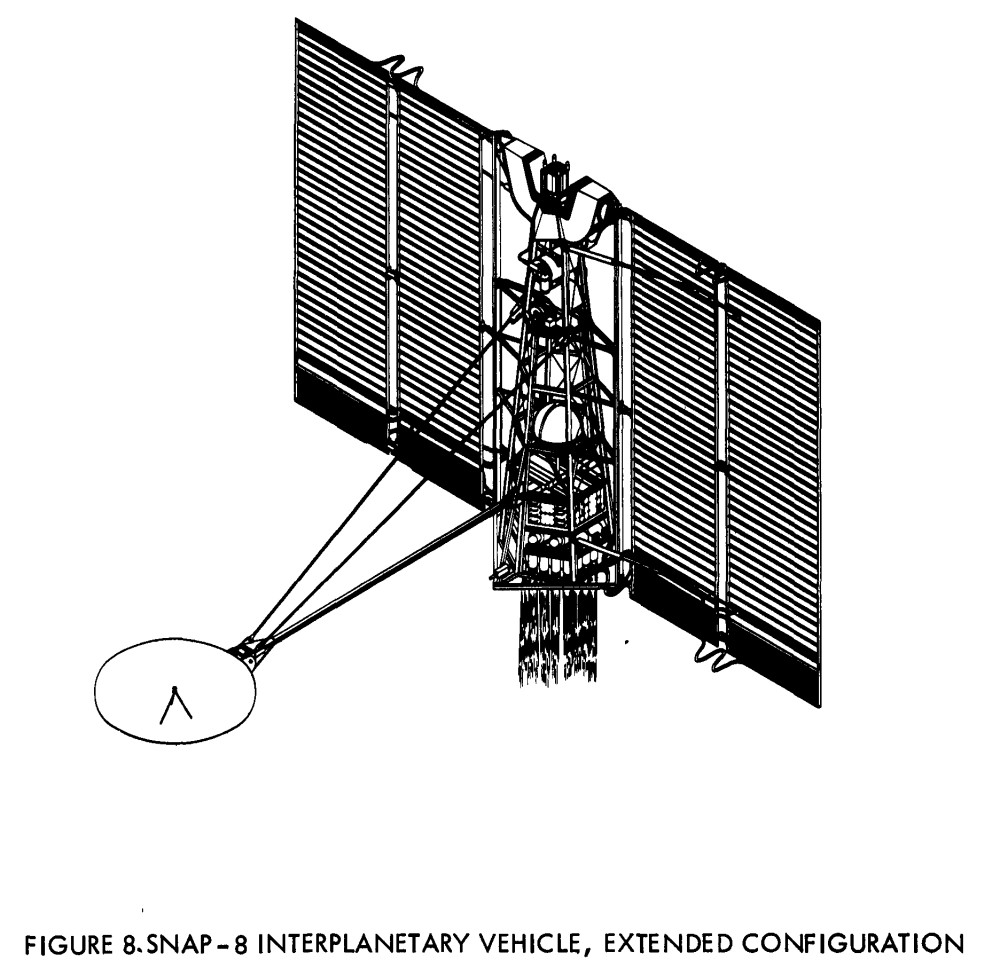
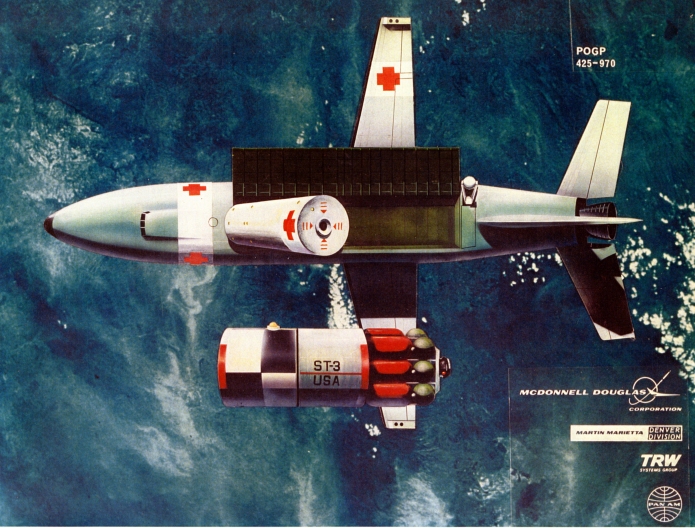
For the APR Patreon I try to acquire as much interesting aerospace documentation as I can, and these items fall into two categories:
- Stuff that I can afford. This stuff winds up in the APR Patreon catalog of potential monthly rewards for patrons.
- Stuff I can’t hope to afford.
There’s a lot of the latter category of stuff. Sometimes it’s because the item has a ridiculously high Buy It Now price or starting bid, or because the item will be popular among bidders, or because it’s *really* good/big and thus worth every penny. But unaffordable is unaffordable.
However, there is an option for “stuff I can’t afford:” crowdfunding. I’ve done this a number of times with considerable success, and I’ve just done so again, winning a trio of General Dynamics documents describing a 1965 program to develop a logistics system for extending the Apollo lunar exploration program:

This set of documents was just much too expensive for an individual (well, I’m sure Jeff Bezos or Elon Musk wouldn’t have flinched), but with a group of like-mined funders it came in at $30 per person. So what happens now:
1: I wait for it to show up in the mail.
2: I make a complete set of scans in 300 DPI grayscale (and color, where appropriate) and convert to PDFs
3: I make the scans and PDFs available to funders, generally via Dropbox
4: I find an appropriate archive for the documents, and then donate the originals to them.
5: And that’s it. The files are shared with the funders, but do not appear on future APR Patreon catalogs or as purchasable, downloadable “Diagrams and Documents.” What the funders choose to do with their scans & PDFs is up to them.
APR Patrons get alerted to each of these occasional “crowdfunding opportunities.” So if you’d like to participate, please considered signing up for the APR Patreon.