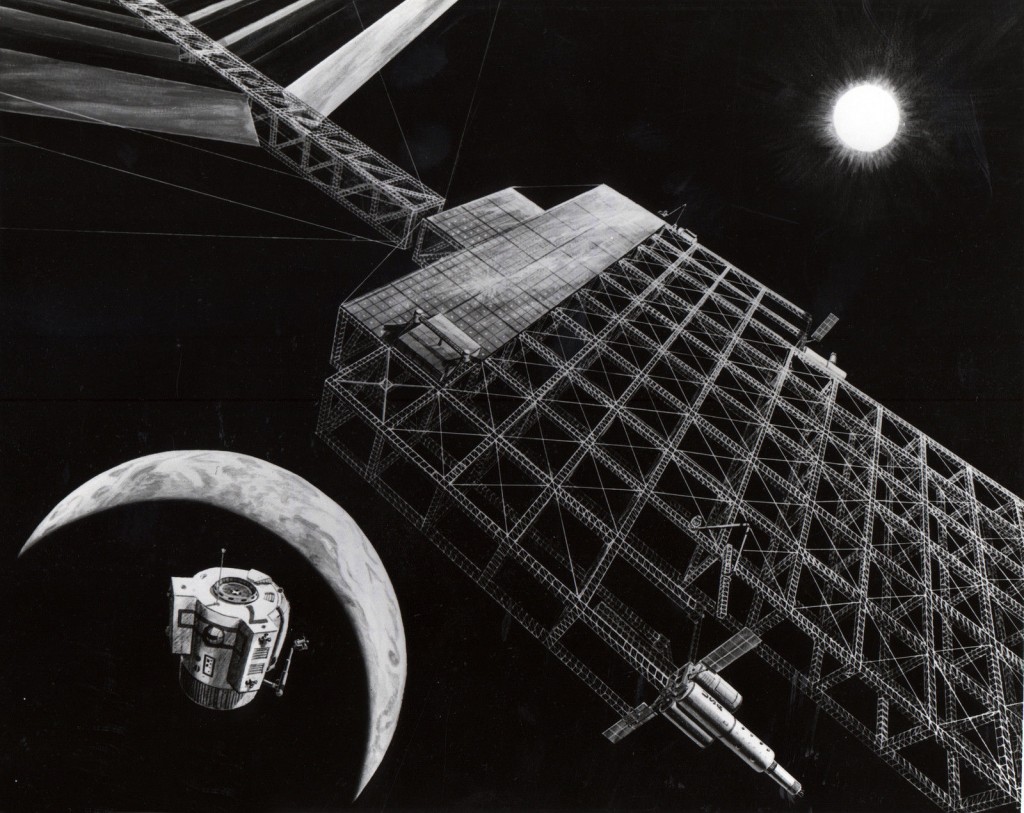
OK, right up front: What Freeman Dyson meant when he first described the concept now called a “Dyson Sphere” was that a civilization sufficiently advanced would build so many space habitats and solar power satellites that the cloud of ’em would blot out the star they orbit. Since the artificial structures would re-radiate the sunlight they receive as lower-energy infra-red (basic physics: if you want to maintain a stable temperature, total energy coming into the system needs to precisely balance total energy leaving), from the outside the Dyson sphere would appear dark… but in infra-red it’d be a great big glowing thing.
The idea of the vast cloud was quickly interpreted as a giant solid “bubble” around the star. This vast construct would absorb all of the suns output, and would result in a monumentally vast place to live. If the star was much like the sun, the Dyson Sphere would need to be at least one AU in radius to keep the temperature roughly Earthlike. But there are of course problems: primary of which is that no material known to science, theorized by science or even guessed at could withstand the stresses involved. Additionally, there’s the problem of gravity. There would be none on the inside of the shell, except for that produced by the star; if you stood on the inside of the shell, you’d fall “up” into the sun. If you stood on the outside of the shell, you’d still have the suns gravity pullign you down… but at 1 AU from the star, that gravity would be miniscule. The gravity added by the sphere itself would be vastly more miniscule, given that its mass would be a tiny fraction of the mass of the star. So to live in or under a Dyson sphere with a Sol-type sun, you’d need artificial gravity habitats, either rotating structures or whatever magical “gravity generators” you can scrape up.
But a new type of Dyson sphere has just been described by two fellers from the Department of Physics of Bo�gazi�ci University, Bebek, Istanbul, Turkey. Instead of building the shell around a Sun-like star… build it around a white dwarf. The resulting shell will be far smaller if it is to be at the “habitable zone,” since white dwarfs are far less luminous than main sequence stars. But a side benefit here is that the reduced Dyson sphere radius (depending on the white dwarf… from about 2,000,000 km to a bit over 4,000,000 k) results in surface gravities right near Earth normal. So humans would be able to comfortably live on the surface, using energy intercepted within the sphere to provide illumination.
The down side is that the problems of physical stresses within the Dyson sphere, already bad with the 1-AU-type sphere, become much worse at the smaller radius and higher gravity loading. But presumably by the time humans are ready to tear planets apart to build shells around distant stars, we’ll have made important advances in the field of materials science.
Download the PDF file of the paper here: