NOTE: this is the second official “PDF Review.” The idea is to present interesting online resources for those interested in the sort of aerospace oddities that you can find in the pages of Aerospace Projects Review. This little project is supported through my Patreon campaign; at current levels, I’ll post two such reviews per month. If you’d like to see more, or just want to contribute to help me along, please consider becoming a patron.
——————-
In 1948, the Langley Aeronautical Laboratory, Langley Field, VA, put oput a technical paper with the snappy title “The Effect of Negative Dihedral, Tip Droop, and Wing-tip Shape on the Low-speed Aerodynamic Characteristics of a Complete Model Having a 45 Degrees Sweptback Wing.” This described the results of wind tunnel testing of a model of the Bel X-1 supersonic research aircraft with swept wings. At the time, supersonic aerodynamics was in its infancy, and while it was known by this point that swept wings had superior supersonic drag than unswept wings, the details were murky.
Numerous studies were made of re-winged X-1’s, including forward-swept wings. As it happened, no version of the X-1 was ever equipped with anything but unswept wings (though the later versions had substantially thinner wings). Such studies were performed by not only Bell Aircraft but also the NACA; the latter studies may have used the Bell X-1 wind tunnel models, but may not have indicated an intention or desire to actually re-wing an X-1. Instead, the X-1 was a known commodity, and by modifying an existing wind tunnel model, changes in performance could be quickly and inexpensively determined without having to design and build entirely new models.
In this study, several different wingtips were evaluated, including squared-off tips, rounded tips and droops tips.
CONCLUDING REMARKS
The results of low- speed tests made to determine the effects of negative geometric dihedral, tip droop, and tip shape on the aerodynamic characteristics of a complete model having a 45 degree sweptback wing are summarized as follows :
1. The use of -10 degree geometric dihedral resulted in a reduction in the average value of the effective-dihedral parameter C2V through the low and moderate lift- coefficient range that was about 65 percent as great as that usually obtained for unswept wings.
2 . Drooping the wing tips 45 degrees (maintaining the same ground clearance as that with -100 geometric dihedral) resulted in a decrease in the average value of C2V through the low and moderate lift-coefficient range equivalent to about -14 degrees geometric dihedral and also caused an increase in the maximum lift coefficient of 0.15.
3. Changes in the wing- tip plan form indicated that C2V was lowest for the parallel and circular tips and highest for the tips skewed either in or out .
4. By changing a square- cut tip to a faired tip of revolution, the maximum value of C2V for the model with parallel tips was reduced by an amount equivalent to about -4 degrees geometric dihedral.
5. Deflecting the wing tip (from zero) resulted in rolling and yawing moments about the same as that produced by a conventional aileron on a similar sweptback- wing model.
This file was originally added to the NASA Technical Report Server in the mid/late 1990s, and featured rather sad 2-bit (black and white) scanning… fine for text, adequate for line drawings, terrible for art & photos. When I re-accessed it for this review to make sure that it was still available, it had been re-scanned and re-uploaded in full color, provided vastly better image quality.
The abstract can be seen HERE. The PDF file can be downloaded directly HERE.
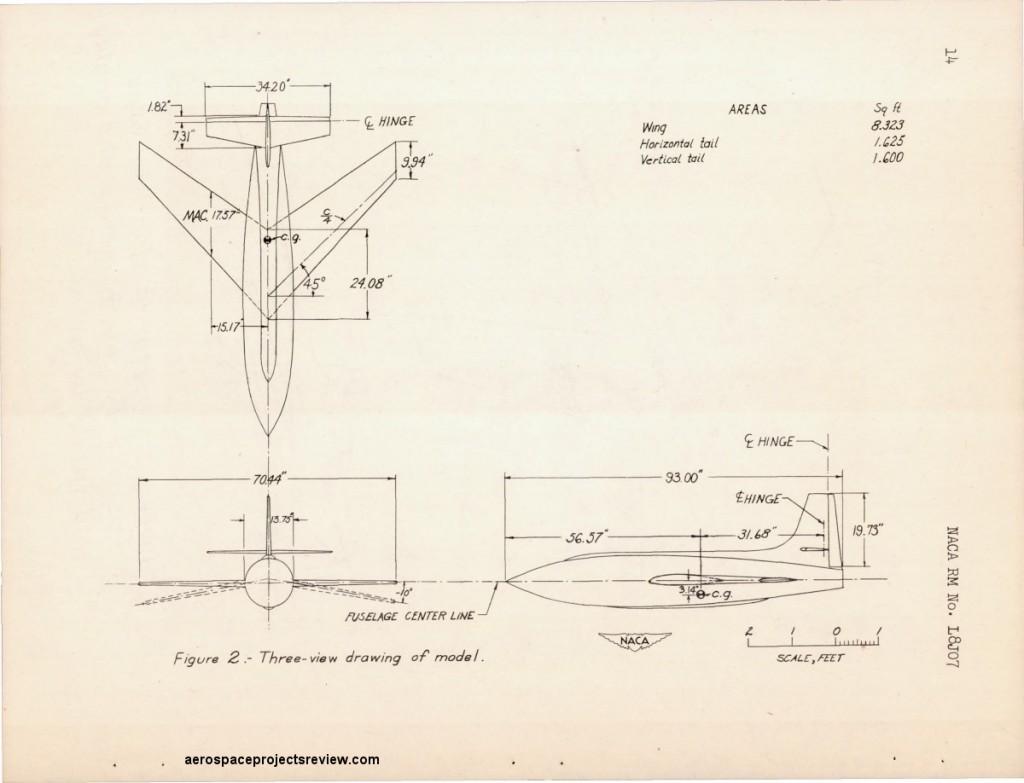
Three-view of the swept-wing X-1 showing levels of dihedral.
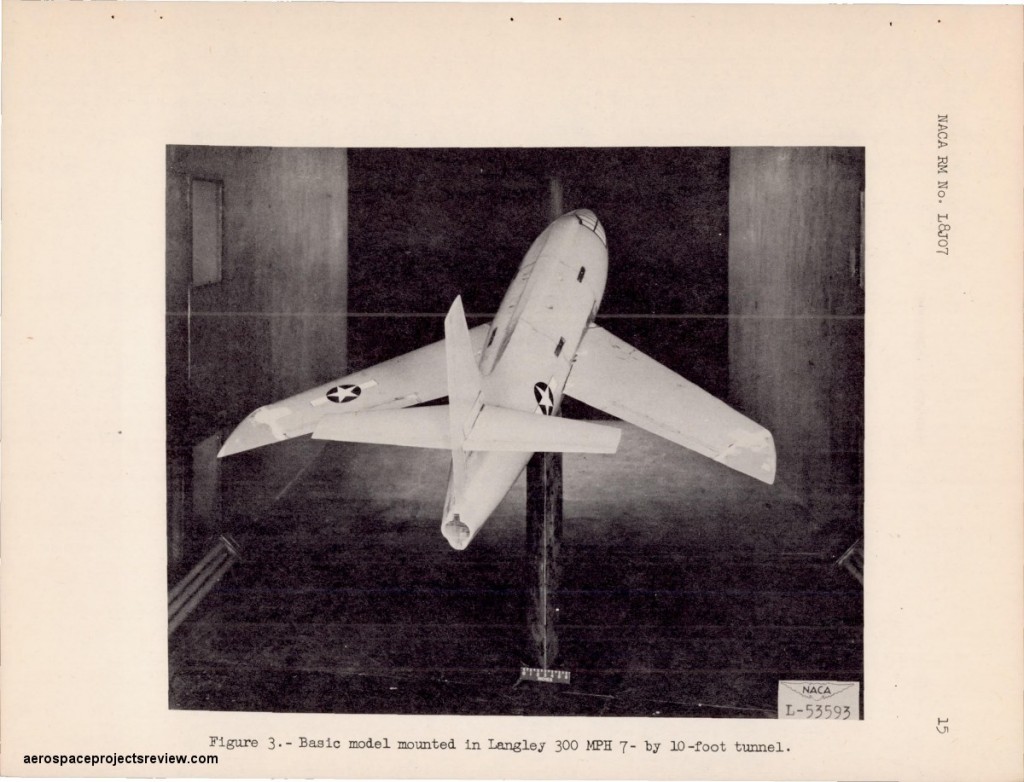
Photo of the wing tunnel model. Note the markings applied to the model. As wing tunnel models are very rarely painted except as needed by the science of the tests, this indicates that this may have been a conventional X-1 wing tunnel model that, after testing, had been painted to turn it into a display model… and then brought back into the shop and re-purposed as a wind tunnel model again.
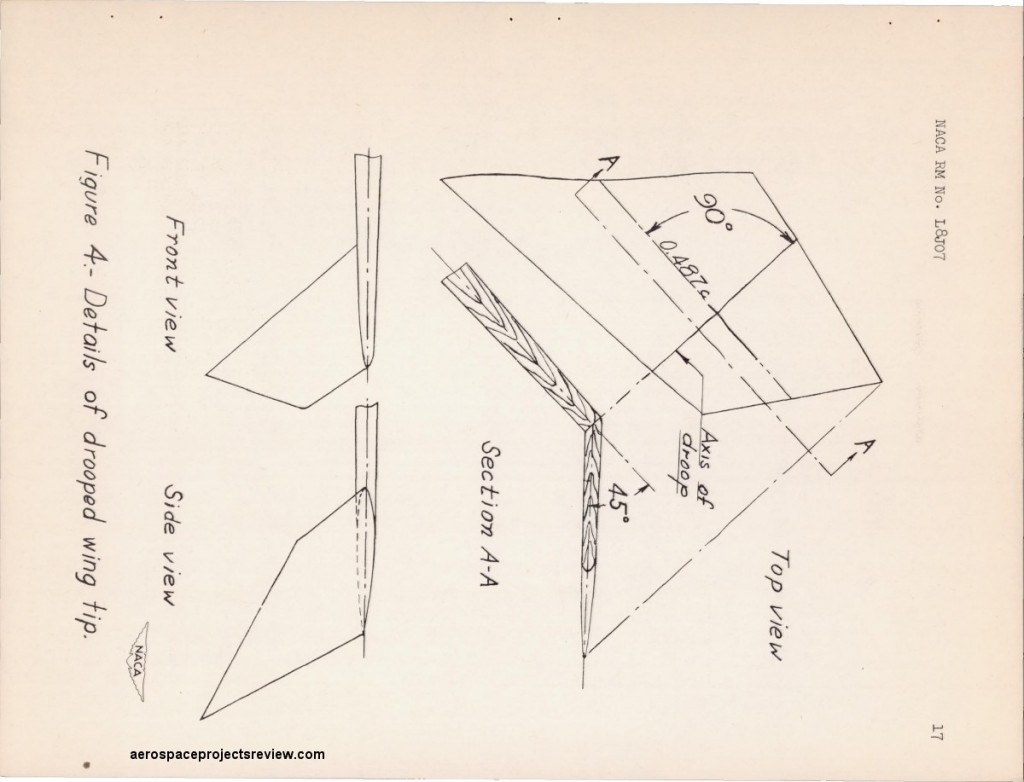
Drooped wingtips studied.
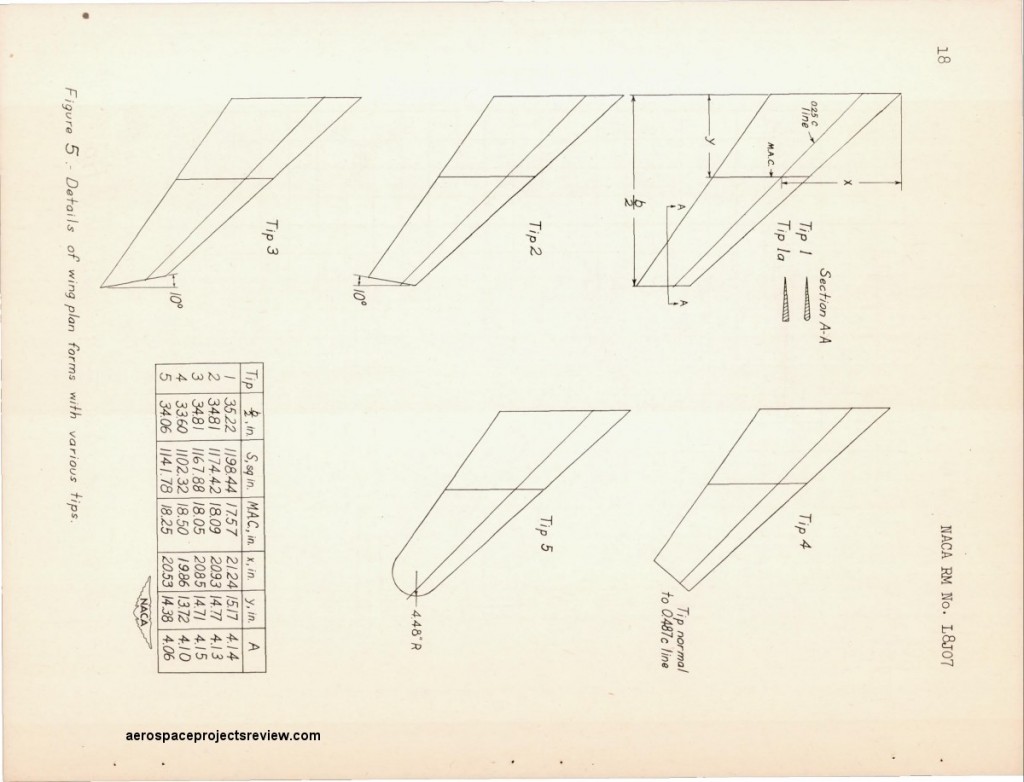
Different wing planforms & tips examined.