New to YouTube:
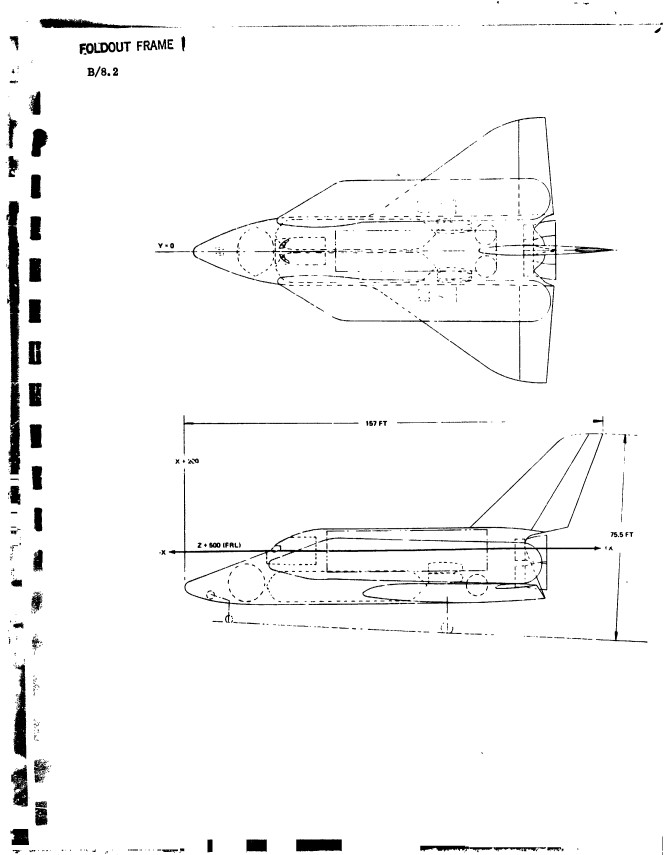
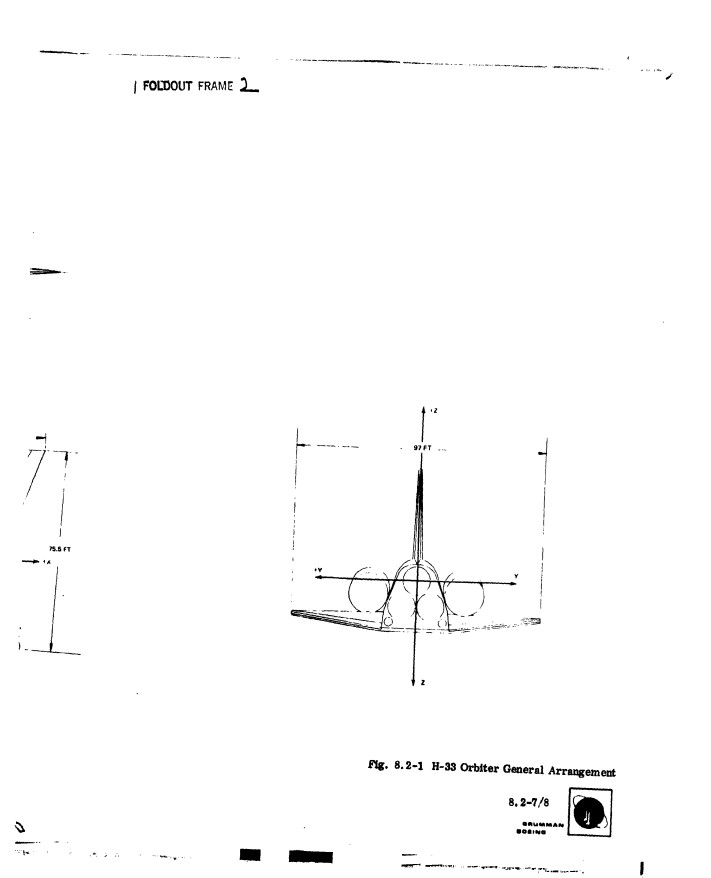
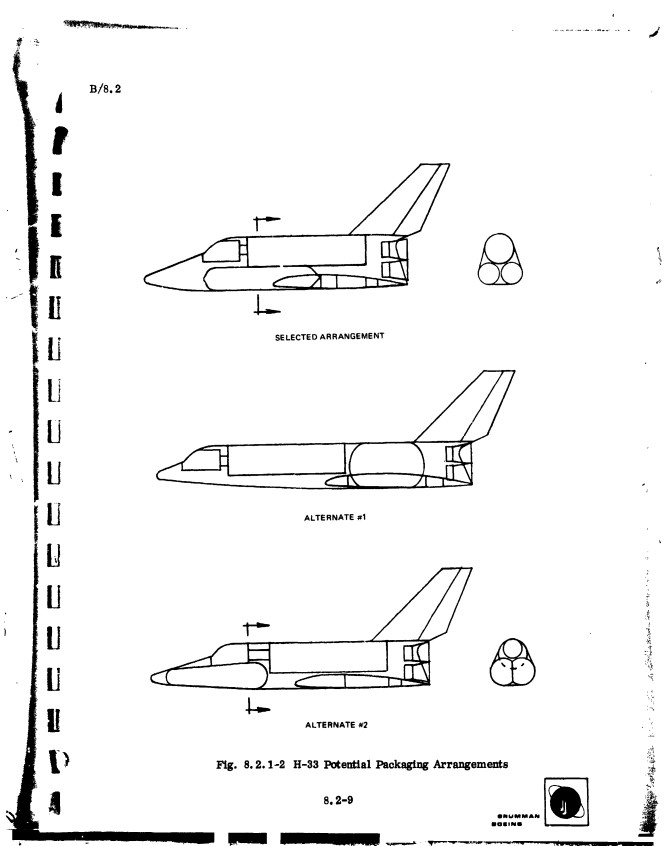
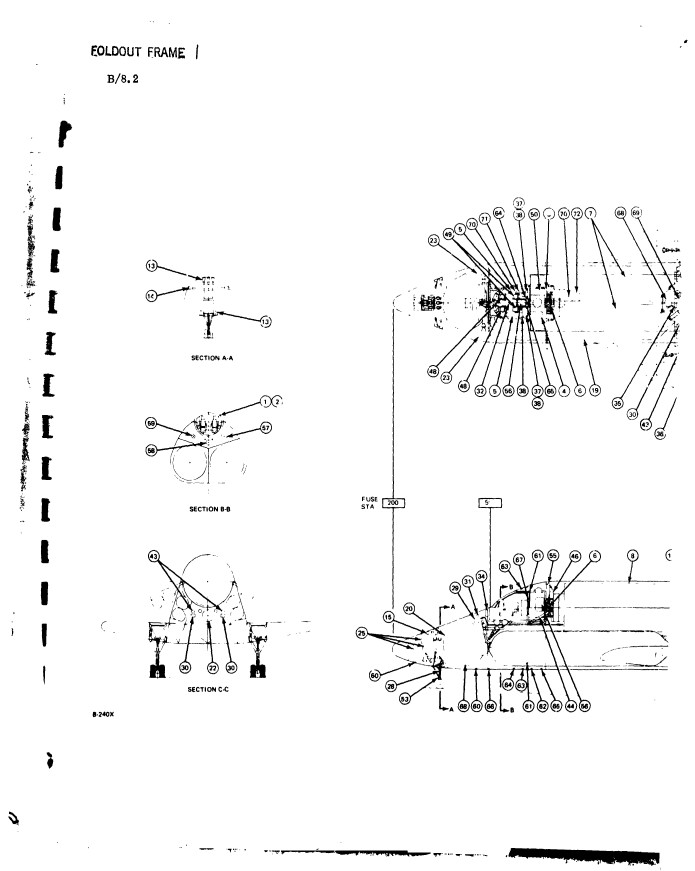
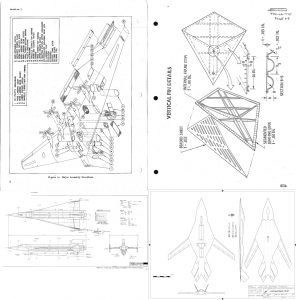
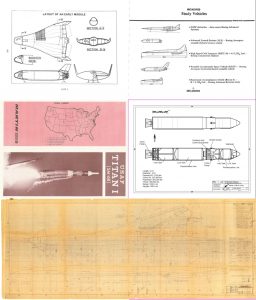
As a followup to the photos of the H-33 display model, here’s a Grumman report from July, 1971, giving a pretty good and well illustrated description of the H-33 orbiter.
The abstract on NTRS can be seen HERE.
The PDF file can be directly downloaded here:
Alternate space shuttle concepts study. Part 2: Technical summary. Volume 2: Orbiter definition
Support the APR Patreon to help bring more of this sort of thing to light!
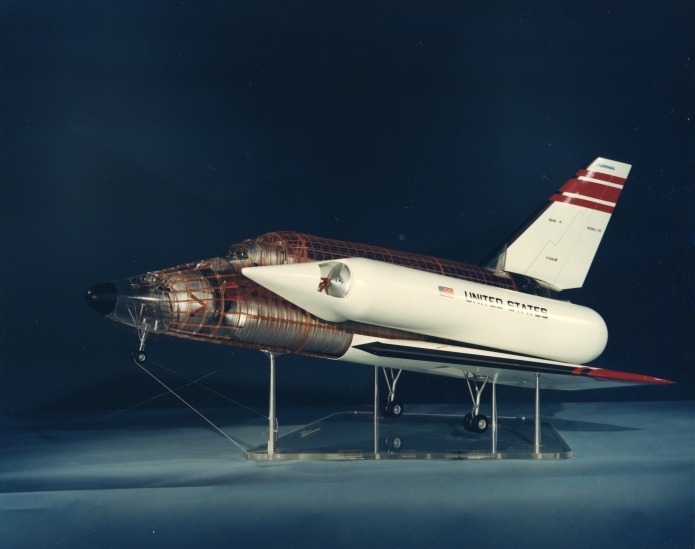
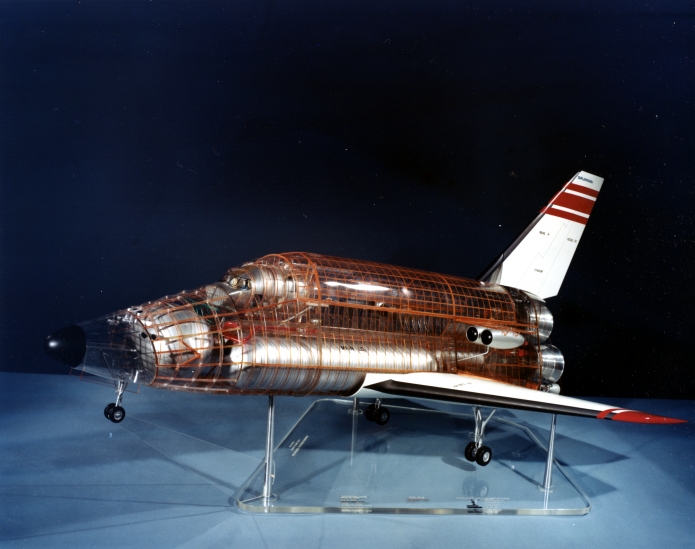
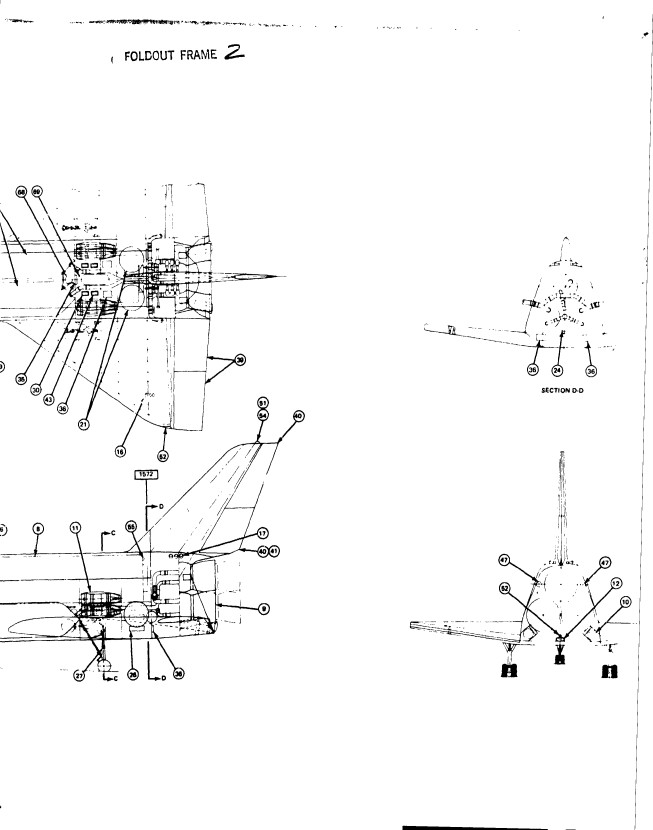
The H-33 orbiter was designed in early 1971 to be launched atop a reusable manned flyback booster, a truly giant supersonic vehicle. The orbiter itself was similar in configuration to the Shuttle Orbiter as actually built, but it differed in that it had internal liquid oxygen tanks and expendable external hydrogen tanks, rather than a single large ET. The NASM has some good photos of a display model of the full system.
The H-33 was a popular design, at least at Grumman. A number of display models were made of it, including this detailed “cutaway” model made – seemingly – of plexiglas.
I have uploaded the full-rez images to the 2017-08 APR Extras Dropbox folder, available to all $4 and up APR Patrons. If interested, wander on by the APR Patreon and sign up. Lots of aerospace goodies available.
Every month, patrons of the Aerospace Projects Review Patreon campaign are rewarded with a bundle of documents and diagrams, items of interest and importance to aerospace history. If you sign up, you get the monthly rewards going forwards; the “back issues” catalog lets patrons aid the APR cause by picking up items from before they signed on. The catalog, available to all patrons at the APR Patreon, has been updated to include everything from the beginning of the project back in 2014 on up to February, 2017.
Below are the items from 2016 (and the first two months of 2017):
If you are interested in any of these and in helping to fund the mission of Aerospace Projects Review, drop by the APR Patreon page and sign up. For only a few bucks a month you can help fund the procurement, scanning and dissemination of interesting aerospace documentation that might otherwise vanish from the public.
Seems I’ve been a wee bit lax on the PDF Reviews I will attempt to rectify that in the future.
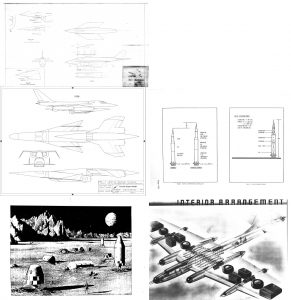
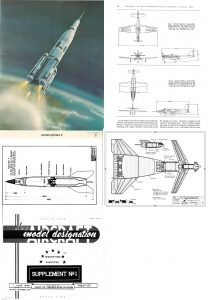
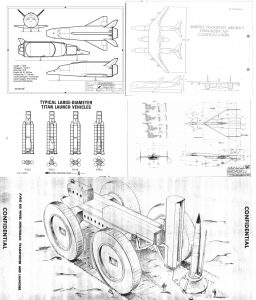
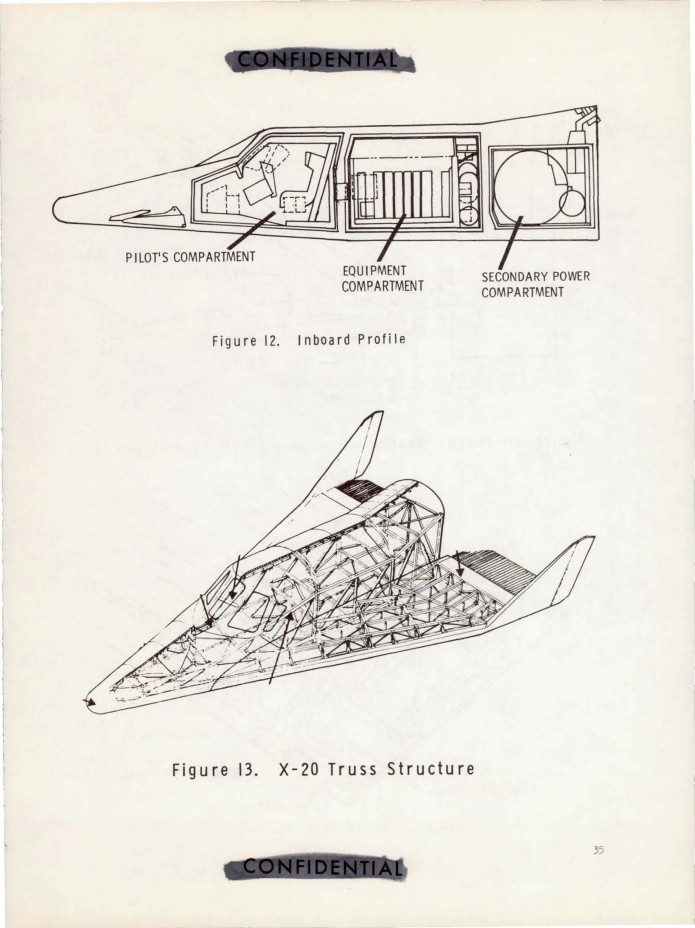
Here is a Air Force conference paper from May, 1964, describing the X-20 Dyna Soar program and vehicle. At this point the program had been cancelled for some months; the configuration shown in the paper was essentially the final design. It’s a decent overall view of the Dyna Soar.
Here’s the link to the abstract:
The X-20 (Dyna-Soar) Progress Report
Here’s a link directly to the PDF.
Support the APR Patreon to help bring more of this sort of thing to light!
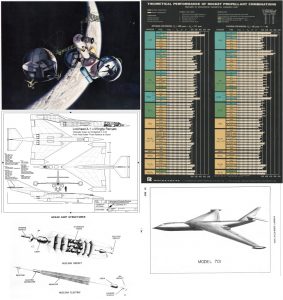
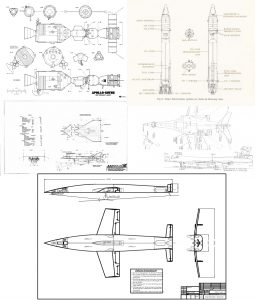
Around 1960, the USAF had high hopes for the development of ASP: “AeroSpace Plane.” ASP was a program to develop an airbreather one- or two-stage-to-orbit spaceplane. The first stage would use some form of Liquid Air Cycle Engine; the inlet would be actively cooled by the liquid hydrogen fuel so that the incoming air would be condensed to liquid, which would allow the liquified air to be stored and fed into high chamber pressure rocket engines. ASP was extremely ambitious, and obviously – since no airbreathing system has made it to orbit (not counting simple turbojet-powered aircraft carrying otherwise conventional rockets such as Pegasus) – it did not work. A fair chunk of change was spent on the concept, but it faded away after a few years. The basic idea of ASP would arise a quarter century later with NASP, to similar levels of success.
A good, well-illustrated article on ASP was published some time back in issue v2N5 of Aerospace Projects Review.
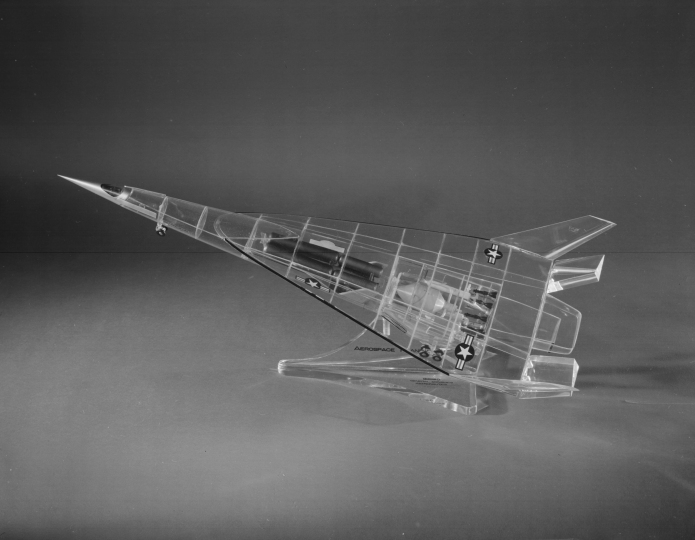
Most of the known ASP designs were produced by Convair. It seems that Convair jumped into the program with both feet, producing not only detailed diagrams of a whole range of vehicles but also artwork and display models. And the latter category included some beautiful see-through models made from Plexiglas. It shows some interior details such as the complex plumbing of the Liquid Air Cycle Engines, as well as the winged second stage tucked into the lower fuselage of the very large hypersonic first stage. In an era long before computer animation, models such a this would be very useful in illustrating complex concepts to customers and bosses.
I have uploaded the full-rez version of this photo to the 2017-07 APR Extras Dropbox folder, available to all APR Patrons at the $4 level and above. If you are interested in accessing these and other aerospace historical goodies, consider signing up for the APR Patreon.
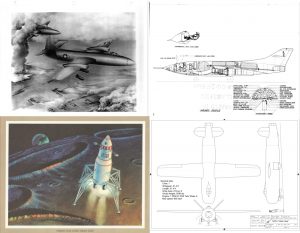
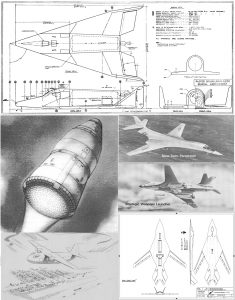
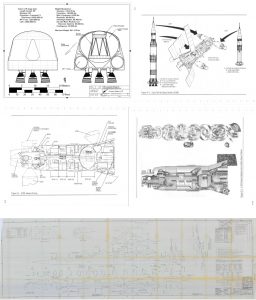
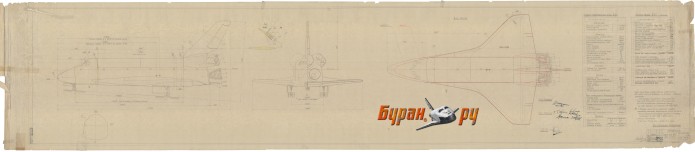
Here’s an interesting one: a detailed large-format diagram of the US Space Shuttle orbiter… as drawn up by Soviet draftsmen in 1976. Interestingly, the top view includes, in red, the basic outline of the Soviet “Buran” shuttle orbiter. A surprisingly high-rez version of this diagram can be FOUND HERE.
The diagram is not entirely accurate, especially with regards to the OMS pod. The rear end of the pod in the side view is distinctly inaccurate. But note the faint lines just ahead of the OMS pods in the top and side views. One of the last noticeable changes to the Orbiters configuration was the change to the forward end of the OMS pod; originally, the pods continued forward onto the cargo bay doors. This continuation was just an aerodynamic fairing; all the equipment an tanks were in the pod aft of the doors.
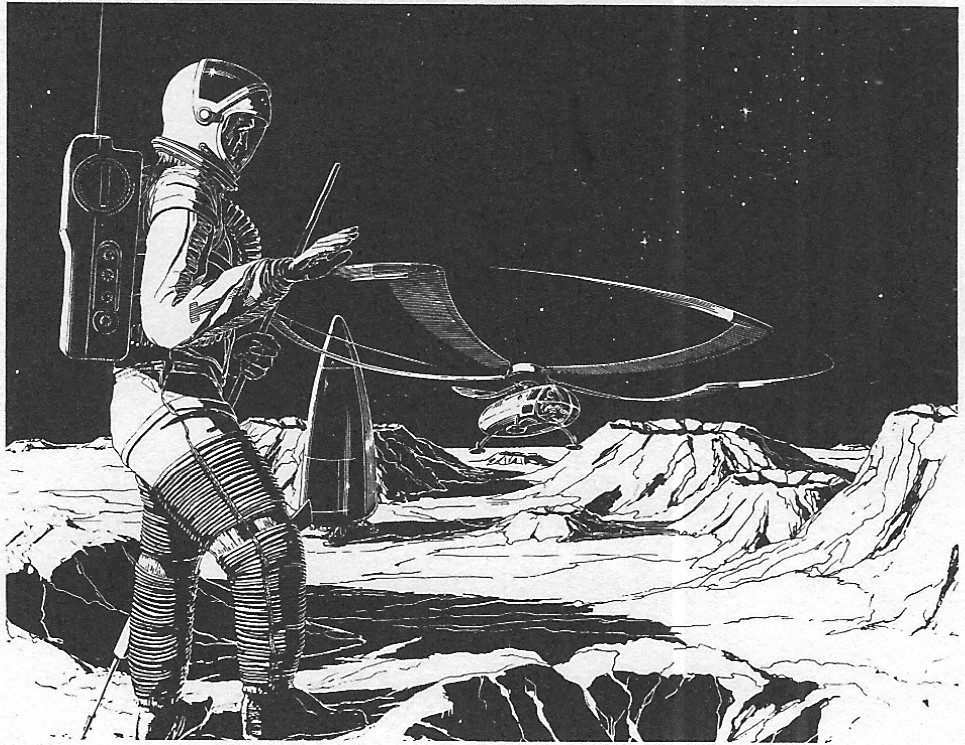
An old (1962 or before) piece of concept art from Kaman illustrating their “ROMAR,” a helicopter meant for Mars exploration. It appears to be powered by rotortip rockets, a decent enough approach for this sort of thing. However, this was before Mariner mars ’64, when the understood density of the Martian atmosphere dropped by more than a factor of ten. As a result, a helicopter like this would need to be made fabulously low-weight in order to fly, something improbable given the needs of a manned vehicle.